


IceRiver KS1 KS2 Hash Board Repair Guide
Ⅰ. Maintenance equipment requirements
1. Constant temperature soldering iron (350-400 degrees), used to flatten the residual tin slag on the surface of the pad and reinforce components.
2. Hot air gun is used for original mounting and soldering. Be careful not to heat for a long time to avoid blistering of PCB.
3. Multimeter, tweezers, electric screwdriver, temperature gun;
4. Solder wire, flux, board washing water, tin-absorbing tape; board washing water is used to clean the flux residue and appearance after maintenance.
5. Adjustable voltage PSU, fixed voltage 12V, current limit 2A.
6. Auxiliary devices: high temperature adhesive tape, thermal paste.
7. Common materials: quick-drying conformal paint, 2000W power supply, interface board data cable, interface board power cable, 12038 fan, control board, stepped spring screws (M4*10), hexagonal cross slot three-combination with pads (nickel-plated, M4*45), cross pan head (NYLOK, M3*10), cross pan head (NYLOK, M3*6).
Ⅱ. Operation requirements
1. After repair, the hash board must be tested more than twice and all are OK before it can pass!
2. After replacing any accessories, the PCB board has no obvious deformation. Check whether the replaced parts and the surrounding parts are missing, open circuit and short circuit.
3. Check the repair tools and test tools to see whether they can work normally.
4. If there are electrolytic capacitors or LED lights at the fault point, be sure to protect them with high-temperature adhesive tape to prevent damage to the capacitors.
5. When powering on the hash board board, pay attention to the fact that the negative power cable (black) must be powered on first, then the positive power cable (red), and finally the data cable. When disassembling, the order must be opposite to the installation order. First remove the data cable, then the positive power cable (red), and finally the negative power cable (black).
Note: The outer power terminal is positive (+), and the terminal close to the plastic socket interface is negative (-).
Ⅲ. Whole miner structure and principle
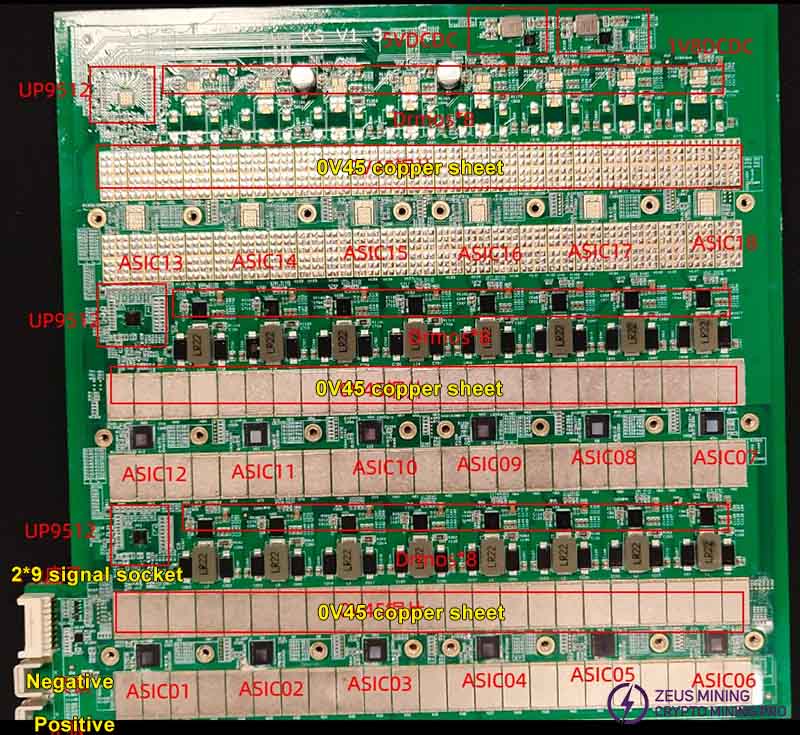
1. The KS1/KS2 model consists of a control board controlling four hash boards, each of which consists of 18 / 12 ASIC chips.
When assembling the whole machine, please note: the KS2 model has 4 hash boards, with a total of 72 ASIC chips; the KS1 model has 2 hash boards, with a total of 24 ASIC chips. All ASIC chip signals are connected in series, and the power is connected in parallel in groups of 6.
Model | Number of chips on a single board | Blank chip position |
KS2 | 12 | ASIC13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 |
KS1 | 18 |
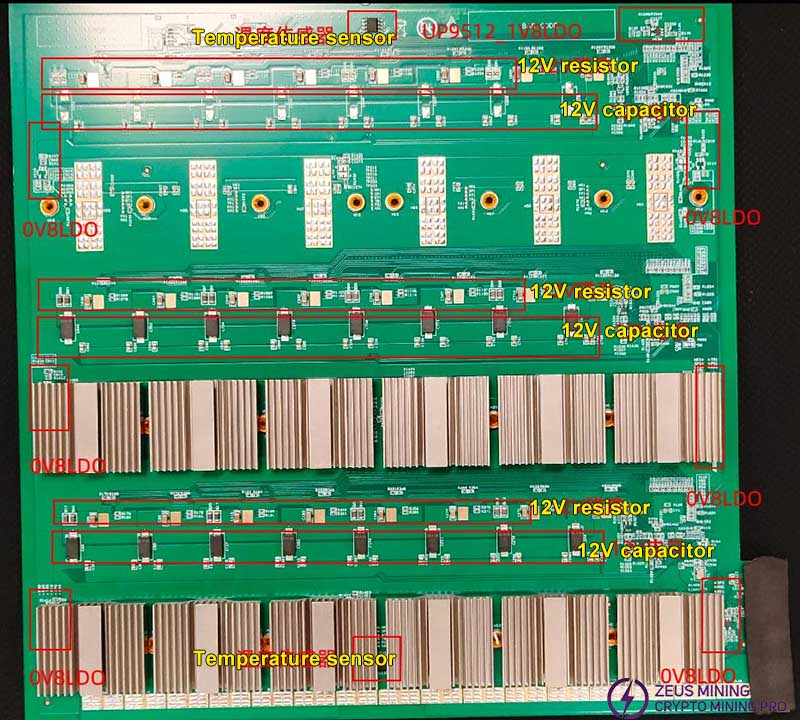
2. Main powering chip
(1) Chip U130 (Gs9238): 12V→1.8V
(2) Chip U134 (SGM2036-ADJ): 5V->1.8V
(3) Chip U4 (Gs9238): 12V→5.0V
3. ASIC chip powering is powered by 3 groups of voltages
(1) ASIC chip main voltage (uP9512) 0.45V.
(2) ASIC chip VDDPST/VDDPLL1V8 voltage (Gs9238) 1.8V.
(3) ASIC chip VDD0P8/VDDPLL0V8 voltage (SGM2036) 0.8V.
IV. Normal single board test process of hash board
Step 1: Use a barcode scanner to record the barcode on the KS1 and KS2 miners and the QR code on the board, and make a record.
Step 2: Connect the data cable and power cable between the control board and the hash board, including the power cable (yellow positive and black negative), the power terminal on the outside of the hash board is the positive pole (+), and the terminal close to the plastic socket interface is the negative pole (-), connect the negative pole first, then the positive pole. Among them, the data cable must be connected to the outermost interface.
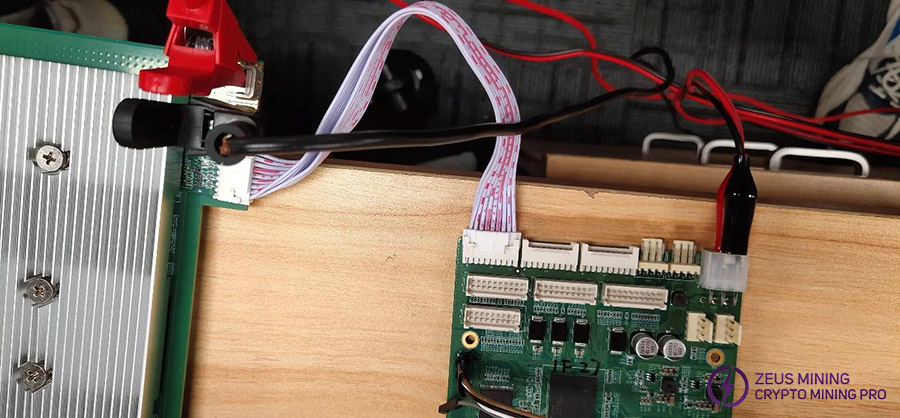
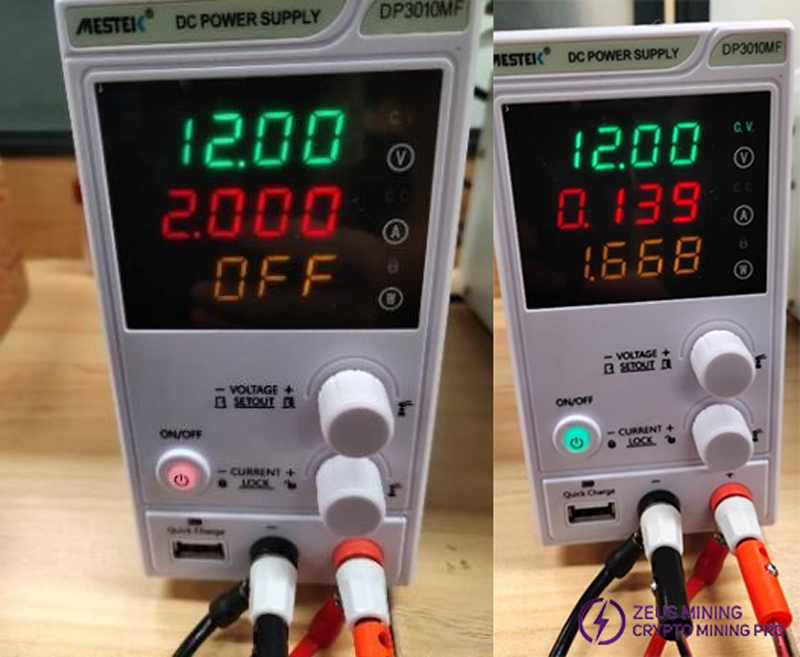
Step 3: Connect the network cable to the control board, make sure the PSU current is limited to 12V@2A, and power on.
Step 4: At the moment of power on, there is only about 12V@0.1A current. At this time, only the control board is powered, and only the temperature sensor on the hash board is powered. Moreover, it can be found that the red LED light on the hash board is not on.

Step 5 (Network cable test method): Use the group control software to scan and connect to the machine in the current network segment.
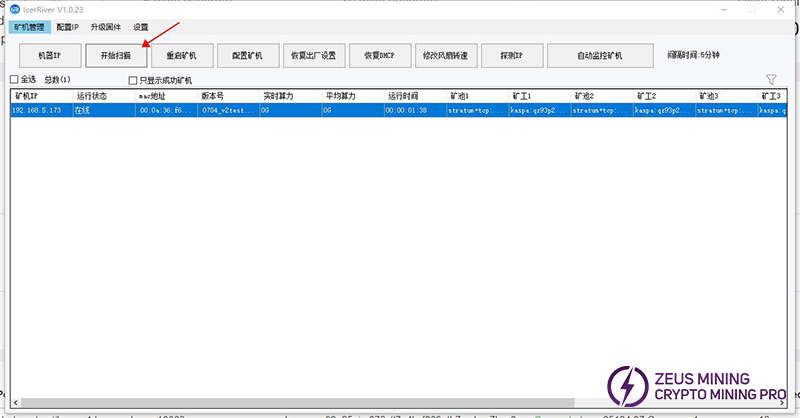
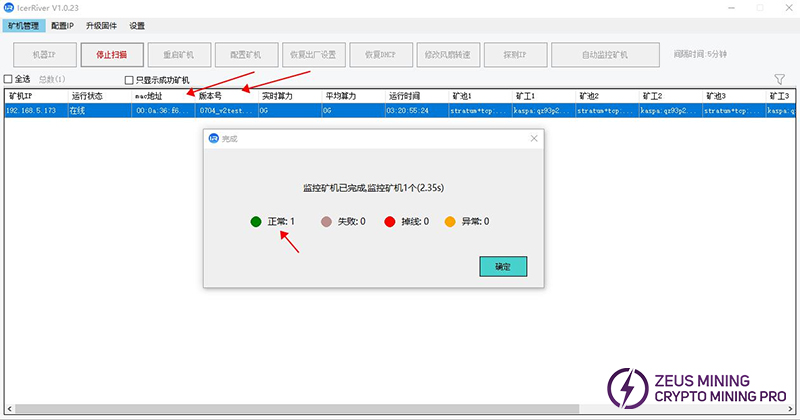
When the group control software scans: MAC address and version number, it means that the current miner is officially connected to the local area network.
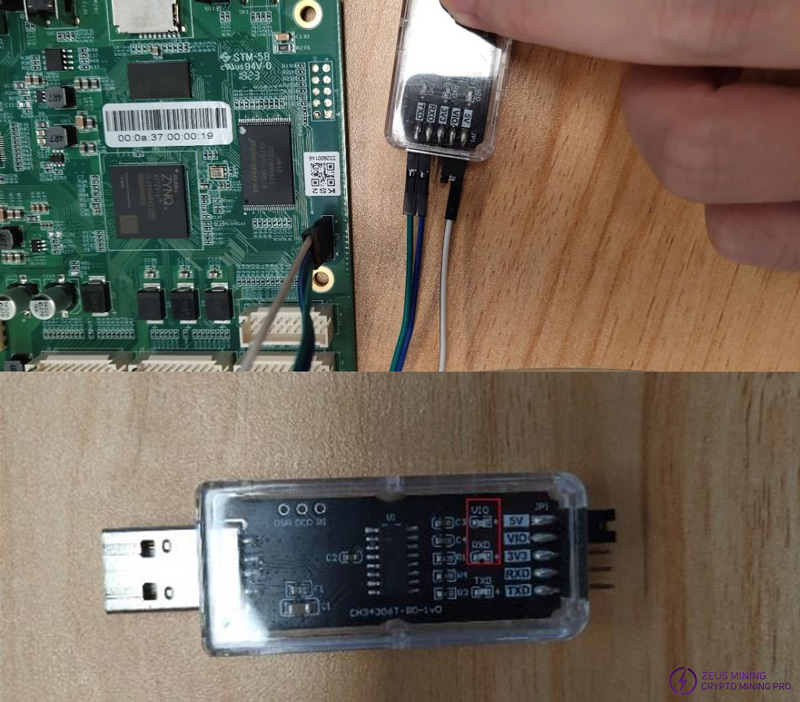
Step 6 (Serial port test method): Connect the serial port cable to the control board.
The blue and green wires are connected to the serial port cable respectively, and the white is connected to GND. After plugging into the computer, the red LED and blue LED in the red frame are always on, and the green LED outside the red frame will only flash when a command is entered.

Step 7: Automatically run the single board test program.
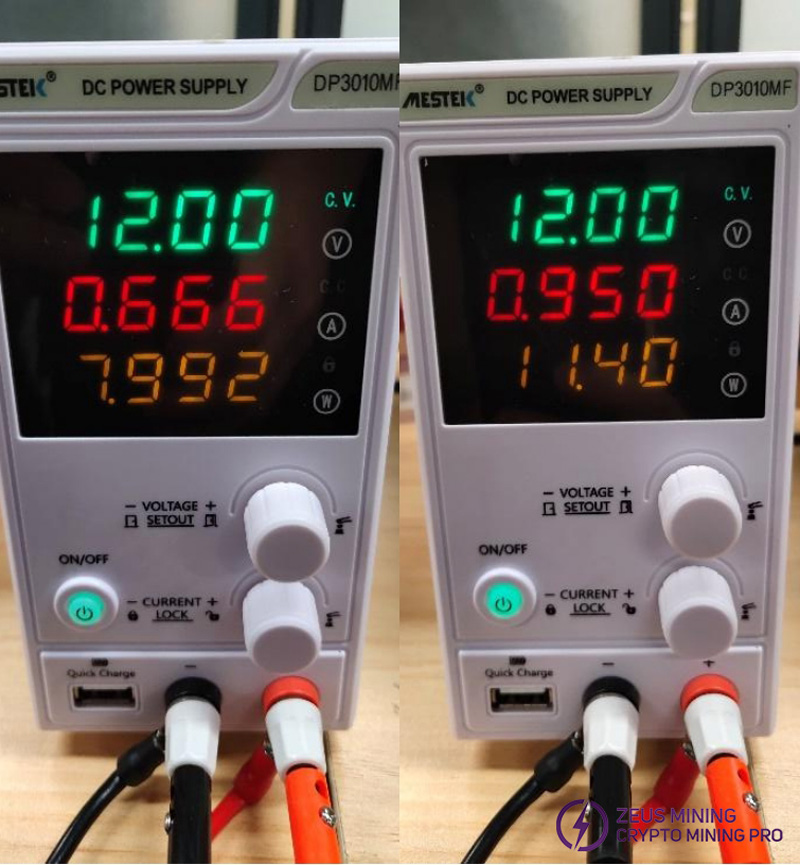
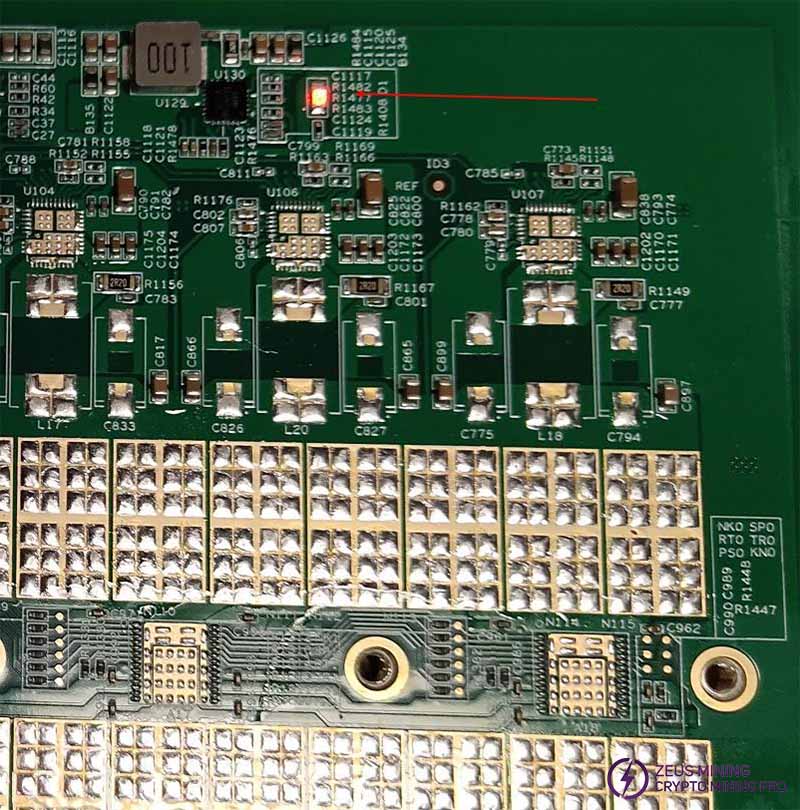
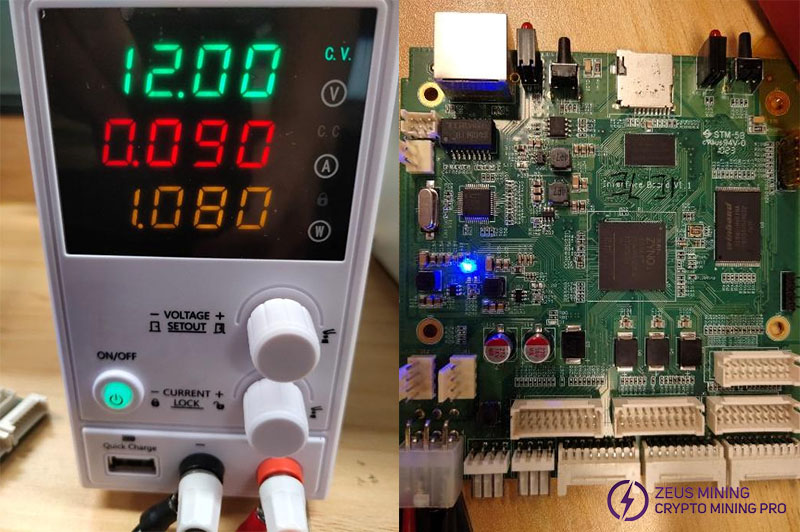
Step 8: While the program is running, the red LED light (position number: D1) on the hash board lights up, and the current rises to about 12V@0.7A\1A.
In the figure below: the left figure is the KS1 current, and the right figure is the KS2 current.

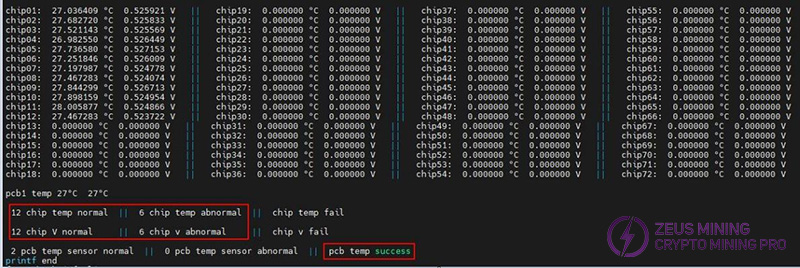
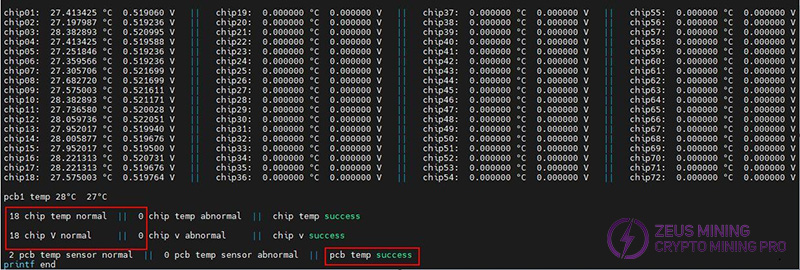
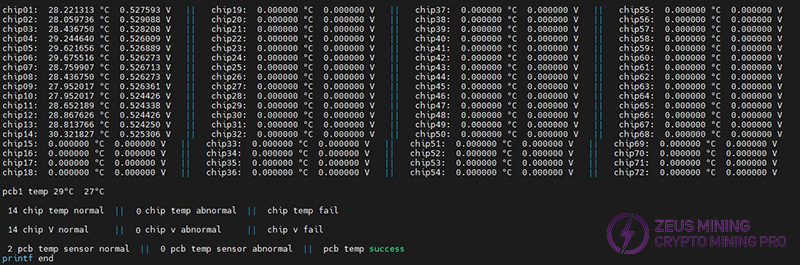
Step 9: After the program is finished, observe the results. The results show that the chip voltage, chip temperature, board temperature, and quantity are consistent with the number of chips on the board (12 / 18).
KS1 chip quantity, chip temperature and PCB board temperature:
KS2 chip quantity, chip temperature and PCB board temperature:
Normal voltage of chip test point under normal working condition:
Ⅴ. Common faulty phenomena and troubleshooting steps of the hash board
The normal power-on current range of the KS1 / KS2 board is 0.14A-0.15A, and the current range is 0.7A-0.9A after the LED at the 1.8V voltage test point is always on.
When testing the board, the DC adjustable PSU is configured as: 12V voltage, 2A current limit.
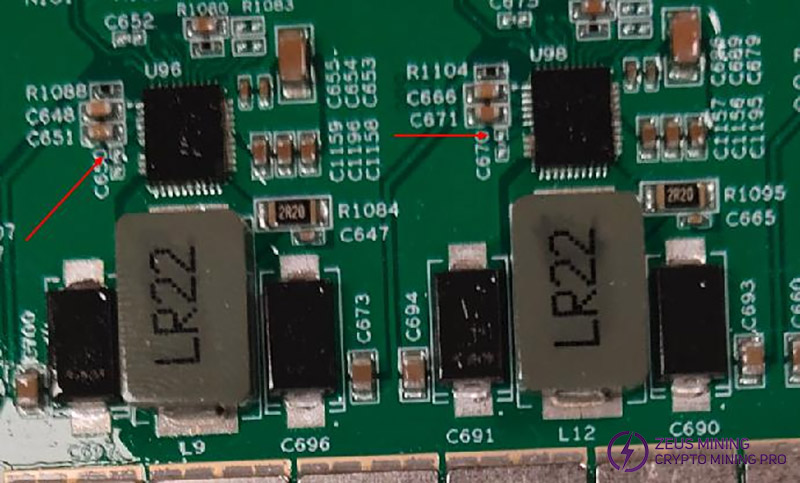
1. Phenomenon: Drmos short circuit
Solution:
Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of Pin41 of Drmos to ground. The normal resistance is about 15KΩ. After Drmos short circuit, the resistance here is only tens to hundreds of ohms (this method is limited to the case of magnetic beads exploded). After confirming that Drmos is damaged, the chip needs to be replaced.
2. Phenomenon: The voltage stabilizer test shows a current limiting short circuit. (The current shows 2A, the voltage is pulled down, less than 12V)
Solution:
Step 1: Test whether the impedance is short-circuited at the 12V powering terminal;
Step 2: If the 12V is short-circuited, start to check each public powering chip (U130, U4), the 8-phase MOS tube that is most likely to fail. The MOS tube positioning method is: use the voltage stabilizer PSU to keep the power-on current limiting state, and quickly sense the serious heating area of the board with our hand. If we can't feel it, we need to disconnect each phase to determine whether the 12V is still short-circuited (only need to disconnect the input magnetic beads at each/8-phase MOS, all need to be disconnected), locate the faulty chip and replace it.
All 8 beads in each phase must be completely disconnected.
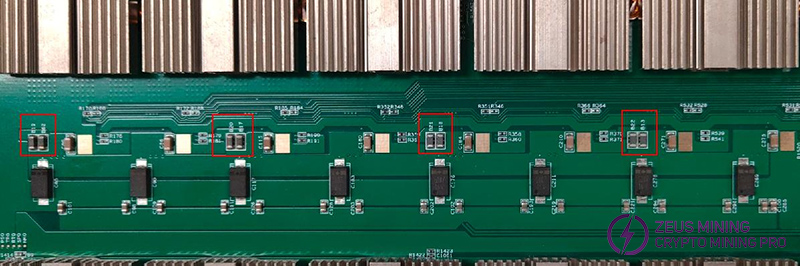
Step 3: If the MOS tube does not get hot or the impedance is still short-circuited after disconnecting all the MOS tube input beads, we need to check the impedance at U130 and U4, and measure whether the impedance returns to normal after disconnecting the 12V input beads.
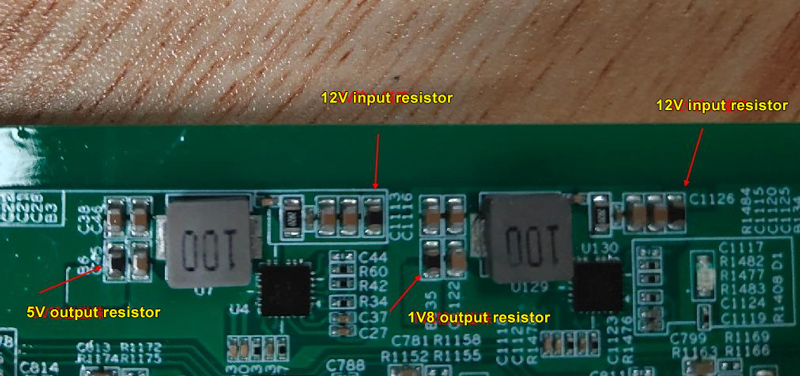
12V-GND | KΩ level |
5V-GND | KΩ level |
1.8V-GND | KΩ level |
3. Phenomenon: The single board test program is interrupted and the current is relatively low. The DC adjustable power supply displays: 12V voltage, 0.5A current (or less than 0.5A current).
Solution:
Step 1: Check if the common 5V power supply has an output.
Step 2: If there is no output, inspect the input voltage of the GS9238 chip to see if it is 12V (note that both sides of the resistor need to be checked). Additionally, check the input and output impedance to ground.
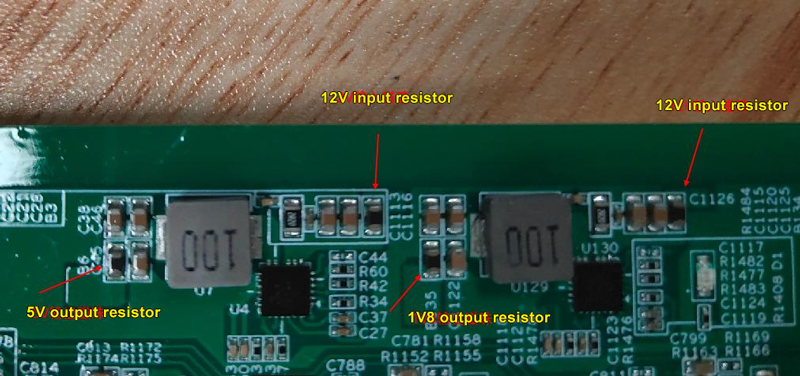
Step 3: If the input voltage is 12V, check the working status of the GS9238 chip, including the enable voltage and feedback voltage.
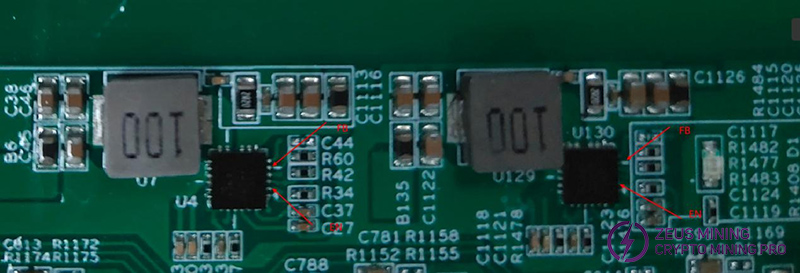
4. Phenomenon: In the single board test program, only detected some chips, and the current is normal.
Solution:
(1) Check if the 1.8V and 0.8V voltages for each ASIC chip are supplied normally. If the powering is not normal, check each chip to determine where the voltage is disconnected and verify the 0.8V LDO output status.
Specific voltage test points for each chip:
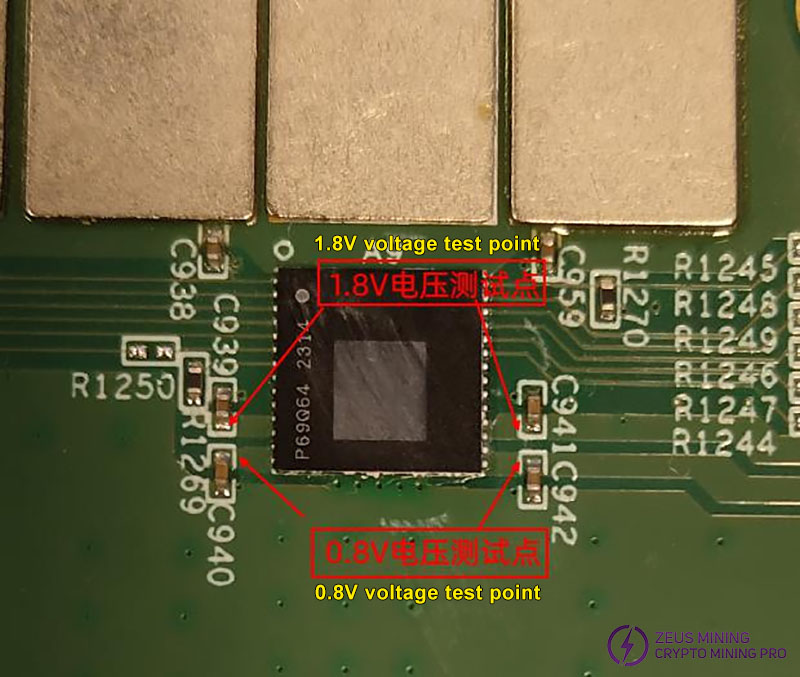
The diagram below shows the total LDO output. If the LDO output voltage is abnormal, power off and measure the resistance to ground at both the LDO input and output. A very low resistance indicates a short circuit at the chip, while a very high resistance indicates a damaged resistor. The normal range is about 7KΩ for input resistance and 0.5~1KΩ for output resistance.
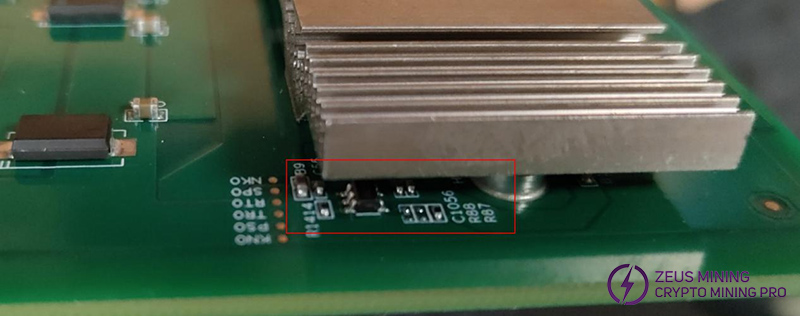
(2) During the single board test program, use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature of each chip. The temperature of the ASIC chips should be around 40°C (at room temperature of 25°C). If any chip reaches or exceeds 50°C and the resistance at the test points on both sides of the chip is abnormal, it indicates the chip is burnt out and needs to be replaced.
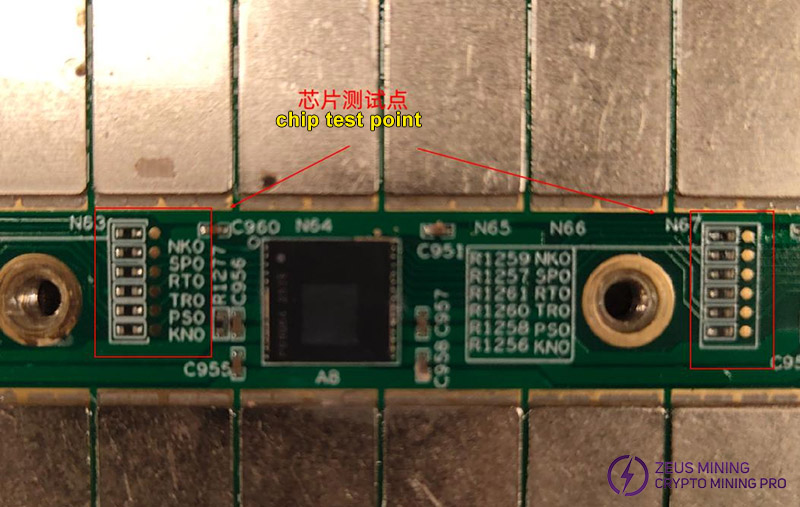
Test Point - Test Point | Resistance |
NK1-NK1 | MΩ level |
SP1-SP1 | MΩ level |
RT1-RT1 | MΩ level |
TR1-TR1 | MΩ level |
PS1-PS1 | MΩ level |
KN1-KN1 | KΩ level |
NK0-NK0 | KΩ level |
SP0-SP0 | MΩ level |
RT0-RT0 | MΩ level |
TR0-TR0 | MΩ level |
PS0-PS0 | MΩ level |
KN0-KN0 | MΩ level |
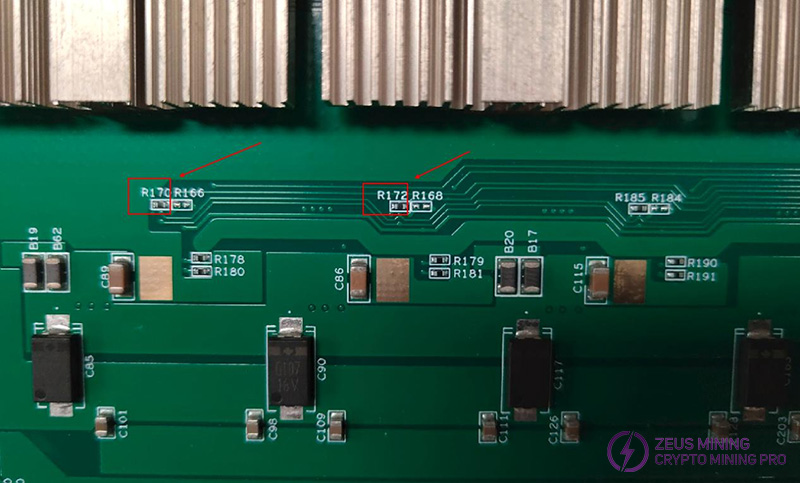
5. Phenomenon: During the single board test, only two MOSFETs heat up while the remaining six in the same group do not.
Solution:
(1) Check the PWM input pin voltage for each MOSFET in the same group, which can be measured at the resistor on the back of each MOS.
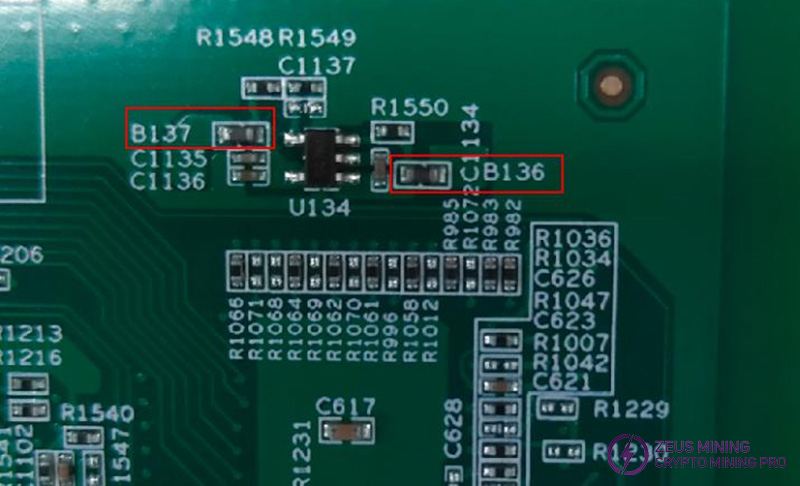
(2) Check if the 1.8V powering for the uP9512 chip is normal. If not normal, it indicates the uP9512 has entered cold start mode. Measure both sides of B136 and B137 to determine if the issue originates from the input or output.
6. Phenomenon: The temperature sensor shows no temperature or an abnormal temperature.
Solution:
(1) Check if the voltage at the temperature sensor pins is normal.
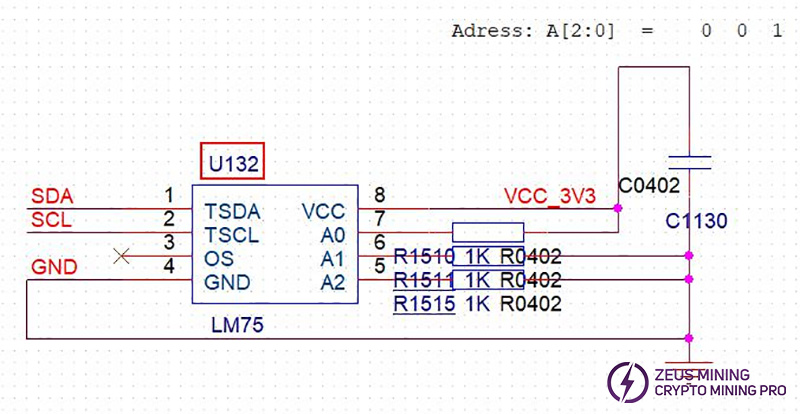
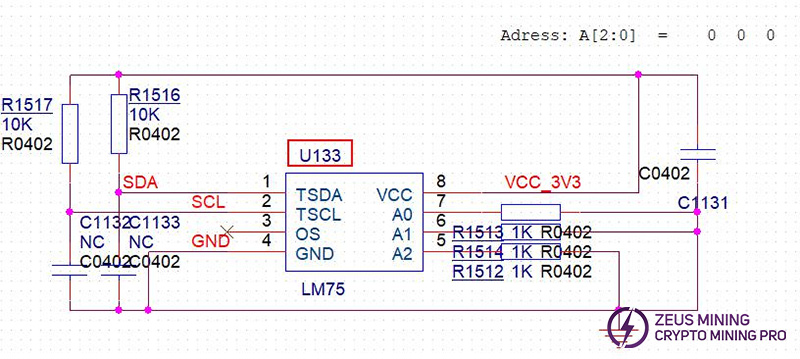
(2) If the voltage is abnormal, check if the interface and 3.3V powering are normal.

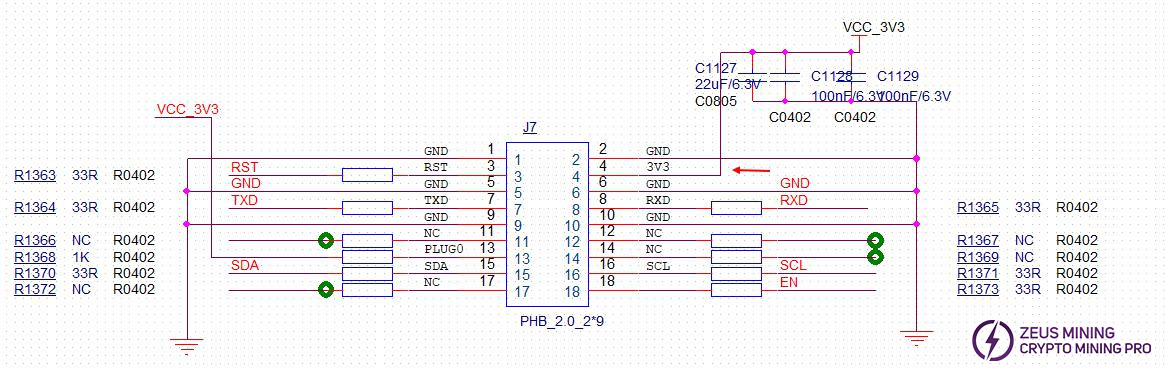
7. Phenomenon: The system does not enter the main program for a long time after powering on, the fan does not turn, and the Web backend cannot be accessed.
Solution:
(1) Check if two blue LEDs (designators: D1, D6) on the control board are lit.
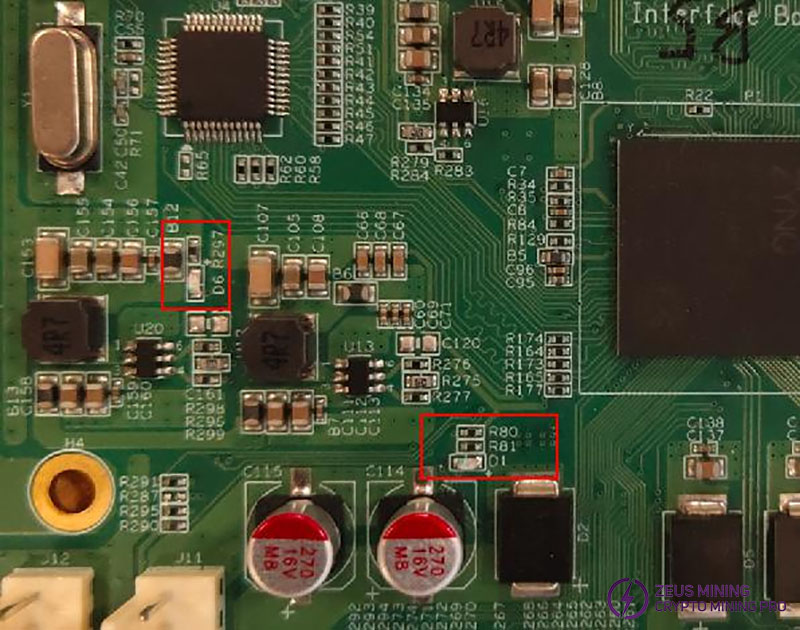
(2) Check if TP3, TP4, TP5, and TP6 on the control board show voltages of 1.0V, 1.8V, 1.5V, and 3.3V respectively.

(3) If all these voltages are normal and one blue LED (designator: D6) is lit, it indicates a Flash memory fault or an internal file error, and the Flash memory needs to be replaced.
8. Phenomenon: The result of the hash board single board detection is that the chip is missing or garbled.
Solution:
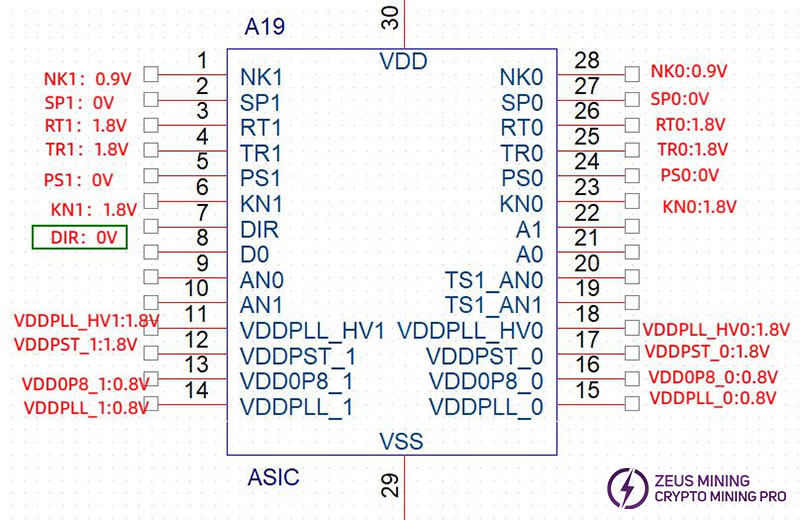
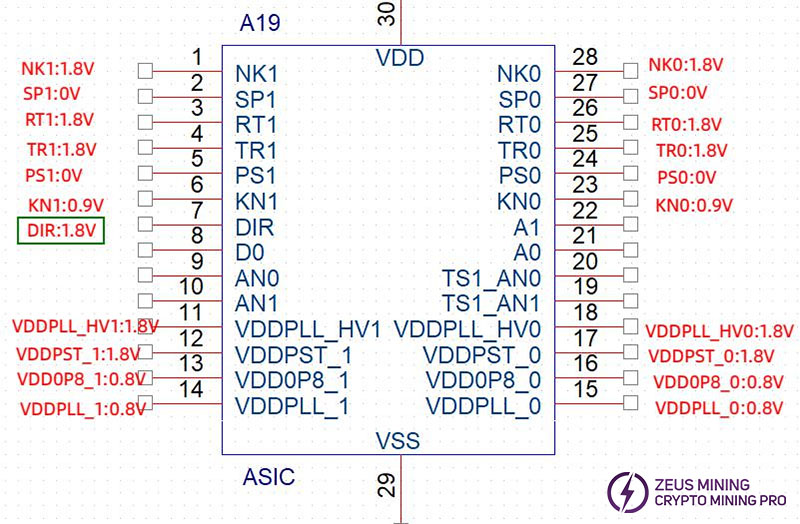
Step 1: Keep the hash board running the single board program and use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the DIR pin of the ASIC chips. The measurement results will generally be either Vdir=1.8V or 0V.

Step 2: Based on the results from the first step, use the short-circuited method:
If Vdir=1.8V: Use a short-circuit wire to pull up the PS0 pin of the ASIC chip. Note that the pull-up voltage must be 1.8V.
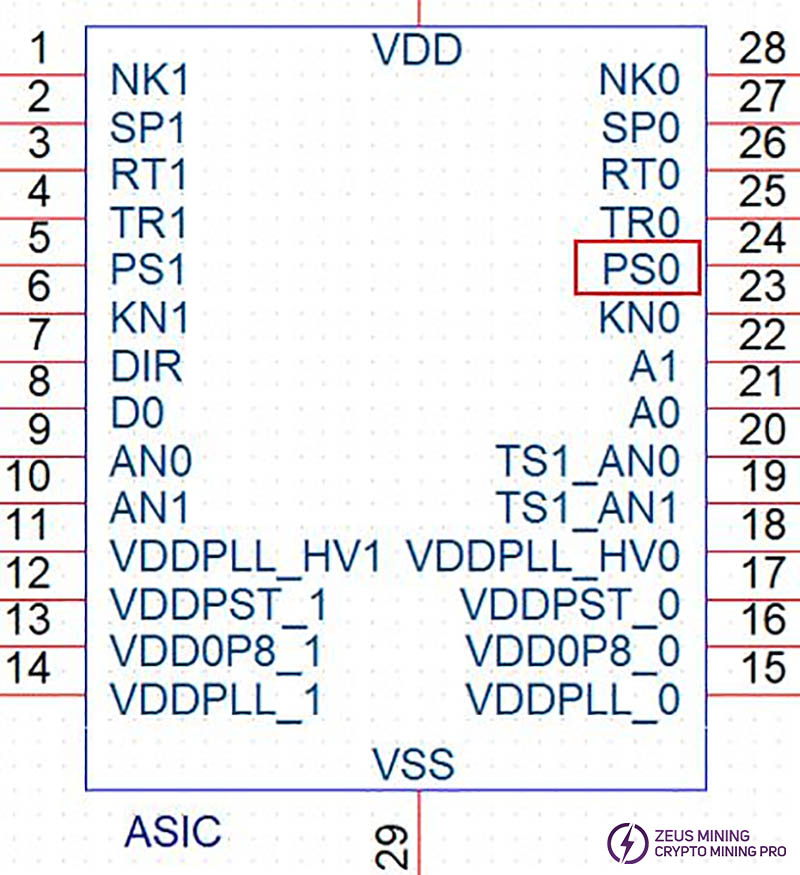
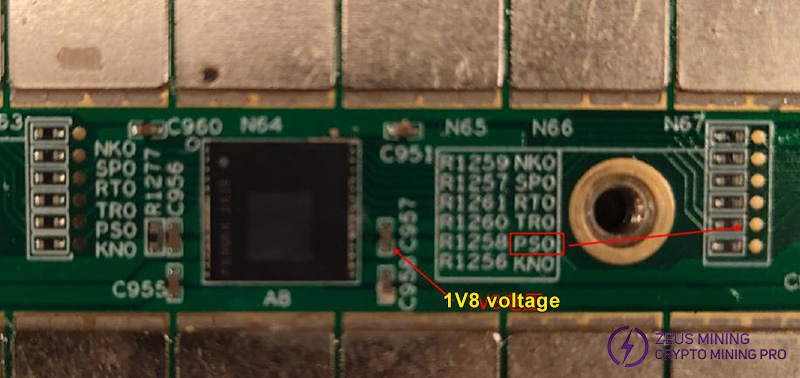
If Vdir=0V: Use a short-circuit wire to pull up the SP1 pin of the ASIC chip. Note that the pull-up voltage must be 1.8V.
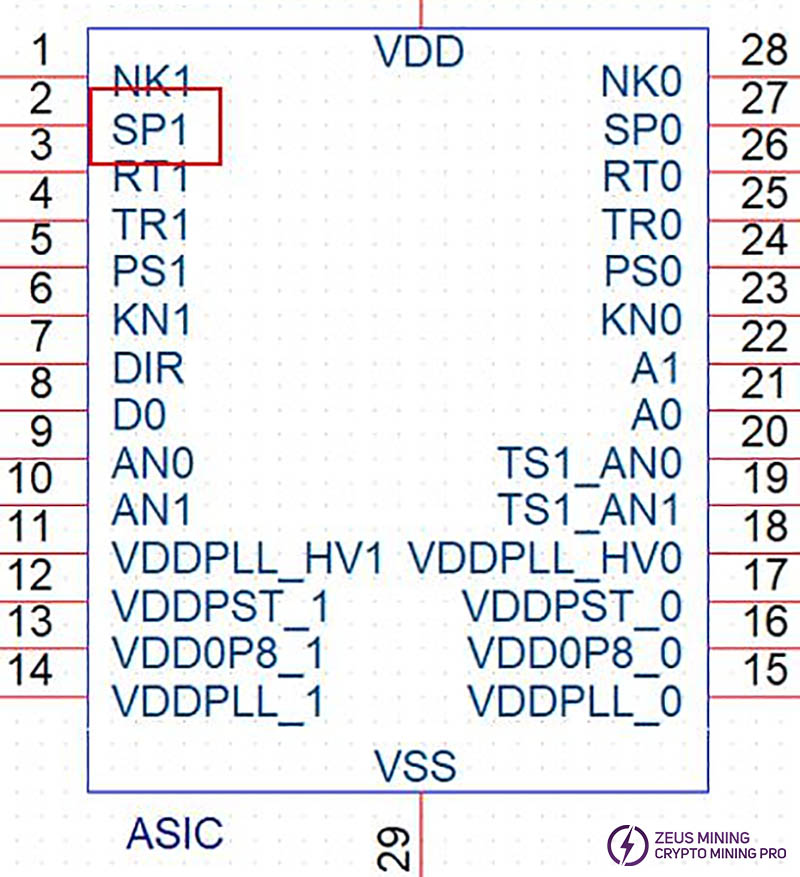
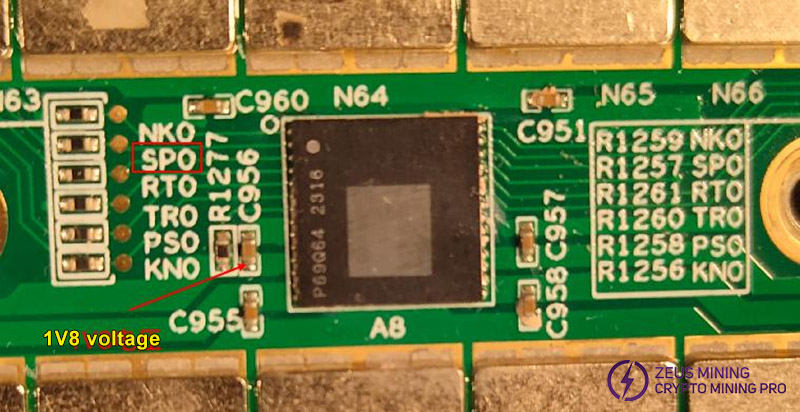
Step 3: Continue to observe the results of the single board test program. If the chip still displays garbled data, repeat steps 1 to 3 for the preceding chip until no garbled data is produced. This indicates that the subsequent chip to the currently tested chip is faulty and needs to be replaced. Run the single board program again to verify.
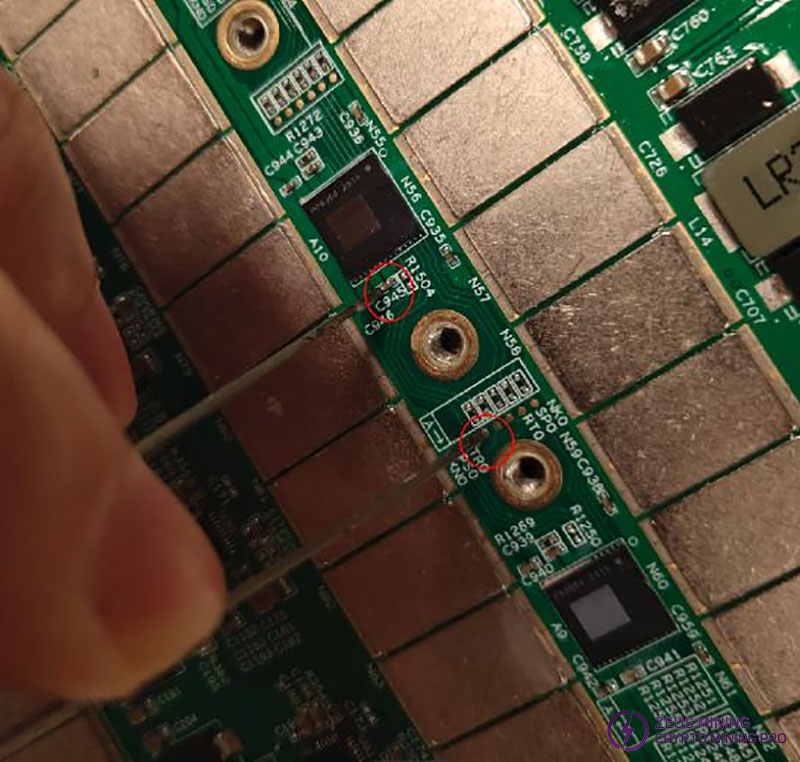
Step 4: As shown in the diagram, when the voltage at the DIR pin is measured to be 1.8V, pull up the PS0 voltage. If the single board program stops automatically at the 14th chip, it indicates that the first 14 chips are not faulty. Continue pulling up the PS0 / SP1 signal for subsequent chips until the faulty chip is identified.
VI. Usage of Test Fixtures (It is recommended to use the KS test fixture. Click here to learn more about the detailed usage method)
Step 1: Insert the TF card with the KS1 test program into the card slot on the control board.
Step 2: Connect the control board, ribbon cable, and hash board. First, connect the negative clip (black) to the inner power terminal of the board, then connect the positive clip (red) to the outer power terminal of the board. Once connected successfully, turn on the DC adjustable PSU.
Step 3: Use the serial tool to print out the voltage and temperature information of the ASIC chips on the current hash board. Ensure that the number of chips matches the actual number on the board and that both the temperature and voltage are normal before proceeding with the complete machine assembly for the hashing test.
VII. Assembly of KS1 and KS2
(1) Clean the hash board that has passed the single board test using cleaning solution and an air pump.
(2) Apply conformal coating to the areas excluding the interfaces and ASIC chips.
(3) Apply thermal paste and install the heatsink. Note: The amount of thermal paste should be approximately 2/3 of the chip length and should cover the reflective area on the chip accurately.

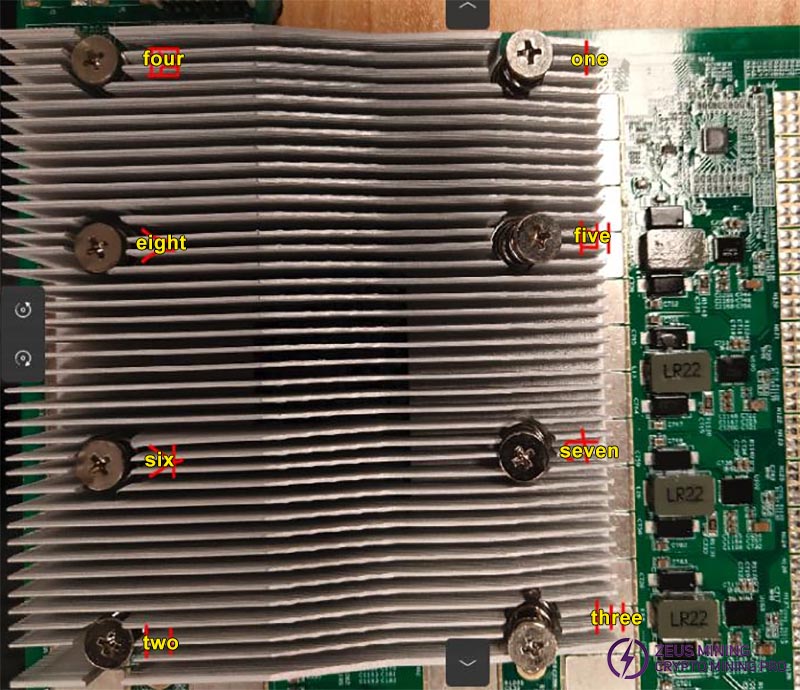
(4) Place an insulating washer at the end of the step screws, set the torque to 9, and tighten the screws in the order shown in the picture, from small to large.

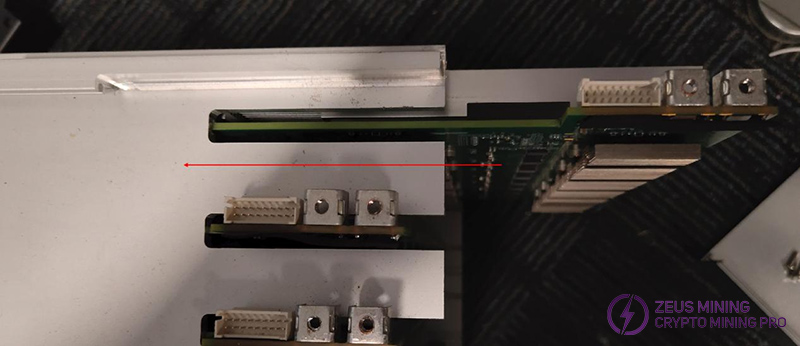
(5) Insert the power cable and data ribbon cable into the control board.
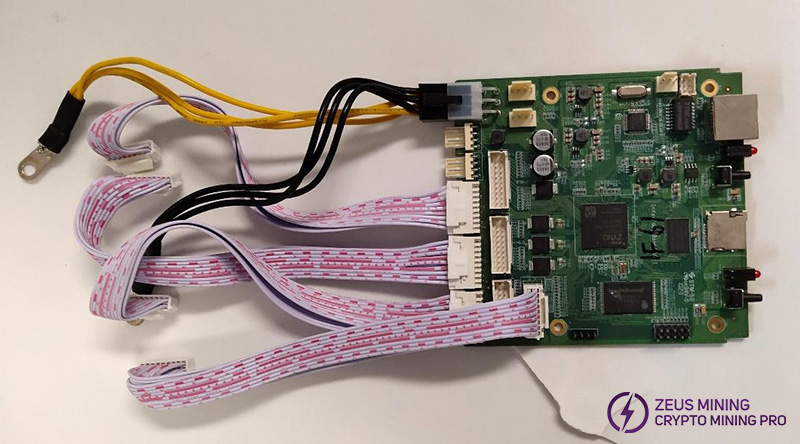

(6) Insert the hash board vertically into the chassis. Insert two hash boards for KS1 and four hash boards for KS2.
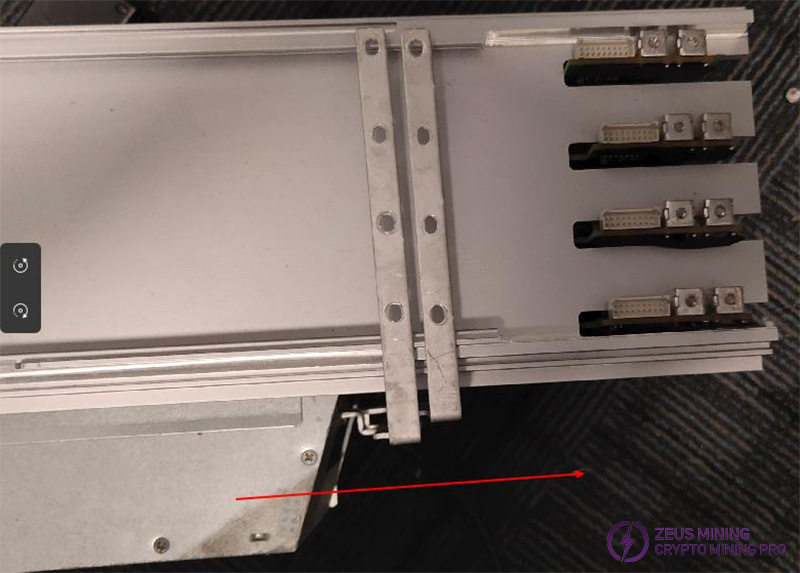
(7) Insert the 2000W PSU parallel to the side of the chassis, then insert the control board parallel to the top of the chassis.

(8) Connect the conductive copper strip to the 2000W PSU and the hash boards, set the torque to 9, and connect the interface board power cable to the copper strip as well. Ensure yellow is positive and black is negative.
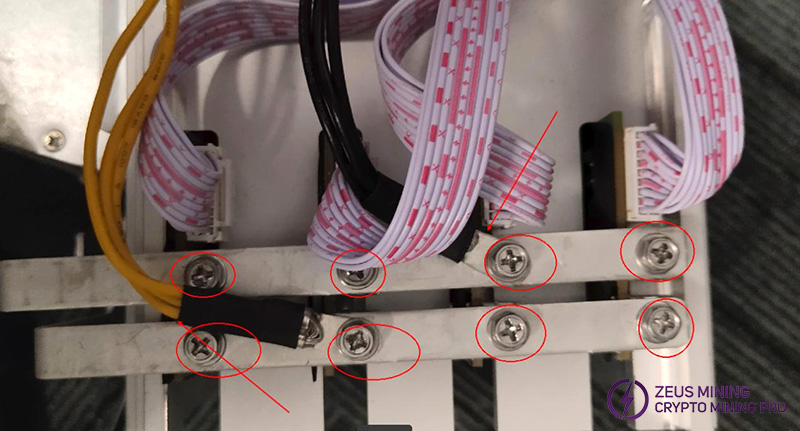

Follow the connection diagram and avoid reverse or short connections.
The screws connecting the conductive copper strip to the hashing boards must be tightly fixed with 8 screws, and the copper strip to the power supply must be fixed with 4 screws.
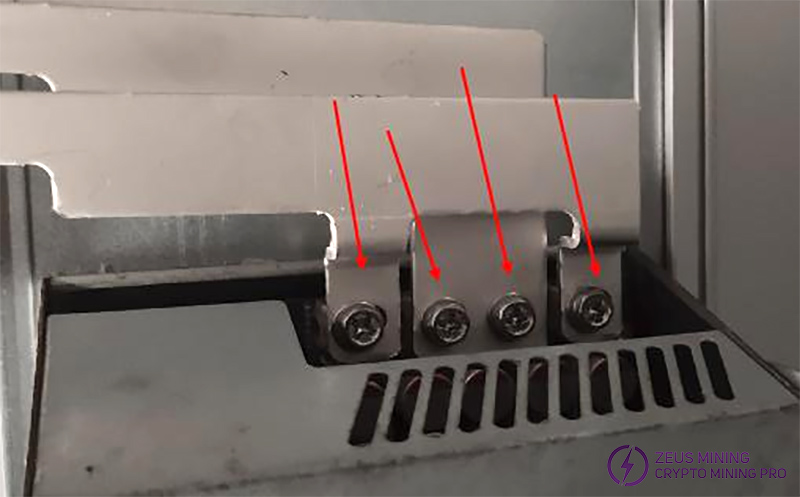
Use M4*10 hexagon head screws with a cross slot and washers, nickel-plated, for these 12 screws.
(9) Connect the data ribbon cable and four fans to the hash boards. The order of the ribbon cables between the hash boards and the control board must match the picture.
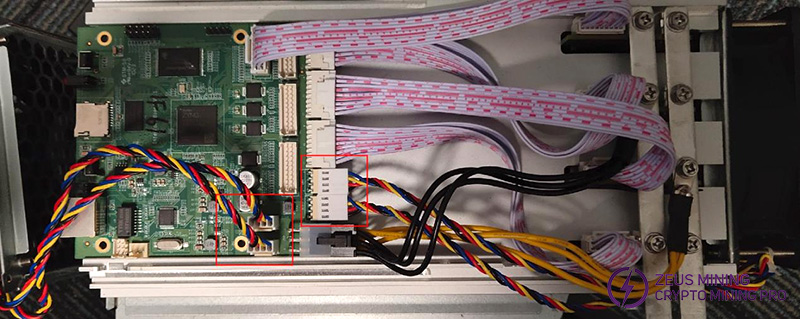
(10) Cover the chassis with the top cover, side panels, power cover, and fans, and set the torque to 9. Notice: each fan is fixed with 4 screws, which should be tightened in a diagonal pattern.
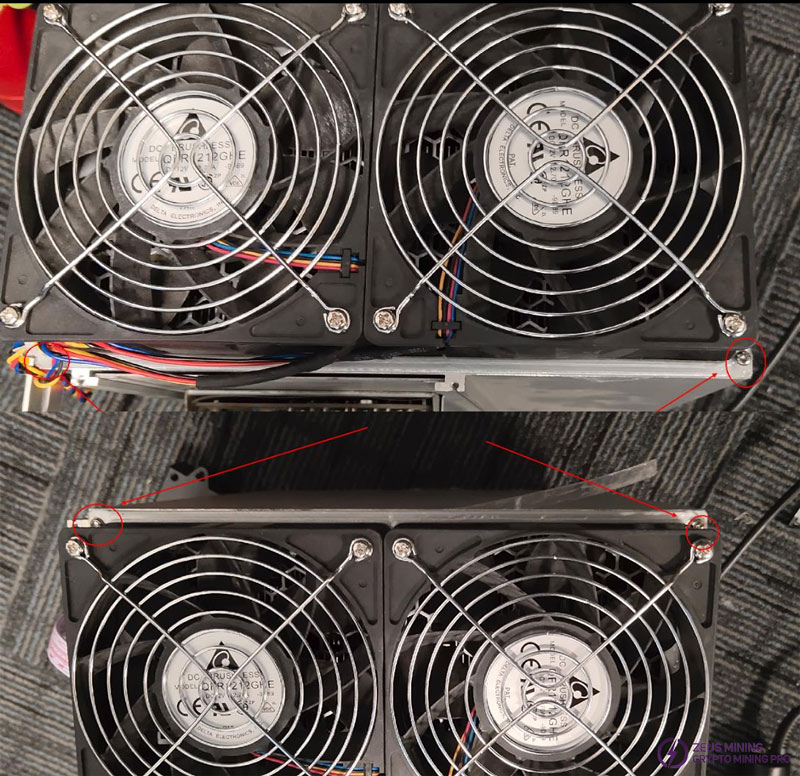

Use M4*45 cross pan head screws, rust-resistant, to fix the fan net.
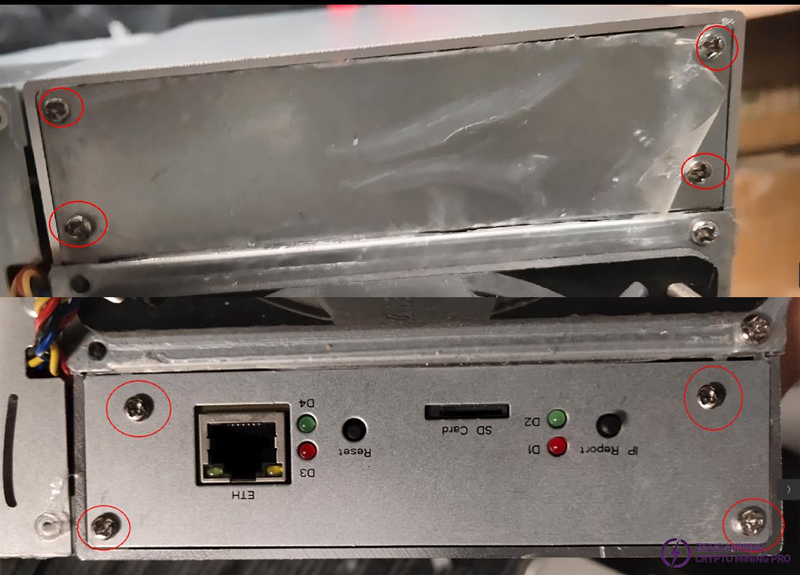
The power panel has 4 screws at the front and back.

Use M3*10 cross pan head screws, rust-resistant, to fix the fans and power cover.
As shown in the diagram, the front and back panels each require 4 screws for fixation. Use M3*6 cross pan head, rust-resistant screws.

(11) Connect the PSU and Ethernet cable, and use the group control software to scan the miners connected to the current network segment.
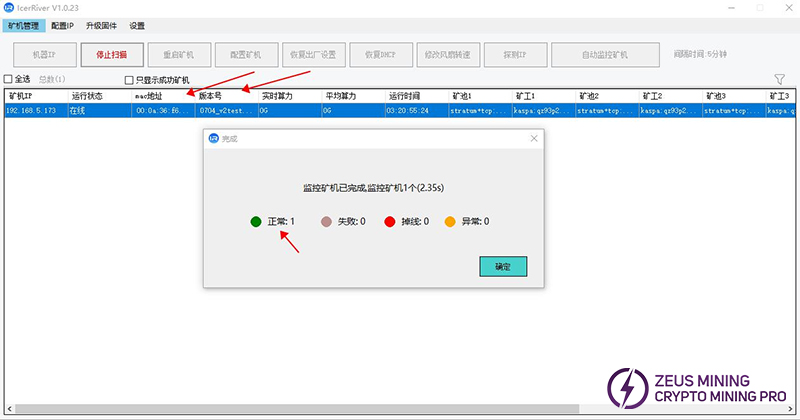
When the group control software detects the MAC address and version number, it indicates that the miner has successfully connected to the local network. Enter the miner's IP address in the browser's address bar to access the Web backend.
(12) Check the Web backend to ensure the hash rate meets the standard and that the fan and board temperatures are normal.
Username: admin
Password: 12345678
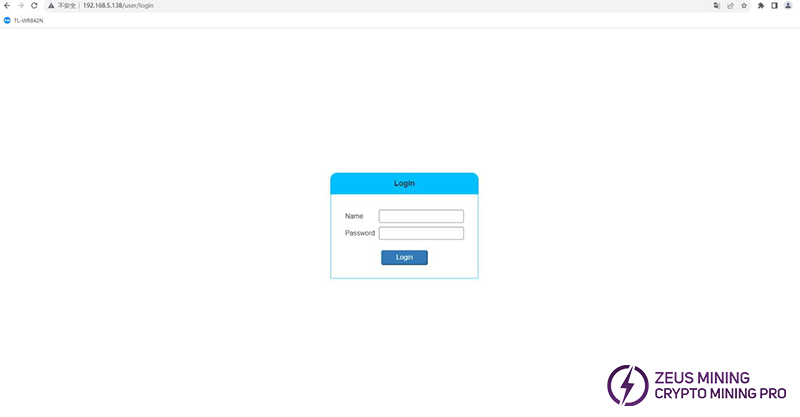
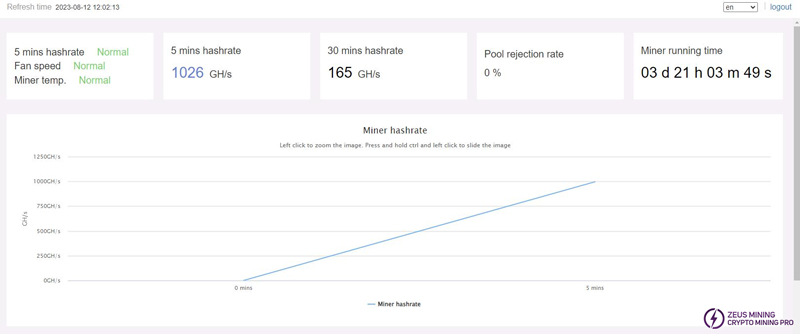
KS1 should reach a hash rate of 1TH/s within 5-10 minutes of powering on, and KS2 should reach 2TH/s. Additionally, ensure that "Fan speed" and "Miner temp" display as "Normal".
VIII. Other precautions
1. Conventional maintenance process
(1) Observe the appearance
(2) Measure the impedance
(3) Power on and measure the voltage
(4) Power on and test
(5) Determine the fault based on the detection information
(6) Locate the fault and re-solder it first before replacing it
(7) Perform aging test after multiple tests after repair
2. Conventional inspection: First, visually inspect the hash board to be repaired to see if there is any deformation or burning of the PCB. If so, it must be processed first; whether there are obvious signs of burning of parts, parts impact displacement or missing parts, etc.; secondly, after visual inspection, the impedance of each voltage domain can be tested to detect whether there is a short circuit or open circuit. If found, it must be processed first. Thirdly, check whether the voltage of each part is normal.
3. Conventional short circuit detection is necessary to avoid burning chips or other materials due to short circuit when power is on.
4. Unless necessary, generally do not operate the ASIC. If it is determined that the ASIC has failed, it must be powered off. If necessary, remove the corresponding power chip.
5. After the repair is completed, clean the tin slag on the surface of the board and power it on/install it for testing after it cools down naturally.