


Why is the hashrate displayed on the backstage of the miner different from the hashrate of the mining pool? This is a normal phenomenon. This article will describe several reasons for the inconsistency between the miner's backstage hashrate and the mining pool's displayed hashrate:
1. The update time of the hash rate displayed by the miner and the mining pool is different
Usually, the hash rate update time of the mining pool and the miner is inconsistent. For example, the real-time hash rate displayed by the Binance Pool is the average hash rate of the last 15 minutes, and the calculation time of other mining pools ranges from 10-30 minutes. The miner in the miner's hands may show that the hash rate is refreshed every 5 seconds, so the hash rates on the two sides are different. When the hash rate is normal, the difference between the two data will not be too significant. However, when the hash rate fluctuates significantly due to miners or other external reasons, the two data will appear to be very different.
2. The rejection rate is caused by network reasons, and the mining pool only displays the real effective hash rate
Let me talk about the rejection rate first because the "answer" returned by the miner is through the network, so when the network environment is poor, network fluctuations during the transmission process will cause the mining pool to receive the incomplete "answer" (packet loss) and reject it. If the "answer" of the previous calculation problem has not been transmitted to the mining pool, and the mining pool has already burst blocks for the next "calculation problem," then this "answer" does not meet the new standard and will be rejected by the mining pool. No "answer" is even received, the actual effective hash rate drops significantly.
Many rejections/total submissions = rejection rate. The number of "answers" received by the mining pool is not equal to the number of "answers" sent by the miner to the mining pool, and the miner's real effective hash rate will also be lower. To give miners a more intuitive income calculation, the mining pool's hash rate display refers to the real and effective hash rate received. In contrast, many mining pools display the hash rate converted from all the "answers" sent by the miners to the mining pool. (Regardless of whether it is valid or not, it is recorded by the mining pool), which also explains why the hash rate in many mining pools is higher, but the income is lower.
If the rejection rate is high, it is recommended to check the network environment. Common scenarios include:
1) All miners in the same router or switch exceed the standard: It is recommended to check the network as a whole and try to replace the router or switch.
2) Individual miner exceeds the standard: Changing the network cable and network port connector to the miner is recommended to try.
3. The calculation method of hash rate between miners and mining pools is inconsistent
The backstage hash rate GH/s(RT) of most miners is reversed based on the frequency of the hash board: each miner has N hash boards, and the hash rate is calculated according to the frequency of each hash board. The miner's hash rate is obtained by adding the hash rates of these N hash boards. The point is that sometimes the hash board goes offline and does invalid work; some miners will still calculate the hash rate. The mining pool cannot receive this part of the "answer," Of course, there will be a difference in hash rate.
As shown in the figure below, if a particular hash board goes offline for some miners, xxxxxxxxx will appear in the last column (red circle). That is, there is no real hash rate.
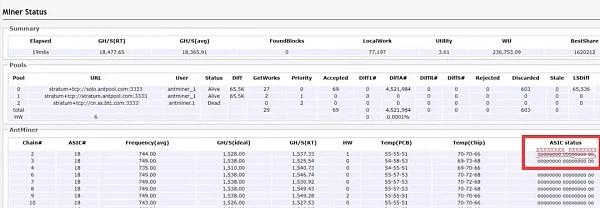
4. The instability of the power supply and voltage of the miner
The hash rate submitted by the miner to the mining pool is related to the stability of the power supply and voltage. Instability will lead to an insufficient power supply and an increase in the rejection rate. A hardware problem causes this. Please check the miner's power supply when it occurs. As shown in the picture, the backstage of the miner will normally display the rejected tasks (rejected column), this is the statistics of the miner itself, that is, this part of the share is rejected when the controller is verified, and it is not connected to the mining pool so that the mining pool will show a low hash rate with 0 rejection rate.
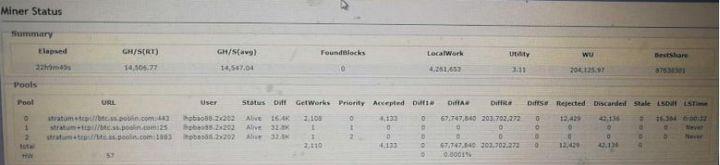
5. The hash rate is stolen by third-party software
In extreme cases, it is also a situation that we do not want to encounter, that is, if you have used third-party software, mainly when mining with graphics cards, the mining software will be used, and harmful software developers will steal a small part of the hash rate for private purposes. So at this time, the only way to avoid it is to choose trusted software on the market.
6. After flashing the "problem firmware," the impact of the firmware on the miners
The "problem firmware" factor means that many users will flash some overclocking firmware or other malicious firmware of unknown origin. This kind of firmware keeps miners in overclocking work for a long time and causes significant damage to the miners' hardware. At the same time, hardware damage will also reduce the hash rate, and there is also the risk of the hash rate being stolen.