


1. Mining farm electrical system
The power supply work of mining farms must meet the following basic requirements to serve miners well, ensure the needs of miners, networks and domestic electricity consumption, and do an excellent job of energy saving:
1) Safety: In the supply, distribution and use of electrical energy, personal accidents and equipment accidents should not occur.
2) Reliable: It should meet miners' requirements for power supply reliability. The reliability requirements for power supply have changed with the operation and use of miners with significant hash rates.
3) High quality: It should meet miners' requirements for quality, such as voltage and frequency.
4) Economy: less investment in the power supply system and lower operating cost.
In addition, in the power supply work, the relationship between the part and the whole, the current and the long-term should be reasonably handled, not only to take care of the current interests of the part but also to have an overall perspective, to be able to take into account the overall situation and adapt to development.
The mining farm's power supply and distribution system is composed of the total step-down substation (high voltage distribution station), high voltage distribution lines, workshop substations, low voltage distribution lines and electrical equipment. Several different types of power supply and distribution systems are introduced below:
1) Total substation
The total substation is responsible for transforming the external power supply voltage of 220-110kV into the high-voltage distribution voltage of 35-10kV in the plant area, and supplying power to the substations or transformers in the plant area.
2) Mining farm substation
The mining farm substation reduces the voltage of 35-10kV to 380/220V and then supplies power to the miners through the low-voltage distribution line.
3) Distribution line
The distribution lines are divided into high-voltage distribution lines in the plant area and low-voltage distribution lines in the workshop.
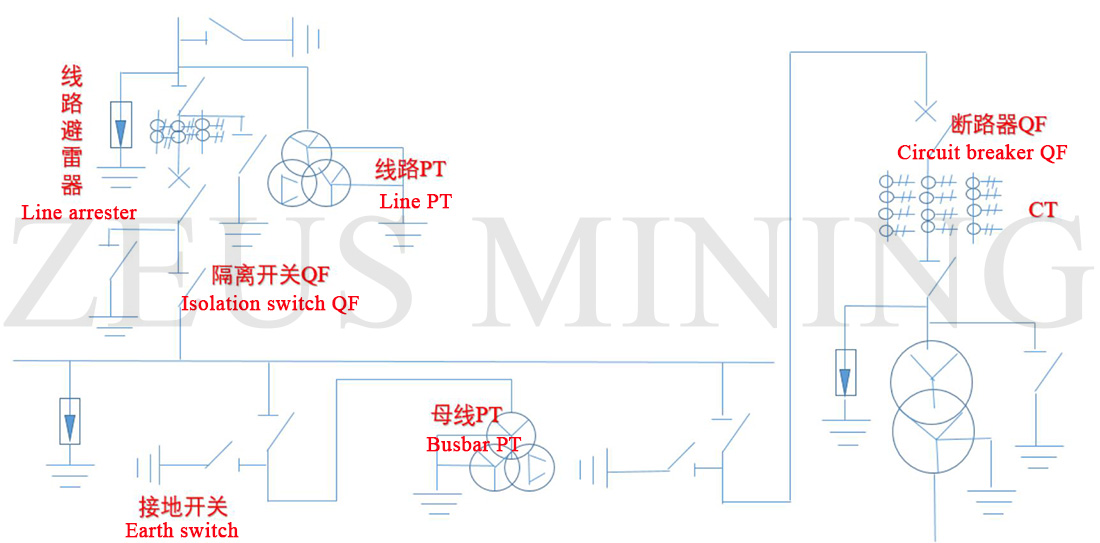
Main wiring diagram of mining farm power supply: high voltage part
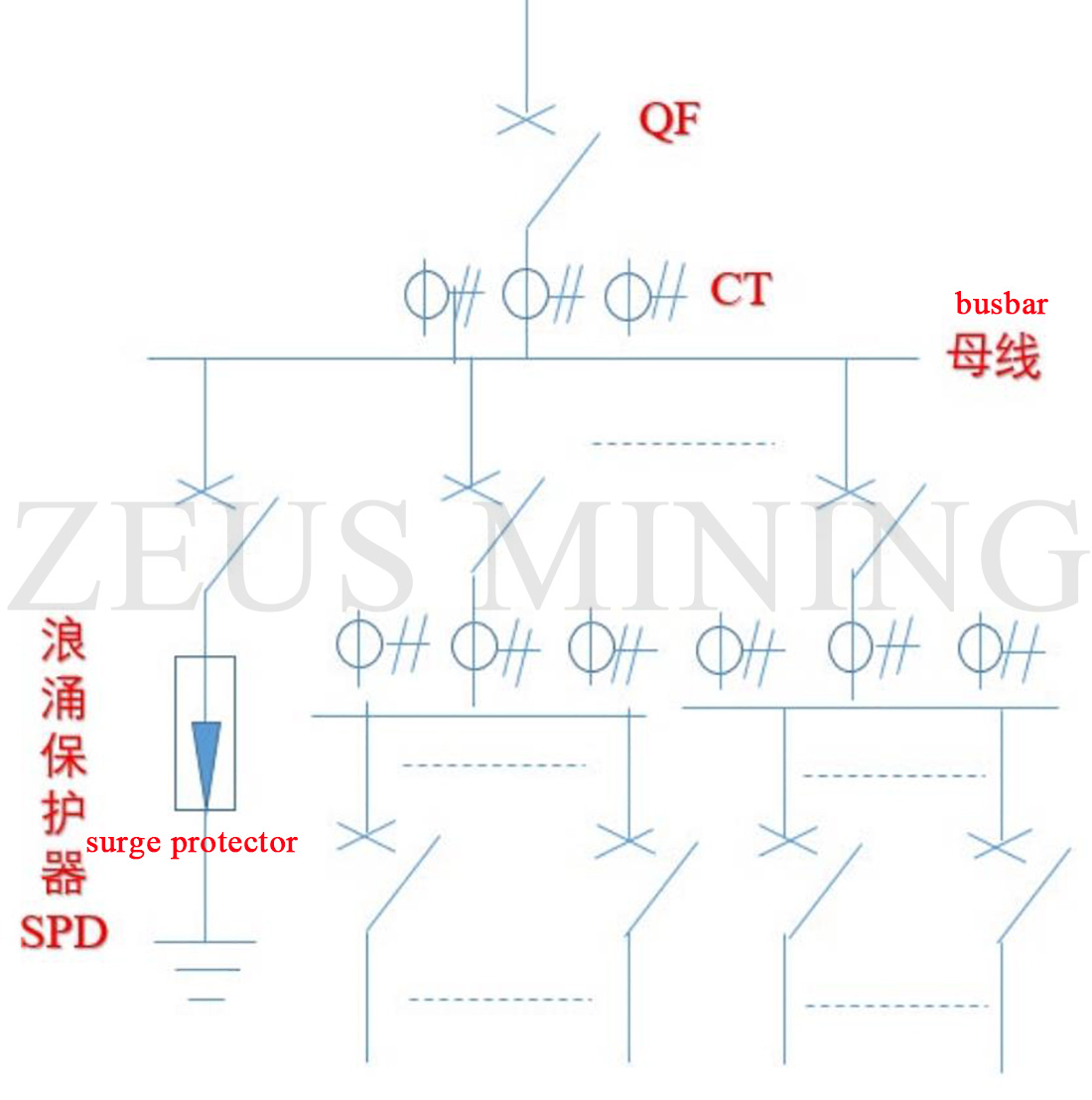
Main wiring diagram of mining farm power supply: low voltage part
2. Mining farm power supply equipment
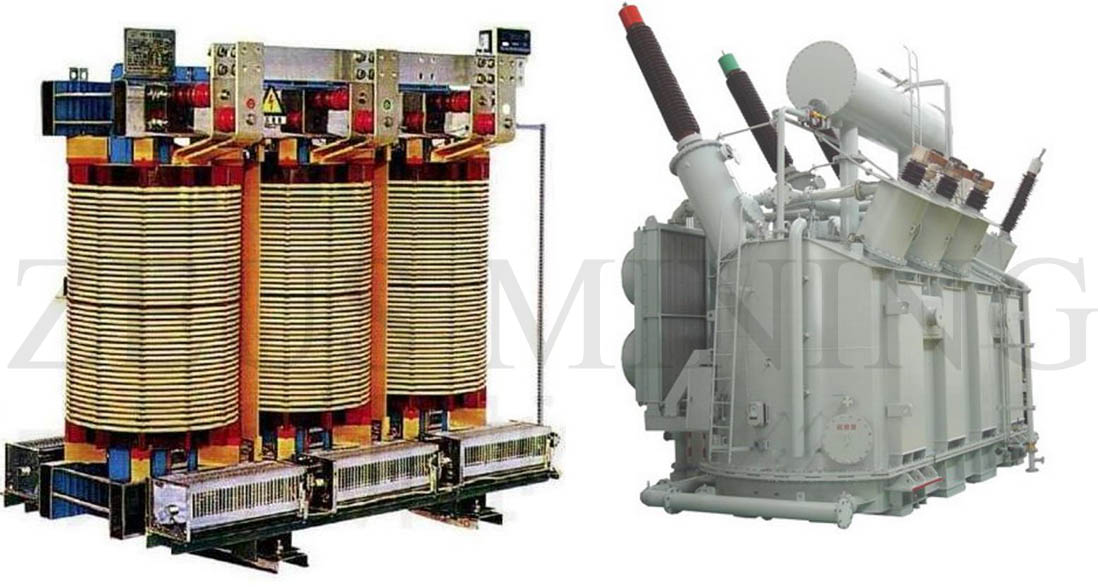
1) Transformer
A transformer is a static electrical device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to increase or decrease the AC input voltage to an AC output voltage of the same frequency. Classification by insulation method: oil-immersed and dry. At present, the voltage level of the dry transformer is only 35kV, and the capacity is smaller than that of the oil transformer, about 2500kVA.

2) High voltage switch cabinet
The high-voltage switchgear comprises vacuum circuit breakers, isolating switches, relay protection devices, grounding switches, voltage transformers, current transformers, live displays, secondary instruments and secondary control circuits.
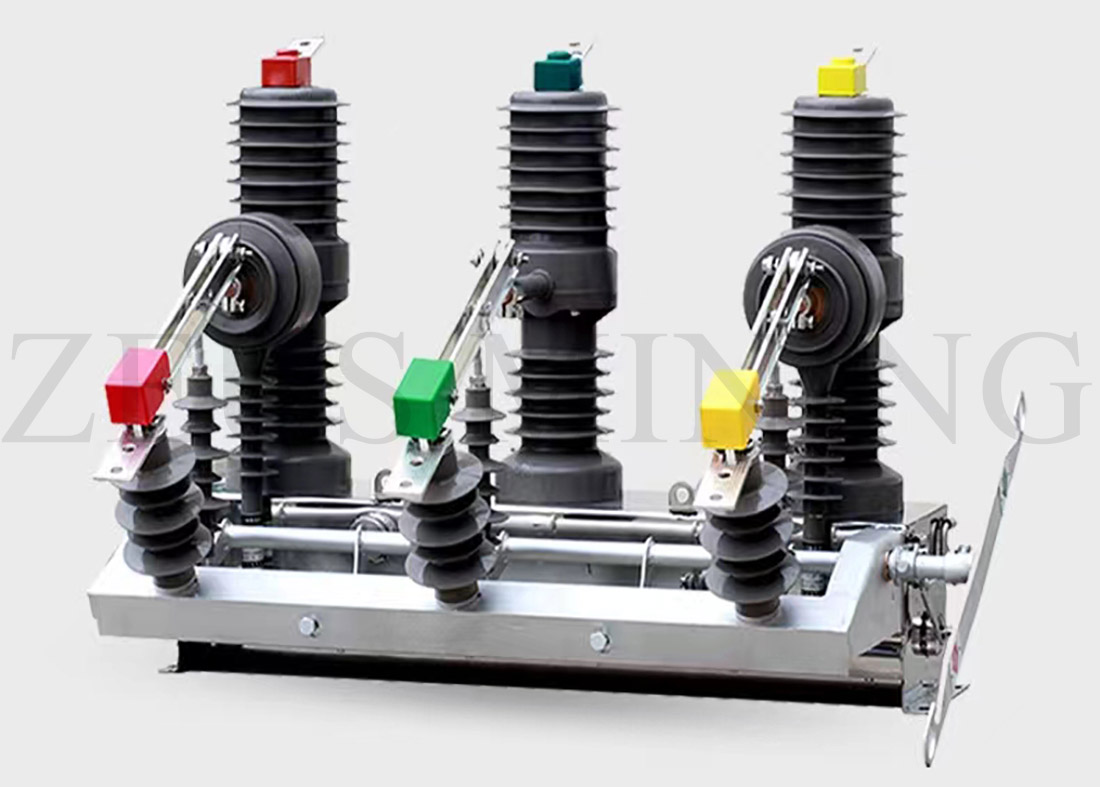
3) Outdoor vacuum circuit breaker
Outdoor vacuum circuit breakers are also commonly referred to as outdoor pole switches. It is a circuit breaker installed outdoors. It can realize the protection of short-circuit current: quick-break, over-current, overload, single-phase grounding and other protections.
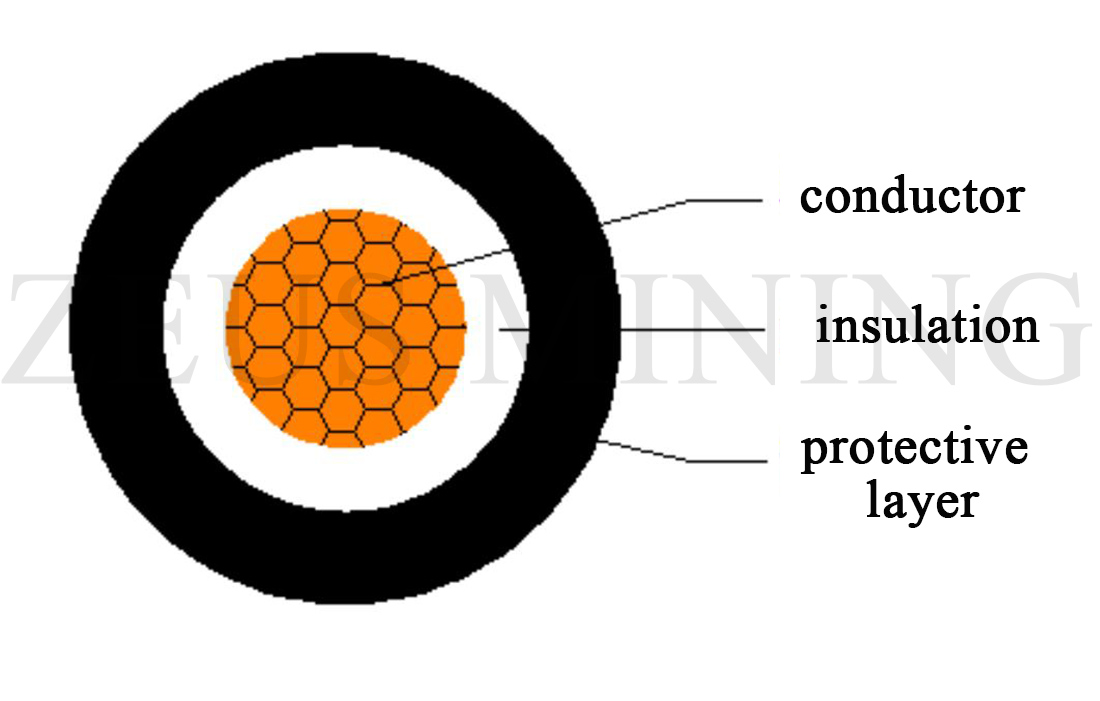
4) Cable
The basic structure of wire and cable comprises three parts: conductor, insulating layer and protective layer.
Conductor: transmits current, guides the way of power transmission;
Insulation layer: withstand voltage and play an insulating role;
Protective layer: protect the cable insulation from the influence of the external environment and prevent mechanical damage, etc.
According to the use characteristics, laying conditions and safety of various types of wires and cables, some wires and cables may only have conductors without insulation and protective layers (such as bare wires), or only conductors and insulation without protective layers (such as plastic cloth wires, etc.), in addition, the cable can be designed to be fire-resistant, fire-resistant, shielded and other structures according to the requirements of use, but still must meet the basic requirements of the three major parts.
5) Low voltage switchgear
The complete low-voltage switchgear is suitable for power plants, power stations, industrial and mining enterprises and other power users as power distribution systems with AC 50HZ, rated working voltage 380V, and rated current working 3150A as power, lighting, and the role of power conversion, distribution, and control of power distribution equipment.
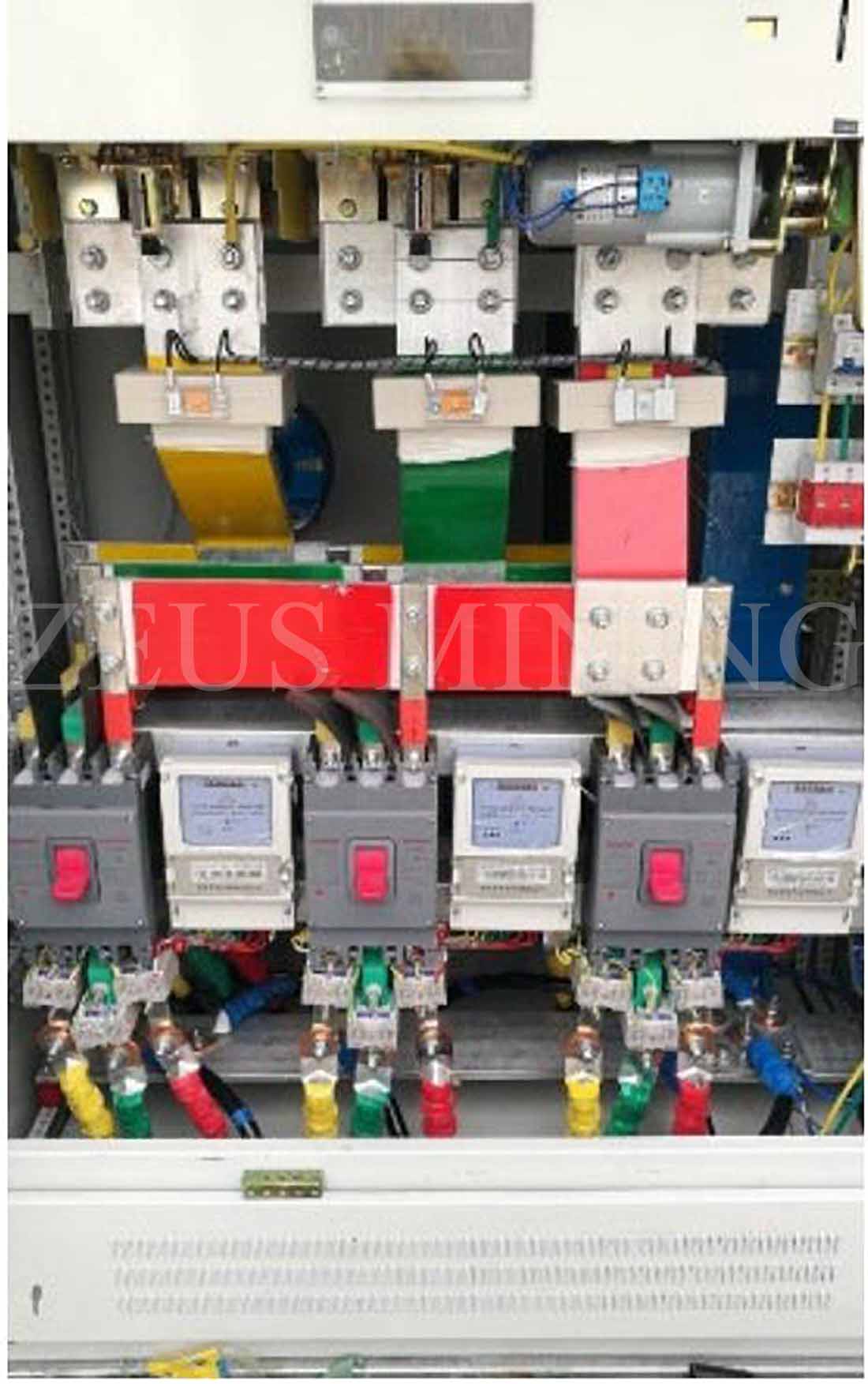

6) Low voltage circuit breaker
Low-voltage circuit breaker: a switching appliance that can connect and break normal load current, overload current, and short-circuit current and has the functions of automatic voltage loss, under-voltage, overload, short circuit and leakage protection.
a. Mainly divided into miniature circuit breakers, molded case circuit breakers, frame circuit breakers, and intelligent universal circuit breakers.
b. The trip units mainly include thermal trip units, magnetic trip units, thermal-magnetic trip units, electronic trip units and electronic intelligent trip units.
c. Overload long-time delay protection: The thermal type (bimetal element) is used for overload long-time delay protection (thermal tripping).
d. Short-circuit protection: a magnetic field is generated by the current, and the magnetic force of the magnetic field pulls the armature to make the tripper act. It has no time limit and has an instantaneous tripping function.

3. Inspection of electrical equipment
Electrical equipment is one of the most critical equipment to ensure the normal operation of miners. Electrical equipment failure will directly jeopardize the safe and stable operation of the mining farm's power system. Therefore, the electrical equipment is often inspected so that when it is abnormal, it can be discovered and taken measures in time to avoid accidents and ensure the system's normal operation.
According to the relevant national electrical regulations, combined with the actual situation of the equipment under the jurisdiction of each branch, the electrical class equipment inspection management system is formulated as follows:
1) Requirements for inspectors
a. Inspectors should have a strong sense of responsibility, a correct attitude, careful observation, and quick thinking;
b. Earnestly study theoretical knowledge and understand equipment structure, performance and operating parameters.
2) Equipment inspection should be based on the characteristics of preventing seasonal accidents and focus on inspection items in different regions and seasons, such as:
a. From January to March, inspection focus: equipment contacts, oil level, gas pressure, insulators, wire sag, fire-fighting equipment, sealing and heating of terminal boxes and mechanism boxes, fire prevention, small animal prevention measures, snow prevention, freezing prevention, and ice prevention hazard and anti-pollution flashover measures.
b. Key points of inspection from April to June: equipment contacts, oil level, gas pressure, lightning protection facilities, fire protection measures and fire-fighting equipment, flood control equipment and measures, ventilation and cooling facilities, buildings, and framework foundations.
c. Key points of inspection from July to September: equipment contacts, oil level, gas pressure, insulators, lightning protection facilities, wire sag, sealing and moisture-proofing of terminal boxes and mechanism boxes, fire prevention measures and fire-fighting equipment, measures against small animals, and flood-proof equipment and measures, ventilation and cooling facilities, waterproof and anti-leakage rain measures, buildings and framework foundations.
d. From October to December, the inspection focus: on equipment contacts, oil level, gas pressure, insulators, fire protection measures, and fire fighting equipment, measures to prevent small animals, thermal insulation and heating measures, anti-snow, anti-freeze, anti-ice damage, anti-pollution flashover measures, etc.
3) Inspection method
The gradual process from the normal equipment to the occurrence of hidden dangers is accumulating quantitative changes. In this process, the quantitative changes in the equipment are expressed by specific characteristics. Therefore, by inspecting the equipment with the method of "seeing, listening, touching, smelling, and measuring," you can find these reflected characteristics in the process of quantitative change in time, deal with the equipment accident before the qualitative change occurs, actively prevent the qualitative change, and prevent the occurrence of the accident.
a. Look: It is mainly used for analysis and judgment of inspection items such as equipment appearance, location, temperature, pressure, color, lighting, signal, and indication, such as transformer oil level, oil temperature inspection, and cable temperature inspection, etc. Determine whether there is any abnormality by observing the operation of the equipment, and record relevant data such as temperature, pressure, number of actions, leakage current, etc.
b. Listen: mainly through the sound to judge whether the equipment is running normally. For example, when the transformer runs normally, its sound is a uniform humming sound, and when it runs at an over-rated current, it will emit a high and heavy humming sound, etc. By analyzing and judging whether the sound of the equipment is normal, whether there is abnormal sound, whether there is abnormal corona sound, discharge sound, etc., it can be determined whether there is any abnormality in the operation of the equipment.
c. Touch: By touching the device's shell without electricity, determine whether the temperature and vibration of the device are abnormal. For example, touch the transformer shell, and check whether the temperature is normal and whether there is a significant difference from usual.
d. Smell: judge whether the device has overheating, discharge, and other abnormalities by smell. For example, it can be judged by smell whether the smell of the device is normal and whether there is any abnormal smell, such as a burnt smell.
e. Measurement: through the method of measurement, master the exact data. For example, according to the change of equipment load, use an infrared thermometer to test whether the temperature of the contact point of the equipment is abnormal and whether it exceeds the normal temperature.
4) Precautions
a. Unless there are particular circumstances, it is not allowed to change the operation mode, start and stop equipment, etc.;
b. Report problems on time and fill in the work record form;
c. Necessary tools, such as flashlights, electric pencils, etc., should be carried during inspection;
d. Wear protective equipment and keep a safe distance when inspecting the transformer.
5) Inspection of work content
Device name | No. | Inspection content | Inspection standard |
Backstage monitoring | 1 | Switch status indication | The switch status is consistent with the actual operating status of the site, and the relevant alarm information is processed in time. |
2 | DC screen status | Input switch status, voltage, current status, alarm status. | |
3 | Transformer alarm information | If any alarm information is found, it should be confirmed, reported and dealt with on the spot in time. | |
4 | Comprehensive protection | If any alarm information is found, it should be confirmed, reported, and dealt with on the spot in time. | |
High voltage switchgear | 1 | Switch position | The opening and closing indicators indicate correct and consistent with the actual operating state. |
2 | Switch casing, supporting porcelain bottle | Check that the casing and supporting porcelain bottles are clean and intact, without damage, cracks, and corona discharge noise. | |
3 | Connecting line | 1. Check that the switch leads and clips are firmly crimped, have good contact, no discoloration, and no cracks in the copper-aluminum transition; 2. Check whether there is heat by checking the color change of the wire and the clip, whether there is a rise in hot air, aggravated oxidation, whether the temperature indicator or color-changing paint has melted and discolored, and turning off the lights at night to check whether there is redness, an infrared thermometer can be used for temperature measurement; 3. In rainy and snowy weather, check the leads and clips, and compare whether there is snow melting and water vapor to check whether there is heat; 4. Check whether there are broken strands or burn marks in the lead wires at high places, and a telescope can be used. | |
4 | Switch sound | There should be no abnormal sound from the switch. | |
5 | Two time | 1. Clean the terminal block; 2. The secondary wire has no looseness and heat discoloration; 3. The holes of the second line of the cable are tightly sealed; 4. The protection device indicates normal. | |
Isolating switch | 1 | Main contact parts such as contacts, leads, clips, etc. | 1. The wire has no broken strands; 2. The joints are in good contact; 3. Observe whether there is hot airflow in the joint, severe discoloration, intensified oxidation, whether the temperature indicator is discolored and melted, turn off the lights at night to check for redness, etc., check whether there is heat, and use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature; 4. In rainy and snowy weather, check the main contact parts of equipment leads, wire clips, and the primary contact parts of the knife gate, and compare whether there is snow melting and water vapor; 5. No hanging foreign objects. |
2 | Pillar | It should be in good condition, clean, and without damage or discharge traces. | |
3 | Operating mechanism | 1. The locks of the anti-mistake locking device are in good condition and the locking is reliable; 2. The mechanical interlocking device should be complete and reliable; 3. The door of the mechanism box is tightly closed. | |
4 | Transmission link | No bending deformation, loosening, corrosion. | |
5 | Grounding switch | Normally in the "point" position, the booster spring has no broken strands, and the latching is good. | |
Lightning arrester | 1 | Exterior | Clean and undamaged, no discharge phenomenon. |
2 | Ontology | 1. The body is not inclined; 2. The foundation has no cracks, and the fixing screws are not loose or corroded. | |
3 | Discharge counter | Record the number of actions if the discharge counter is in good condition. | |
4 | Arrester lead | The lead wire is intact, the contact is firm, and the wire clip has no cracks. | |
5 | Ground | The grounding is good, and the grounding wire is not rusted. | |
Transformer | 1 | Sound | The sound is normal, with no noise or uneven discharge sound. |
2 | Upper oil temperature | 1. The thermometer of the transformer body is in good condition and not damaged; 2. Record the oil temperature value of the upper layer of the transformer; the upper oil temperature limit is 85℃, and the temperature rises limit: is 55℃. | |
3 | Oil level | 1. The oil level indication of the transformer is normal; 2. The oil level gauge should be free of damage and leakage, and no oil scale should affect the inspection of the oil level. | |
4 | Ontology | 1. There is no oil leakage at the connection between the body and the casing; 2. The casing is in good condition, with no damage, clean, discharge traces; 3. The grounding electrode is firmly welded and has no rust phenomenon; 4. The color of the silica gel in the ventilator is not discolored by moisture. | |
Low voltage distribution cabinet | 1 | Busbar | Use a thermometer to test the equipment to detect the temperature of the busbar joints and observe whether there is discoloration and intensified oxidation. |
2 | Switchgear | 1. There is no abnormality in the appearance inspection of the switch cabinet; the cabinet door is tight, the cabinet body is not tilted, and the paint is not peeled off; 2. Use a thermometer to test the switch cabinet to see if the temperature is normal and does not exceed 80°C. | |
3 | Current Transformer | The shell is free of cracks, carbonization, melting, burn marks and smoke, and no abnormal odor. | |
4 | Instrument indication | Indicator lights, meters, etc., display normal. |
4. Overhaul of electrical equipment
High-voltage switch cabinets, power transformers, low-voltage switch cabinets, power distribution boxes, overhead lines, and power cables shall be subject to annual maintenance. In addition, for lightning rods and other grounding devices, the grounding resistance value must be measured every spring and meet the requirements of the regulations.
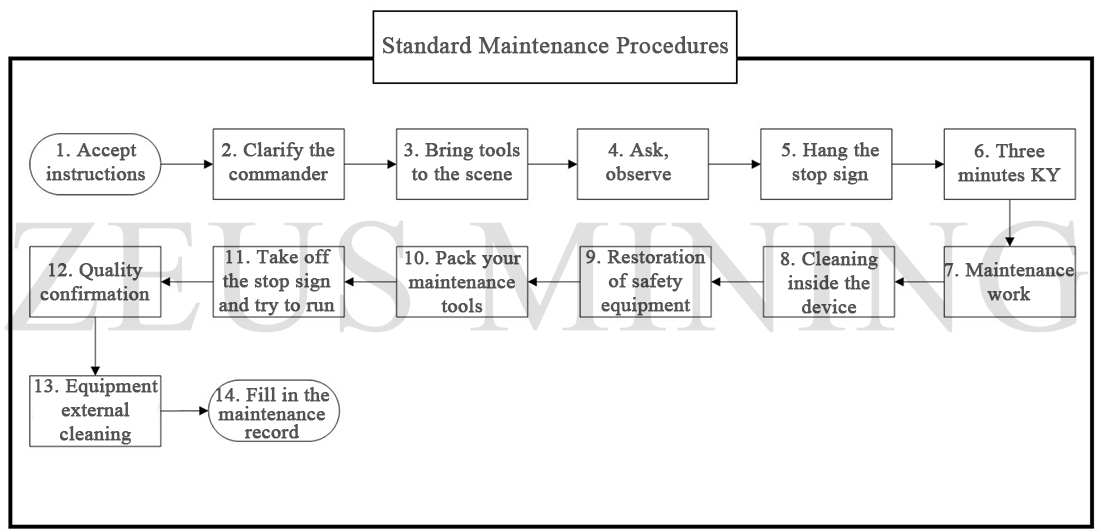
1) Maintenance content
Routine maintenance content: regular sanitation of distribution box, cabinet room floor, wall, etc.; screw tightening of the secondary circuit; daily maintenance of voltmeter, electric meter, etc., indicator lights in good condition; flexible operation of various switches check and debug.
Scheduled maintenance content: regular dust removal and inspection and tightening of busbars and secondary control circuits; regular inspection of cable-to-ground and interphase insulation resistance; regular inspection of grounding, zero-row, and grounding goodness of each cabinet; The grounding of the transformer is checked for the goodness of the ground.
2) Power outage before maintenance

Before the operation, wear insulating boots and insulating gloves:
a. Power failure: low-voltage household circuit breaker - sub total circuit breaker - sub-ring main unit circuit breaker - closed ring main unit grounding switch;
b. Electricity inspection: the front end of the low scoring total circuit breaker (no electricity display) - the high voltage end of the inspection;
c. Discharge: check the high voltage end (no power display) - display sequentially from low voltage to high voltage;
d. Grounding: first, clamp the grounding clip to the main ground row - ground phases A, B, and C in sequence.
3) Transformer maintenance

a. Tighten the connecting bolts of each component;
b. Dust and rust on the surface of each component;
c. Check whether the connection bolts of each component are overheated and oxidized;
d. Inventory tools and check for omissions.
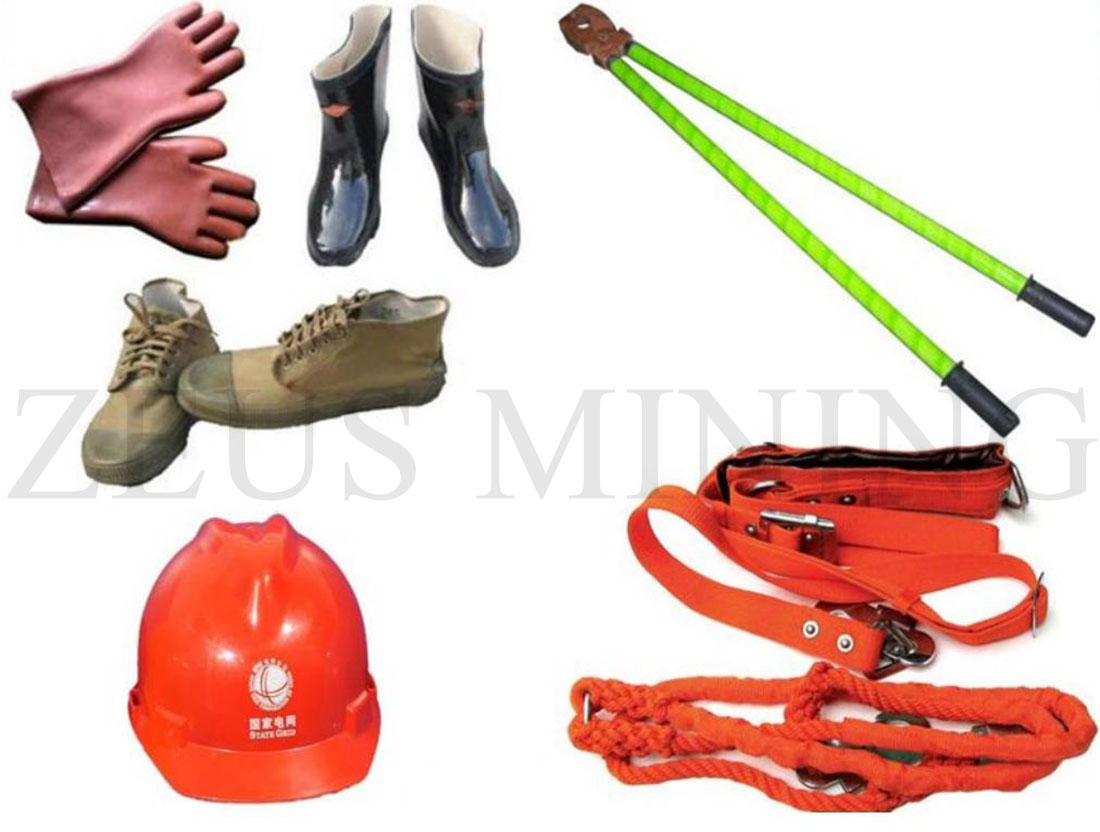
5. Insulation safety equipment
Commonly used high-voltage insulating safety appliances include insulating rods, insulating clamps, high-voltage electroscopes, high-voltage clamp flow meters, etc.
Auxiliary safety equipment includes insulating gloves, tools with insulating handles, insulating boots, insulating shoes, insulating platforms and insulating blankets.
Commonly used low-voltage insulating safety appliances include insulating gloves, tools with insulating handles, low-voltage electroscopes, etc.
Auxiliary safety equipment includes an insulating table, insulating pad, insulating boots, insulating shoes, etc.

6. Emergency handling procedures
1) Emergency procedures for electric shock risk
Purpose | This scheme is formulated to prevent casualties caused by an electric shock at the construction site. |
Duty | 1. Regularly check the equipment's grounding condition, strengthen the equipment's maintenance and regular maintenance, and prevent the equipment from running with trouble. 2. If any abnormality is found, deal with it promptly and correctly and report it in time if it cannot be dealt with. |
Operation method | 1. Quickly cut off the power supply or use an insulating material such as a wooden stick to pick the wire away from the injured person. 2. Before the electric shock person is disconnected from the power supply, ambulance personnel is not allowed to touch the injured person directly with their hands. 3. If the person with electric shock is in a high place, take precautions to prevent falling from a high place. 4. If the injured person is unconscious, check their breathing and pulse; if necessary, perform artificial respiration and CPR until the patient begins to breathe spontaneously and the heart beats spontaneously again. 5. Call the 120 emergency center in time for first aid, 6. Wait beside the patient on the way to the hospital to monitor the condition of the injured. |
2) Electrical equipment explodes and catches fire
Purpose | This scheme aims to prevent casualties and equipment damage caused by electrical equipment explosions and fire at the construction site. |
Duty | 1. Execute electrical equipment operating procedures to prevent over-index operation. 2. Regular maintenance and testing to ensure the equipment is in good condition. 3. Pay attention to checking the oil level change and deal with the leakage fault in time. 4. Conscientiously implement the operating system to prevent the occurrence of wrong operations. 5. If any abnormality is found, deal with it promptly and correctly and report it in time if it cannot be dealt with. |
Operation method | 1. Cut off the power supply of the fire equipment and put out the fire. 2. Report the fire situation to the superior, and call the fire alarm in time according to the situation (with the consent of the superior leader). 3. On the premise of ensuring the safety of personnel, when cutting off the power supply, follow the operating procedures. It is strictly forbidden to pull the knife switch with the load. When operating, you should wear insulating gloves, insulating boots and use insulating appliances of the corresponding voltage level. 4. Carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride, 1211, and dry powder fire extinguishers should be used. It is strictly forbidden to use water or foam to extinguish the fire. 5. When equipment such as cables catches fire, toxic gas will be produced. Therefore, the fire extinguishing personnel should stand in the upper wind position and wear a gas mask. 6. When the oil-filled equipment (transformer) catches fire, the oil drain valve at the bottom of the body should be opened as soon as possible to drain the oil. 7. After the open flame of the equipment is eliminated, observe whether the equipment is wholly cooled to ensure there will be no secondary fire in the equipment. 8. In case of personal injury, call the emergency number 120 in time or send to the hospital for first aid. 9. Clean up the accident scene in time to avoid environmental pollution caused by equipment residues. |
7. Electrical work risks
Involving activities, equipment, and facilities | Risk | Source of risk | Control measures |
Electrical work | Misoperation, electric shock | Failure to perform two-person maintenance work requirements. | Perform two-person overhauls as required by the job. |
Operators do not have safety education and training. | Before construction, the construction unit should be educated on safety, and the construction unit should also provide construction education to the construction personnel. | ||
Personnel working without a license. | Special operators must work with certificates and ensure that the certificates are within the validity period. | ||
Personnel work without a license (work without an operation license). | Personnel works with certificates. | ||
Electric shock | Non-electrical work. | Special operators must work with certificates and ensure that the certificates are within the validity period. | |
Stop (transmit) electricity without hanging corresponding warning signs. | Stop (transmit) electricity and hang corresponding warning signs. | ||
No warning signs are attached after the switch is completed. | After the switch is completed, hang up the warning sign. | ||
Electric shock, personal injury | Not equipped with qualified electrician tools and instruments. | Equipped with qualified electrician tools and instruments. | |
After pulling the switch, the electricity is not checked. | Check the electricity after pulling the gate. | ||
Check and confirm there is no power transmission obstacle before going to the job site. | Go to the job site to check and confirm that there is no power transmission obstacle. | ||
Not equipped with qualified electrician tools and instruments. | Equipped with qualified electrician tools and instruments. | ||
Arc burn | The switch arc chute is damaged or missing. | Check and replace the switch arc chute in time. | |
With load (close) brake. | It is strictly forbidden to open the gate with load (close). | ||
The wrong sequence of operations during a power outage. | In the event of a power failure, follow the operation order of the job ticket. | ||
Arc burns, electric shock | The power-on operation sequence is wrong. | When powering on, follow the operation order of the job ticket. | |
It is not confirmed that the inverter has stopped working, and the switch of the upper-level substation is turned off. | Confirm that the inverter has stopped working and the switch of the upper-level substation is turned off. | ||
The indicating meter has not been checked to confirm any voltage. | Check the indicating meter to make sure there is no voltage. | ||
Equipment damage | The meter indication is not checked for correctness. | Check that the meter indicates correctly. | |
It is not confirmed through the visual window whether the knife switch is in the closed position. | Check whether the knife switch is closed through the visual window. | ||
Rinse with water. | It is strictly forbidden to use water to rinse. | ||
Not regularly cleaned as required. | Regular cleaning as required. | ||
The isolating switch (knife switch) is not closed in place (contact is overheated). | The isolating switch (knife switch) must be closed and checked and confirmed after closing. | ||
Electrical work | Personal injury | Not equipped with power failure emergency lighting facilities. | Equipped with power failure emergency lighting facilities and ensure complete and easy to use. |
Not wearing insulating shoes and gloves. | Wear insulating shoes and insulating gloves before operation. | ||
Production interruption, electric shock | Open the power unit cabinet door in the running state. | It is strictly forbidden to open the cabinet door of the power unit in the running state. | |
Stop the wrong loop. | Stop the loop according to the operation order of the job ticket. | ||
Cleaning work | Fire, explosion | Scrub equipment and floors with light oil or gasoline. | It is strictly forbidden to use light oil and gasoline to scrub the equipment and the ground. |
Mechanical damage | Do clean up, no warning signs (strangles). | Before cleaning and maintaining the pump, the pump should be stopped, and a warning sign should be hung; it is strictly forbidden to clean and repair the running pump. | |
Other injuries Fall from height | Failure to stand still when cleaning the windows can cause falls and scratches. | Concentrate, hold on tight. | |
Entering a small space for cleaning (falls, bumps). | During the operation in the narrow operating space, it is necessary to concentrate, pay attention to observation, operate prudently, and wear protective measures and labor protection clothing to avoid bruises and bumps. | ||
Static electricity | When cleaning at heights, no protective measures are taken. | Fasten seat belts when working at heights; seat belts and backup ropes should be hung on sturdy and firm components and check whether they are fastened. The safety rope cannot be hung on moving and unstable objects with sharp corners. | |
Work handover | Personal injury | Incorrect working attire. | Wear labor protection products to prevent mechanical strangulation of clothing and hair from being stirred by the pump and static electricity generated in flammable and explosive places. |
Mechanical damage | Bump. | The succession inspection is careful and careful to avoid the human body bumping the equipment. |
Dear Customers,
Hello, April 4, 5 and 6, 2025 (GMT+8) are the traditional Chinese festivals - Qingming Festival. Our company will suspend shipments during these 3 days and resume shipments on April 7 (GMT+8). We are deeply sorry for the inconvenience. Thank you for your understanding and support.
Best wishes,
ZEUS MINING CO., LTD