


Antminer HS3 KA3 Hash Board Repair Guide
Ⅰ. Repair platform / Tools / Equipment Preparation
1. Platform requirements:
Anti-static repair workbench (the workbench needs to be grounded), anti-static wrist strap and grounding..
2. Equipment requirements:
(1) Constant temperature soldering iron (350℃-380℃), pointed iron head is used for soldering small chips such as chip resistors and capacitors.
(2) Heat gun and heating platform (350℃-400℃).
(3) BGA repair workbench is suitable for chip / BGA disassembly and soldering.
(4) Multimeter is equipped with a welded steel needle and a heat-shrinkable sleeve for easy measurement.
(5) Oscilloscope (UTD2102CEX+ oscilloscope is recommended).
(6) Network cable (Requirement: connected to the Internet, stable network).
3. Test tool requirements:
(1) APW12 power supply (APW121417b and power adapter cable production: use thick copper wires for the positive and negative poles of the power supply to connect the power supply and the hash board. It is recommended to use 4AWG, copper wires with a length of less than 60cm, only for PT1 and maintenance testing). Used for powering hash boards.
(2) When using the test fixture with V2.1 or V2.3 control board (test fixture material number ZJ0001000001), the positive and negative poles of the power supply of the test fixture need to be equipped with discharge resistors. It is recommended to use cement resistors of 20 ohm and above 100W.
4. Maintenance auxiliary materials/tools requirements:
Solder paste M705, flux, circuit board cleaning solution with absolute alcohol, thermal conductive gel, planting tin tool(6*6 chip size), solder absorbing wire, solder ball (ball diameter recommended 0.4mm).
(1) Circuit board cleaning solution is used to clean up the flux residue after maintenance.
(2) Thermally conductive gel (specification: FujipolySPG-30B) is applied on the surface of the chip after maintenance.
(3) When replacing a new chip, it is necessary to tin-plant the pins of the chip first, then solder it to the hash board, and evenly apply thermal conductive silicone grease on the surface of the chip. Finally install the heat sink.
5. Repair auxiliary tools:
(1) Scanning gun: recommended ZD2200 Wired Scanner
(2) Adapter board RS232/TTL adapter board 3.3V
(3) Self-made short-circuit probes are soldered with needle wires, need to add heat-shrinkable sleeves to prevent short-circuiting between the probes and the small heat sink.
6. Common maintenance spare material requirements: 0402 resistors (0R, 51R, 10K, 4.7K), 0402 capacitors (0.1uF, 1uF).
Ⅱ. Operation Requirements
1. Pay attention to the technique when replacing the chip. There will be no obvious deformation of the PCB board after replacing any accessories. Check whether there are any open or short circuit problems in the replacement parts and surrounding parts.
2. Maintenance personnel must have certain electronic knowledge, more than one year of maintenance experience, and be proficient in BGA/QFN/LGA packaging and soldering technology.
3. After maintenance, the hash board must be tested twice or more and the results are 0K, in order to pass!
4. Check whether the tools and fixtures can work normally, determine the maintenance station test software parameters, test fixture versions, etc.
5. To test the replaced chip, test the chip first, pass and then perform the functional test. Ensure that the small heatsink soldering is OK and large thermal instalation in place (each thermal adhesive must be applied evenly after the installation of a large heatsink). and the cooling fan is at full speed. To use chassis for cooling, it is required to put 2 pieces of hashboard at the same time to form a duct, which is also required (and important) for the single-sided test of production.
6. When measuring signals, 4 fans are assisted for heat dissipation, and the fans maintain full speed.
7. When powering on the hash board, must first connect the negative copper wire of the power supply, then connect the positive copper wire of the power supply, and finally plug in the signal cable. When disassembling, the order must be reversed from that of installation. First remove the signal cable, then remove the positive copper wire of the power supply, and finally remove the negative copper wire of the power supply. If don't follow this order, it is very easy to cause U1 and U2 to be damaged (not all chips can be found). Before testing the pattern, the repaired hash board must cool down before testing, otherwise it will cause test PNG.
8. When replacing a new chip, the pins and solder paste must be printed to ensure that the chip is pre-tinned and then soldered to the PCBA for repair.
Ⅲ. Fixture Setup and Precautions
The fixture should be able to dissipate heat from the hash board and facilitate signal measurement.
1. Fixture model: ZJ0001000001
2. When using the 19 series test fixture for the first time, use the SD card flash program to update the FPGA on the fixture control board, unzip it and copy it to the SD card, and insert the card into the fixture card slot. Power on for about 1 minute and wait for the indicator light on the control board to double flash 3 times before the update is completed (if it is not updated, a certain chip may be reported as defective during the test).

Figure 3-1
3. Production of SD card without heat sink: Use the PT1 program for repair. As shown in the screenshot below, this program can be tested without scanning the code. Repairman needs to dissipate heat to the PCBA when measuring to prevent the board from overheating during testing and measurement.
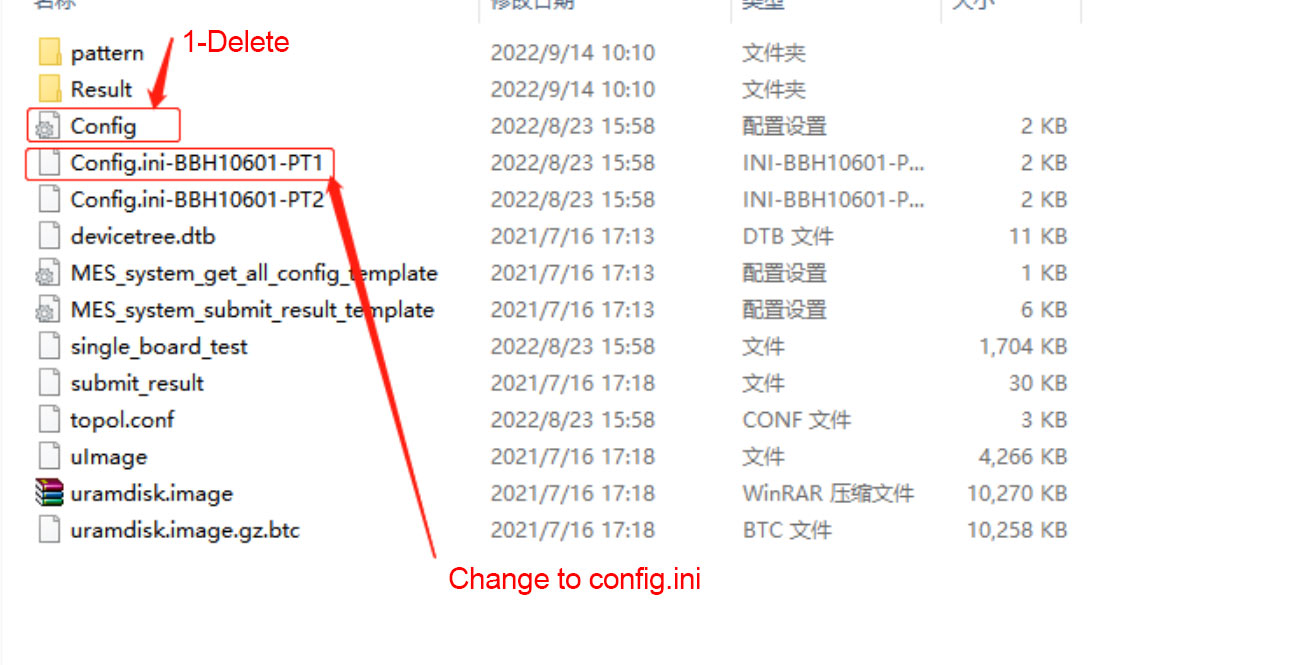
Figure 3-2
4. Production of SD card without heat sink: Double-sided heat sink 8x Patter test requires production of SD card, as shown in the figure below: Change the name of the congfig.ini-BBH10601-PT2 (congfig.ini-BBK10601-PT2) file to config.ini. When testing PT2, you do not need to plug in the code scanner, just plug in the network cable. Please refer to the production heat dissipation method for the heat dissipation method. (Elements: The board is inserted into the chassis, the screws are locked for power supply, and the fan must be at full speed and the ambient temperature should be less than 30°C)
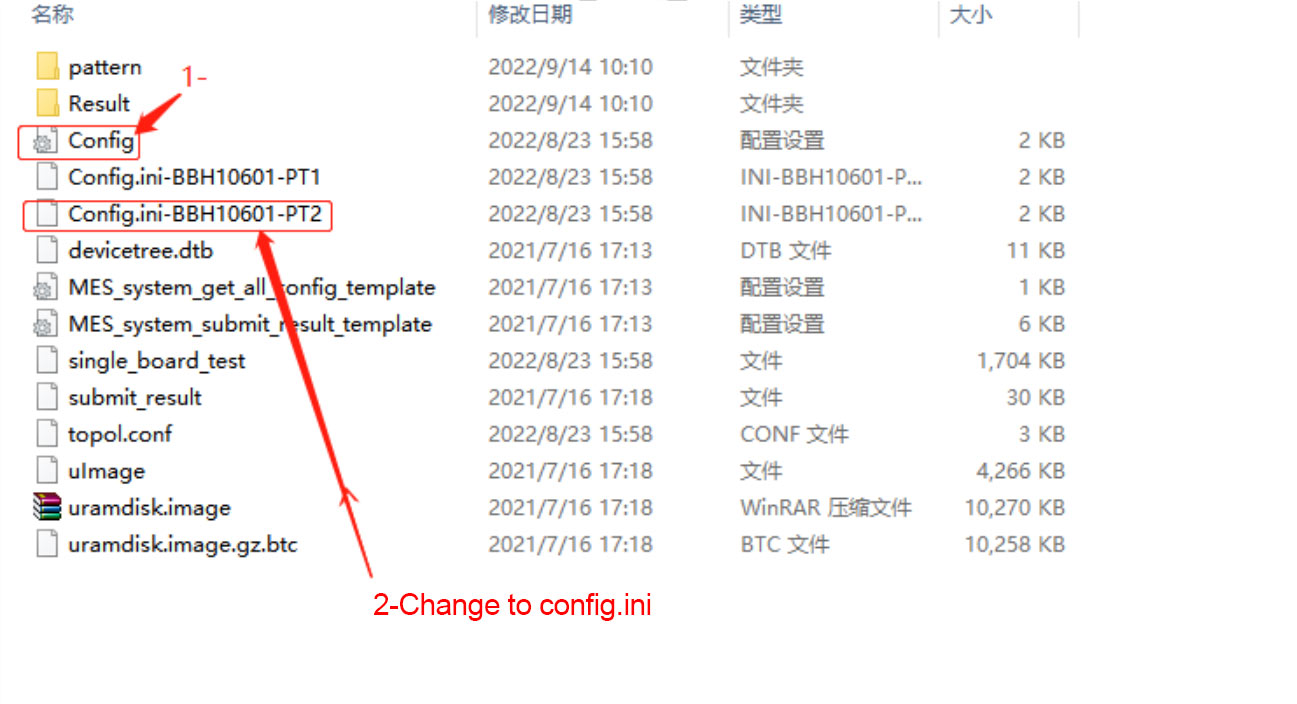
Figure 3-3
IV. Principle and Structure of Hash board
1. Hash board working structure:
Antminer HS3 hash board BBH10601 version uses BM2130 ASIC chip; Antminer KA3 hash board BBK10601 version uses BM2110 ASIC chip.
The BBH10601 hash board consists of 92 BM2130 chips, divided into 46 groups (domains), each group consisting of 2 ICs. The BM2130 chip used in the BBH10601 hash board has an operating voltage of 0.32V. Groups 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, and 40 (7 groups in total) are powered by the 19V output by the boost circuit U7, so that the LDOs in these four domains output 1.2V and 0.8V. The power supply for the remaining domain LDOs is VDD17V input, making them output 1.2V and 0.8V.
(PT2 test, log page view starts from asic0, refer to Figure 4-1)
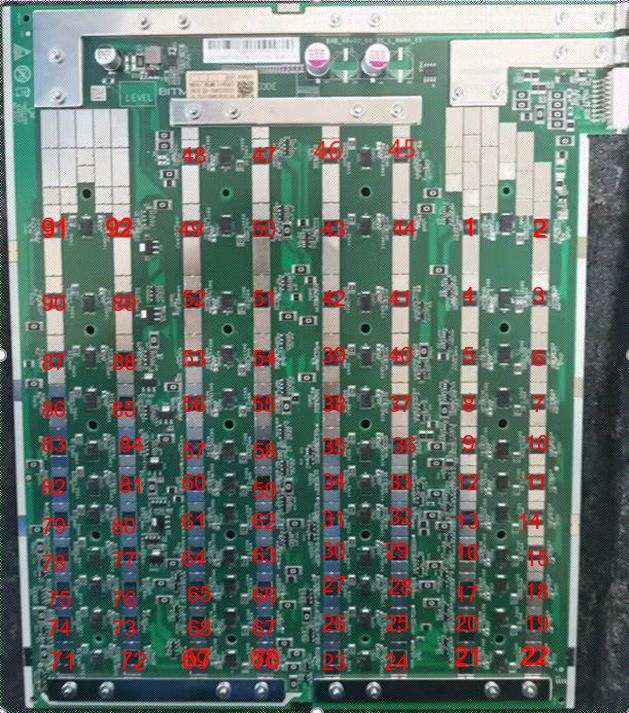

Figure 4-1
(The voltage domain in the test log starts from 0, that is domain0, refer to Figure 4-2)
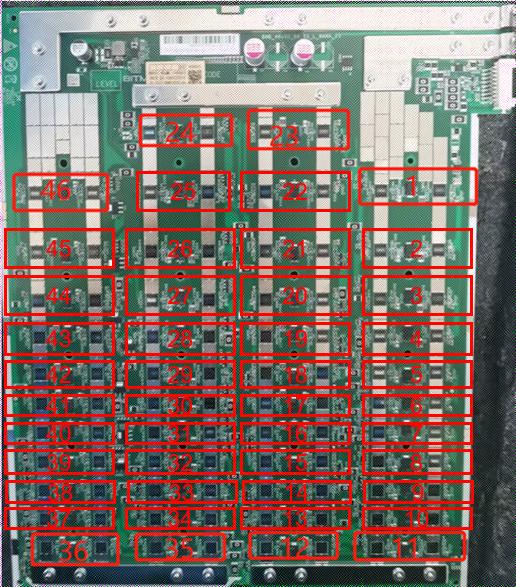

Figure 4-2
2. BBH10601 hash board boost circuit:
The boost is powered from 17V to 19V by the power supply, as shown in Figures 4-3 and 4-4.
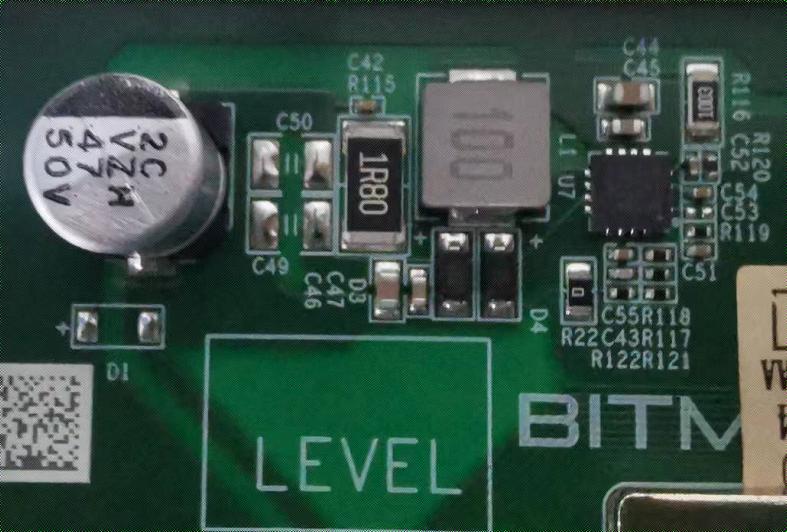

Figure 4-3
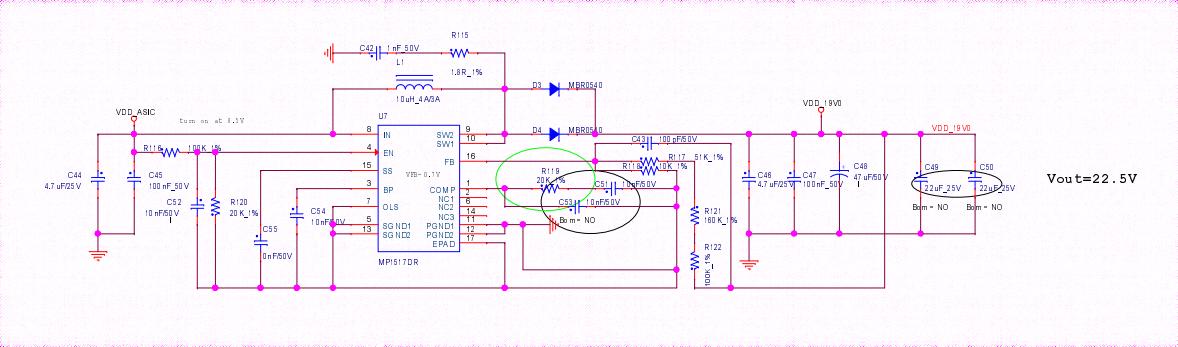
Figure 4-4
3. BBH10601 chip signal direction:
1) CLK (XIN) signal flow direction: generated by Y1 25M crystal oscillator, transmitted from chip No. 01 to chip No. 92;
2) RST signal flow direction: from pin 3 of the IO interface, and then transmitted from chip No. 01 to chip No. 92;
3) CI signal flow direction: from pin 7 of the IO interface, and then transmitted from chip No. 01 to chip No. 92;
4) RX (RI, RX) signal flow direction: from chip No. 92 to chip No. 01;
5) BO (BI, BO) signal flow direction: from chip No. 01 to No. 92;
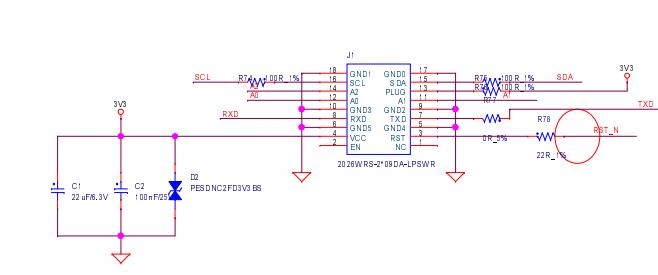
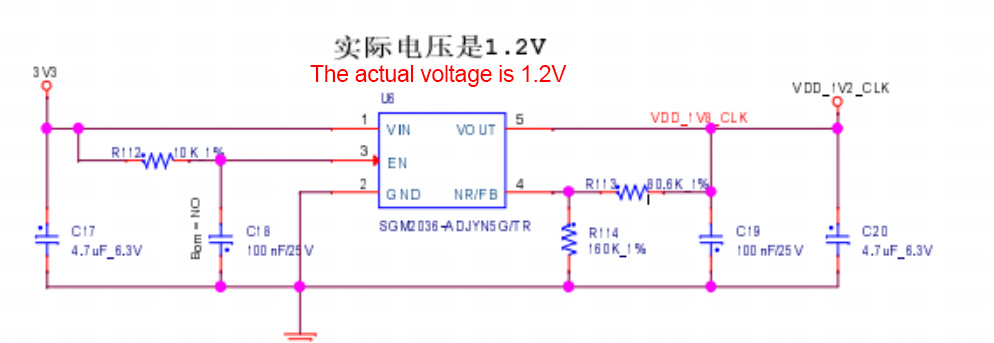
Figure 4-5
4. Whole miner architecture:
The whole miner mainly consists of 3 hash boards, 1 control board, APW121417b power supply, and 4 cooling fans, as shown in Figure 4-6.
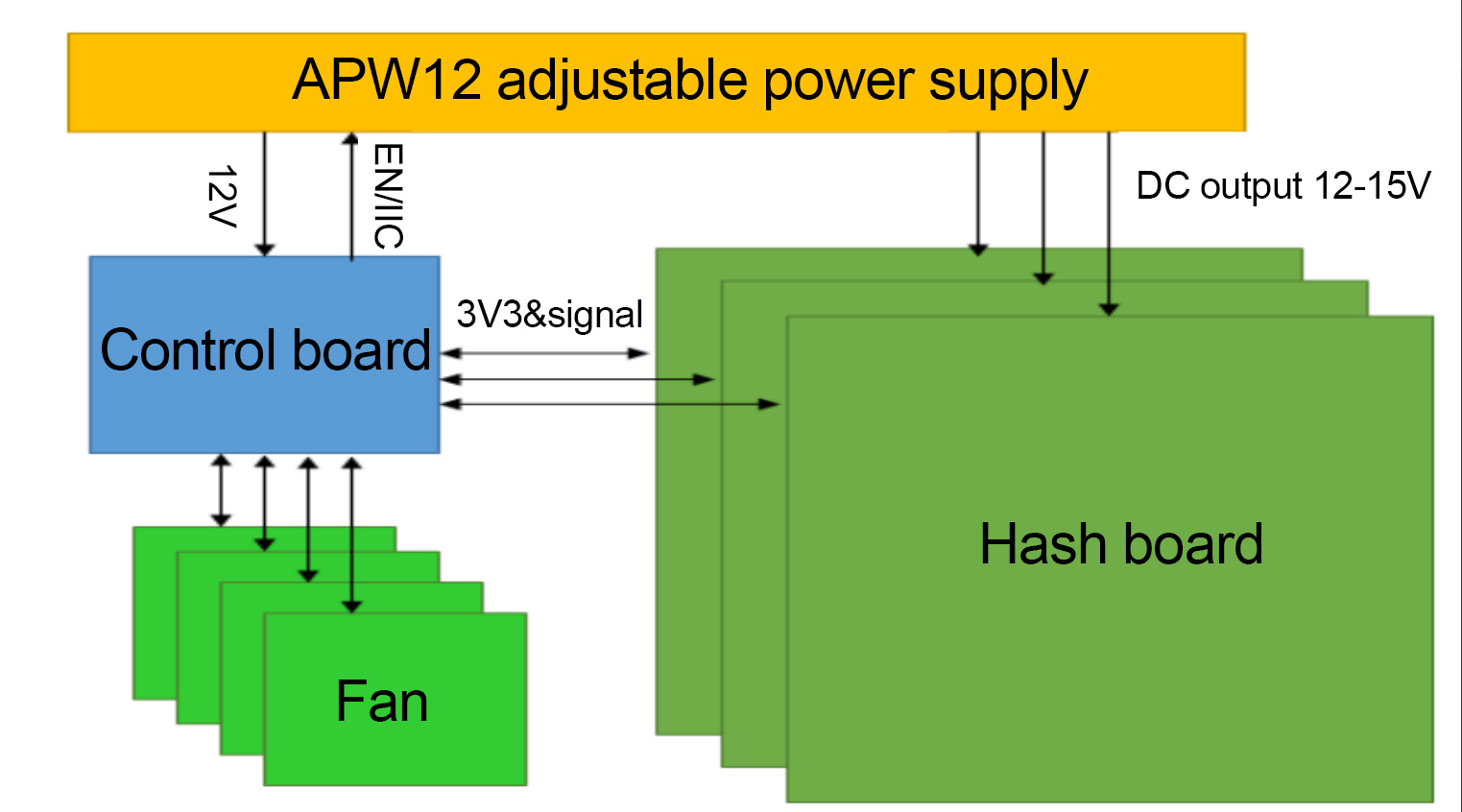
Figure 4-6
V. Common failures of hashboard and troubleshooting steps
1. Phenomenon: The single board test detection chip is 0 (PT1/PT2 station)
Step 1: Check the power output first;
Step 2: Check the voltage domain voltage output. 17V power supply generally has domain voltage. Prioritize measuring the hash board power terminal output;
Step 3: Check the boost circuit output. In the picture, test C29 can measure a voltage of 19-20V.
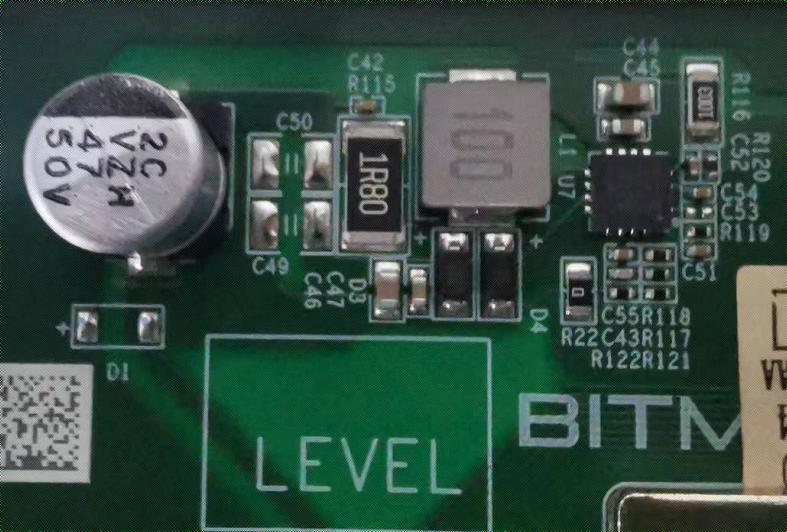

Figure 5-1
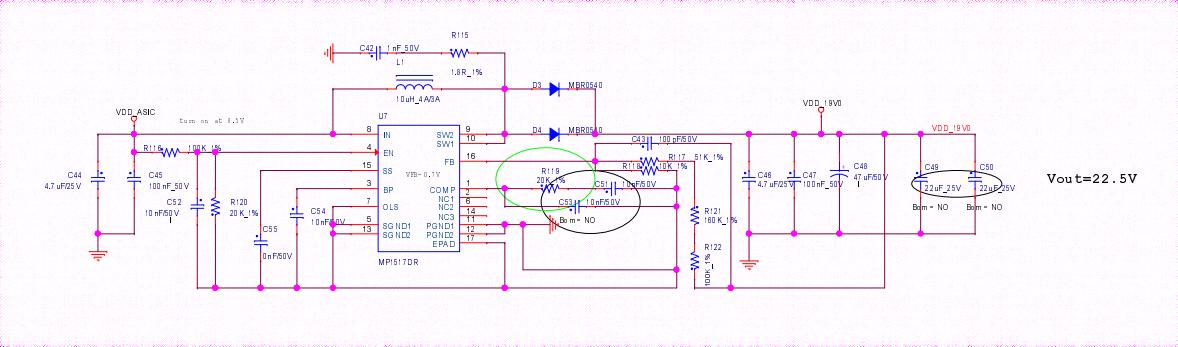
Figure 5-2
Step 5: Check the LDO 1.2V or PLL 0.8V output of each group;
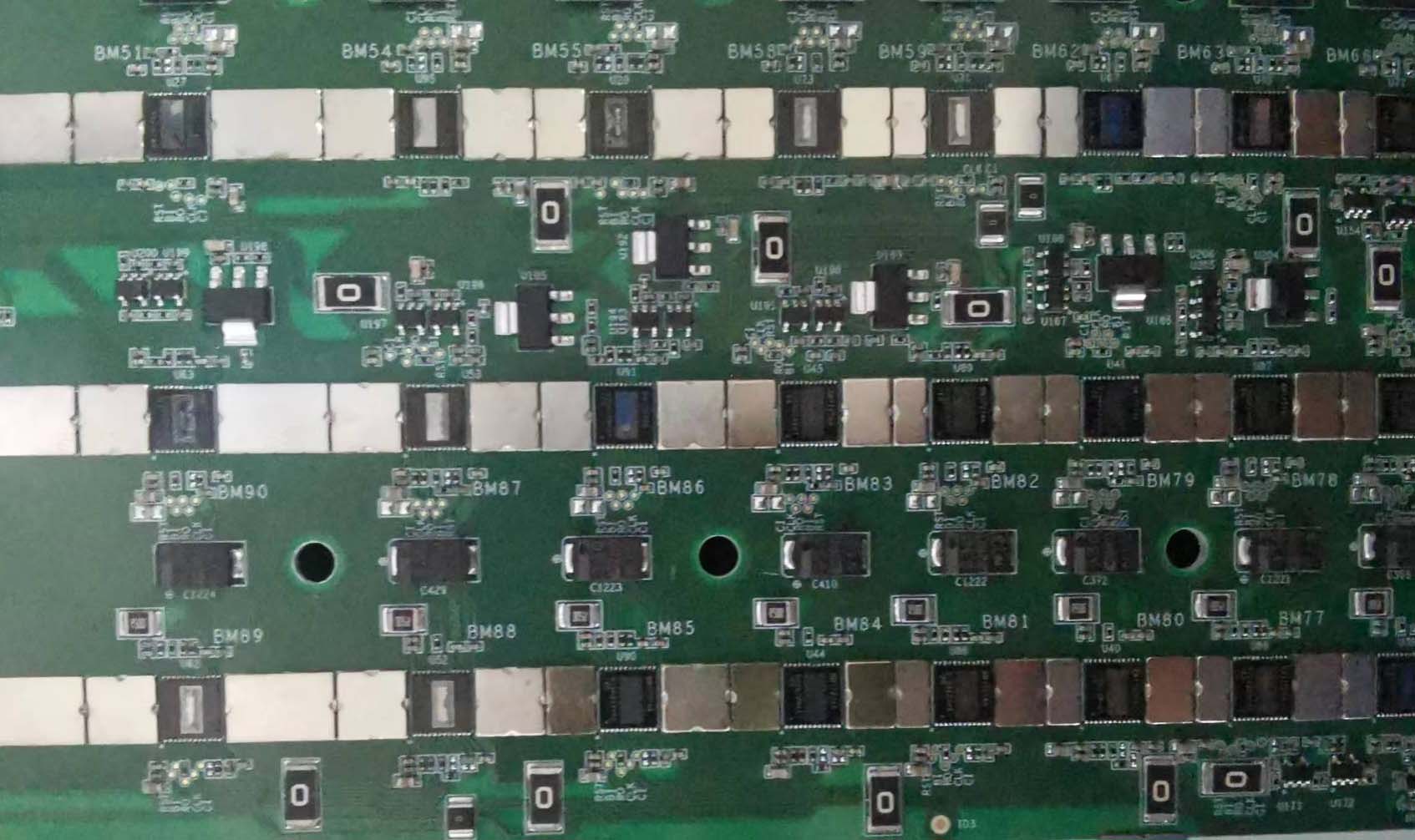
Figure 5-3
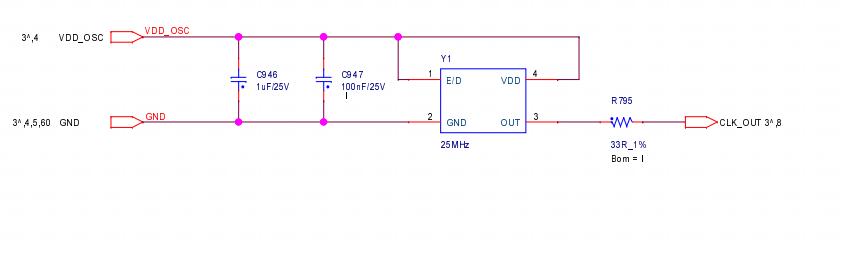
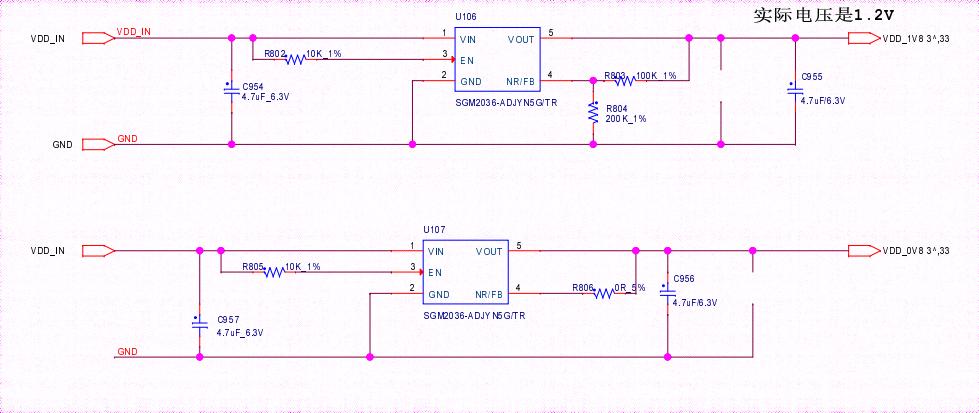
Figure 5-4
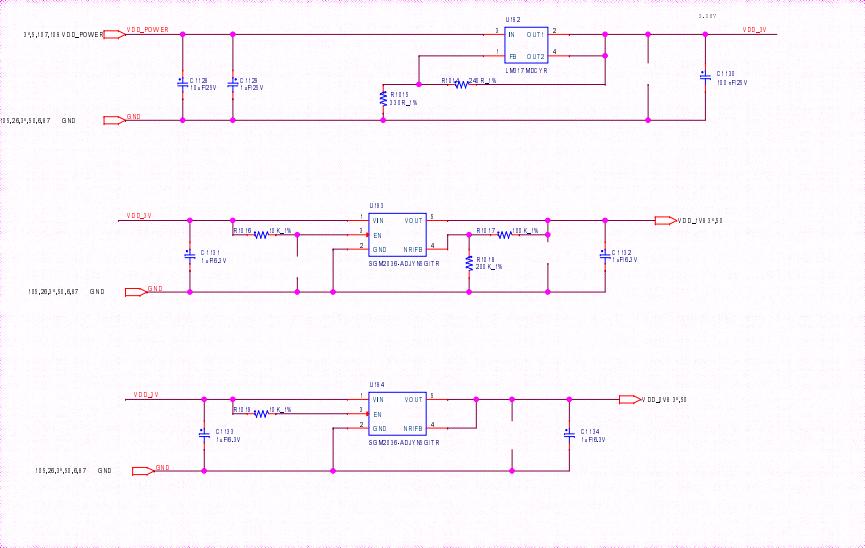
Figure 5-5
Step 6: Check the chip signal output (CLK/CI/RI/BO/RST).
Refer to the voltage value range described in the signal direction. If the measurement encounters a large voltage value deviation, it can be compared with the adjacent group of measured values.
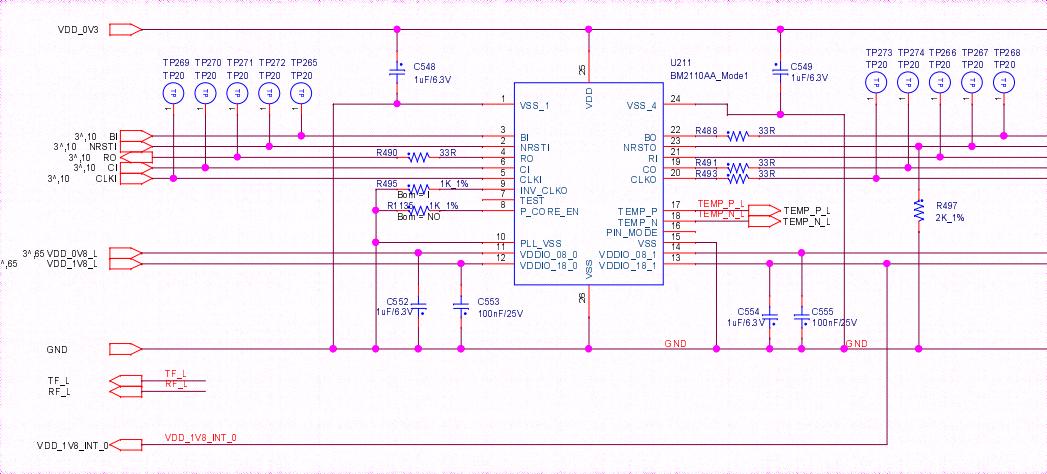
Figure 5-6
2. Phenomenon: Insufficient single board detection chips (PT1/PT2 station)
a) When the display shows ASIC NG: (0), first measure the total voltage of the measurement domain, and then check that the boost circuit 20V is normal. Then use a short-circuit probe to short-circuit the RX test point and 1V2 test point between the first and second chips, and then run the chip finding program. Looking at the serial port log, if 0 chips are still found at this time, it will be one of the following situations:
a-1) Use a multimeter to measure whether the voltages of the 1V2 and 0V8 test points are 1.2V and 0.8V. If not, it may be that the 1.2V and 0.8V LDO circuits in this domain are abnormal. Either the main chip of this domain is not soldered properly, or it is caused by a short circuit of the 0.8V or 1.2V patch filter capacitors, or the IC of the LDO circuit in this domain is not soldered/fake soldered/material damaged.
a-2) Check whether the circuit of U2 is abnormal, such as resistor soldering, etc.
a-3) Check whether the pins of the first chip are not soldered properly (repairs have found that the pins are tinned when viewed from the side, but when the chip is removed, it is found that the pins are not tinned at all).
b) If one chip can be found in step a), it means that the circuit in front of the first chip and the first chip are both good. Use a similar method to check the chips behind b). For example, if the 1V2 test point and RX test point between the 23rd and 24th chips are short-circuited, if the log can find 23 chips, then there is no problem with the first 23 chips; If 0 chips are still found, first check whether the 1V2 is normal. If it is normal, there is a problem with the chips after 23 chips. Continue using the dichotomy method until you find the problematic chip. Assuming there is a problem with the Nth chip, then when 1V2 and RX between the N-1th and Nth chips are short-circuited, the N-1 chip can be found. But when 1V2 and RX between the N and N+1 chips are short-circuited, not all chips can be found.
c) When the LCD displays ASIC NG: (a certain chip is fixedly reported), there are two situations:
c-1) The first situation: (Usually the value of the chip reported during each test will not change). In this case, just follow the normal maintenance method of measuring the signal voltage. (It may also be a resistor collision near the chip)
Figure 5-7
c-2) During the test, assuming that the domain voltage of all the domains in front of the abnormal position is almost all less than 0.32V, while the domain voltage of the rear domain is almost all higher than 0.32V, this case is caused by the unsoldered chip, usually 1.2V, 0.8V, RXT and CLK are not well soldered.
2. Phenomenon: Single board Pattern NG, that is, the reply nonce data is incomplete (PT2 station)
Pattern NG is caused by the fact that the characteristics of one chip are quite different from other chips. Currently, it is found that the chip die is damaged, so you only need to replace the chip. According to log information, the replacement rule is:
a) Check the thermal grease printing quality;
b) If the appearance of the chip is not damaged, just replace the chip with the lowest nonce rate in each domain;
c) Swap the one with the higher nonce and the one with the lower nonce to see if it changes with the chip. If it changes with the chip, just replace the chip. If it does not change as the chip changes, measure whether the voltage in this domain is lower than the normal value. Measure whether the resistance value of the chip pad pin is the same as normal. If not, check whether the resistance value of the small resistor next to it is too high. If it is too high, replace it;
PS: It is important to note that the numbers of domain and asic both start from 0.
3. Phenomenon: B_A X PCS (X chips have insufficient response)
Swap and replace these chips with chips with higher response in other domains to see if there is any effect. If not, just replace these chips.
4. Phenomenon: The chip test is OK, and the PT2 function test serial port does not stop (long-term operation)
Repair method: During the PT2 test, check the serial port print log. When the serial port starts to run for a long time, use a short-circuit probe to short-circuit RX and 1.2V, and start the short-circuit from the first chip. If the serial port stops running after a short circuit, it means the first chip is OK. Use this method to find the chip that remains faulty after a short circuit. Generally, it is caused by damage to a certain chip and needs to be replaced.
PT2 test environment requirements: The temperature of the PT2 test environment must be 20 degrees to 30 degrees. When the ambient temperature exceeds 35 degrees, the software will stop testing. Heat dissipation is required during measurement. The following heat dissipation platform can be used to dissipate heat for PT1 measurements and run DEBUG firmware.
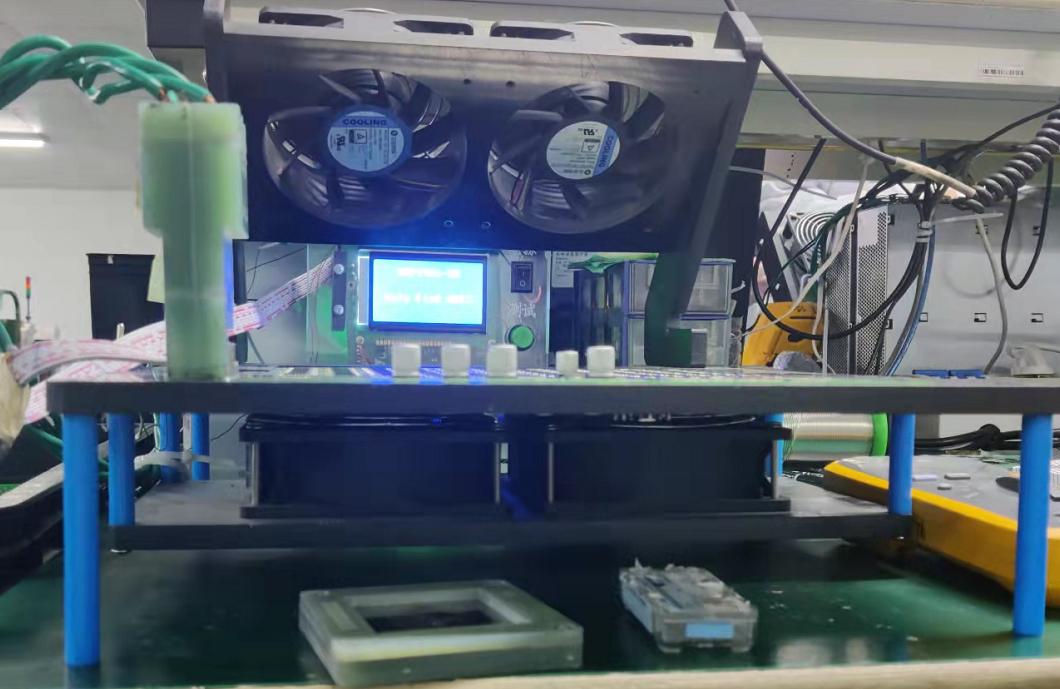

Figure 5-8
2. Chip address error (PT2) Repair method: Just replace the error chip.
3. PNG, which chip has a low nonce, swap it with the one with a high nonce first. If it changes, replace the bad chip.
4. The single board is OK, but the whole miner hash rate is reduced
(1) There is an RX error on a certain chip;
(2) The LDO power supply of a certain domain is unstable, and the resistance value of its series resistor may be abnormal.
Ⅵ. Common problems caused by control board
1. The whole miner is not running
1) Check whether the voltage at the voltage output point is normal. If 3.3V is short-circuited, you can disconnect U8 first. If it is still short-circuited, you can unplug the CPU and measure. For other voltage abnormalities, generally replace the corresponding voltage converter IC.
2) If the voltage is normal, please check the welding status of the DDR/CPU.
Try to update the flash program with SD card:
If the miner needs to start normally, the following 2 steps are required:
a) After the flashing is successful, the green LED indicator light is always on, and then the power is turned off and restarted;
b) Wait 30s after powering on again (the time process for opening OTP);
c) OTP (One Time PRXgramable) is a memory type of MCU, which means one-time programmable: after the program is burned into the IC, it cannot be changed or cleared again.
Notes:
(1) A sudden power outage or less than 30 seconds during the OTP opening process will cause the control board to fail to open the OTP function. If the control board does not start (cannot connect to the Internet), U1 (control board main control IC FBGA) needs to be replaced. The replaced U1 can no longer be used in the 19 series.
(2) U1 cannot be used on other series of models if the OTP function is enabled on the control board.
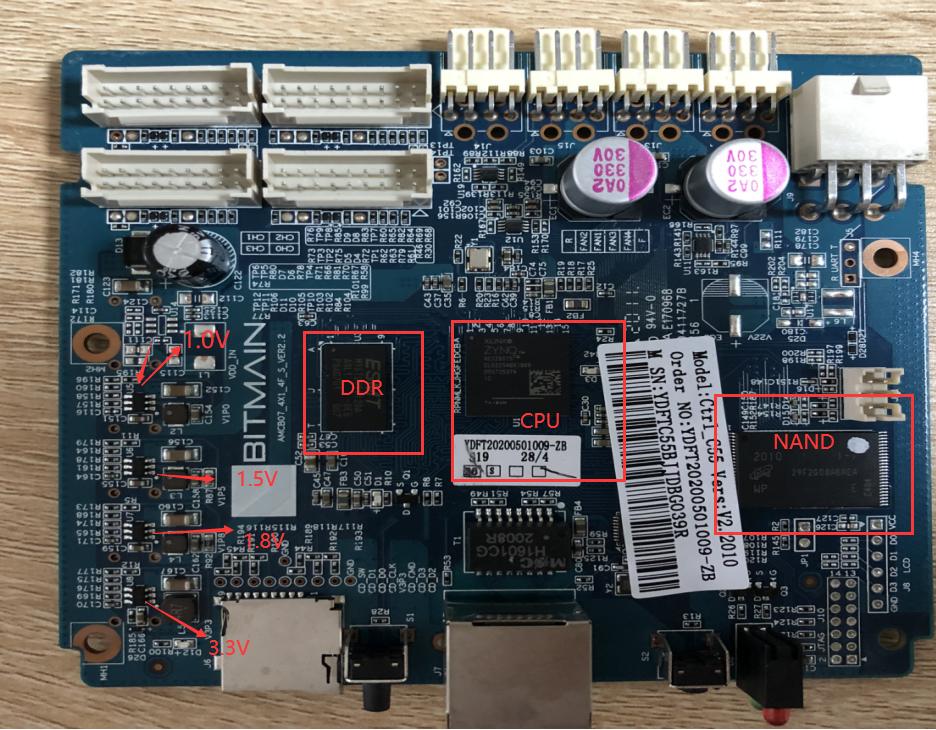
Figure 6-1
2. The miner cannot find the IP
There is a high probability that the IP cannot be found due to abnormal operation. Please refer to the first troubleshooting.
Check the appearance and welding condition of the network port, network transformer T1, and CPU.
3. The miner cannot be upgraded
Check the appearance and welding condition of the network port, network transformer T1, and CPU.
4. The miner fails to read the hash board or has less chain
A. Check the cable connection status;
B. Check the parts of the control board corresponding to the chain;
C. Check the wave soldering quality of the header pins and the resistance around the interface.
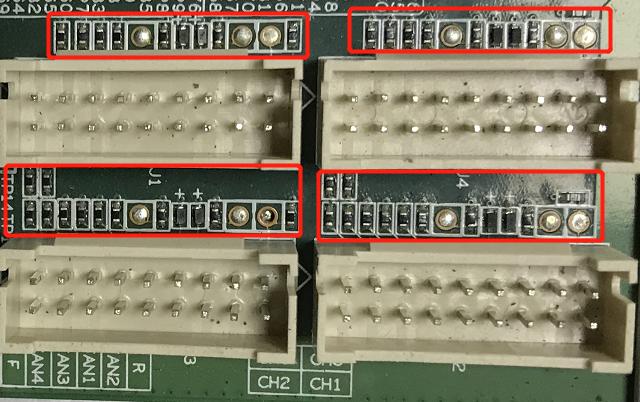

Figure 6-2
VII. Failure Phenomenon of the Whole Miner
1. Initial test of the whole miner
Referring to the test process document, the general problems are assembly process problems and control board process problems.
Common phenomena: IP cannot be detected, abnormal number of fans detected, abnormal chain detected. If an abnormality occurs during the test, repairs must be carried out according to the monitoring interface and test LOG prompts. The maintenance methods for the initial test of the whole machine and the aging test are the same.
2. Aging test: During the aging test, maintenance should be carried out according to the monitored interface test.
1) The fan display is abnormal: Check whether the fan is working normally, whether the connection with the control board is normal, and whether there is any abnormality in the control board.
2) Less chain: Less chain means 1 piece is missing from 3 boards. In most cases, there is a problem with the connection between the hash board and the control board. Check whether there is an open circuit in the cable. If the connection is OK, you can put the board to PT2 test to see if it can pass the test. If it can be tested, it can basically be determined that it is the control board. If it cannot be tested, use the maintenance method of repairing PT2 to repair it.
3) Abnormal temperature: Generally, the temperature is too high. The maximum PCB temperature set by the monitoring system cannot exceed 90 degrees. If it exceeds 90 degrees, the machine will alarm and cannot work normally. This is usually caused by the ambient temperature being too high. Abnormal fan operation can also cause temperature abnormalities. (BBK10601 only has 2 temperature sensors)
4) Unable to find all the chips, the number of chips is not enough: refer to PT1 test for repair.
5) After running for a period of time, there is no hash rate and the mining pool connection is interrupted. Check the network;
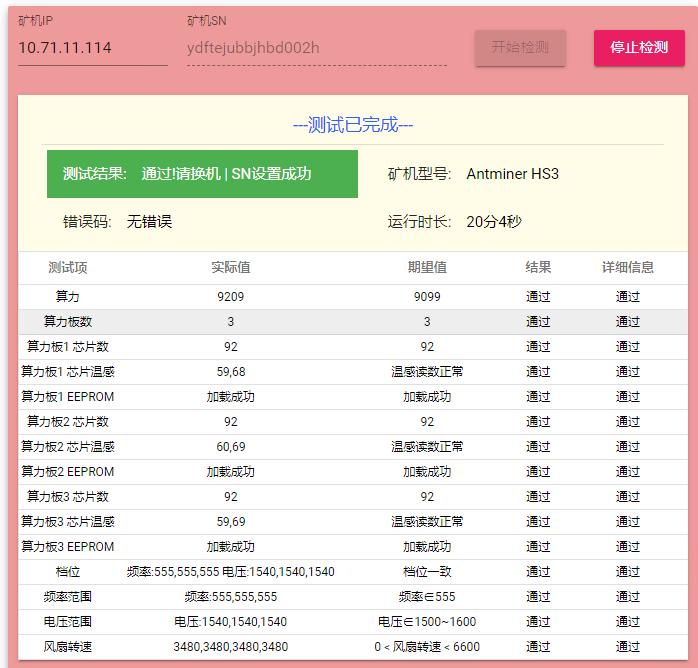
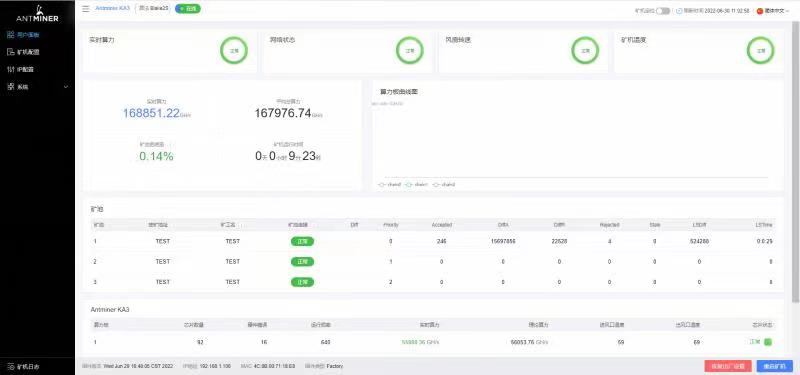
6) Aging test status of normal miner:
7) The hash rate of the whole miner is reduced:
After the single board test is OK and assembled into a complete miner test, one board has a low hash rate: First perform the single board PT2 test to see if the board is OK. If the test chips fail to detect all the chips, repair the single board. If the normal gear is OK after the test, then take out the board separately, use the test jig to transfer it into the De Bug master program for mining, and adjust the fan speed to 95%. The voltage and frequency are adjusted to the working voltage and frequency of the whole machine, and the miner is allowed to mine to see if the machine will reduce the hash rate. If the machine still loses hash rate, then reduce the frequency to 200M, keeping other conditions unchanged. Let the miner mine to see if it will reduce the hash rate, and whether the hash board will display X. If it still shows X and reduce the hash rate, then can remove the heat sink of the hash board and start mining.When waiting for the hash rate to drop, measure whether the domain voltage is normal. Generally, the domain voltage will be abnormal in the domain with problems. Then measure the RI signal to see if the RI signal is broken somewhere. If the RI signal is gone, basically the chip is short-circuited or damaged after being connected to the tin.
Ⅷ. Other notes
Repair flow chart
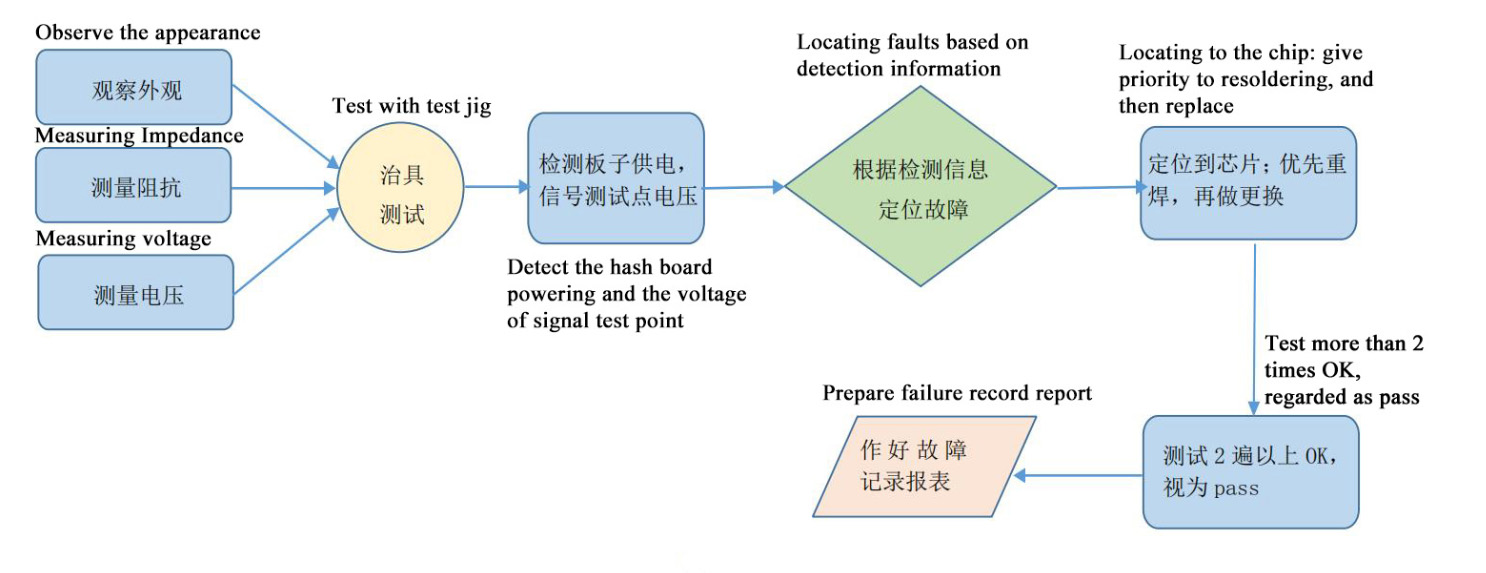
Figure 8-1 Repair flow chart
1. Routine inspection:
(1) First of all, visually inspect the hash board to see if there is any deformation or burning of the PCB. If there is any phenomenon, it must be dealt with first.
(2) Visually inspect whether there are obvious signs of burnt parts, parts impact offset or missing parts, etc.
(3) After the visual inspection is OK, the impedance of each voltage domain can be detected to detect whether there is a short circuit or an open circuit. If found, it must be dealt with first.
(4) Check whether the voltage of each domain is about 0.32V.
2. After the routine inspection is OK (short circuit detection of general routine inspection is necessary, so as not to burn the chip or other materials due to short circuit when the power is turned on), the chip can be tested with the test fixture, and the judgment and positioning can be carried out according to the test result of the test fixture;
3. According to the display results of the tester, start from the vicinity of the faulty chip, and check the chip test points (CO/NRST/RX/XIN/BI) and voltages such as VDD0V8 and VDD1V2.
4. According to the signal flow direction, in addition to the RX signal reverse transmission (No. 126 to No. 1 chip), the other several signals CLK CO BO RST are forward transmission (1-126), find the abnormal fault point through the powering sequence.
5. When the faulty chip is located, it is necessary to re-solder the chip. The method is to add flux (preferably no-clean flux) around the chip, and heat the solder joints of the chip pins to a dissolved state, so that the chip pins and pads are re-run-in and tin is collected to achieve the effect of re-tinning. If the same fault still exists after re-soldering, the chip can be replaced directly.
6. The repaired hash board needs to be tested with a test fixture, and it must pass more than two times to be judged as a good product. For the first time, after replacing the accessories, wait for the hash board to cool down, use the test fixture to test, and when is passed, put it on one side before cooling down. The second time, wait for the hash board to cool down completely before testing.