


Antminer S17e Hash board Repair Guide [EN]
Version date: 2019.11.03
File category: maintenance proposal
Contents of this book: Mainly tells how to S17e Troubleshoot various faults on the hash board, and how to use the test fixture for accurate positioning.
※ The copyright of this article belongs to Beijing Bitmain Technology Co., Ltd. Without the permission of the copyright owner, no unit or individual may reprint, extract or use this work in other ways. If you need to reprint or quote, please contact the official customer service of Bitmain.
1. Maintenance platform requirements
1. Constant temperature soldering iron (soldering temperature is 300‑350 degrees) pointed soldering iron tip is used for soldering small patches such as chip resistors and capacitors.
2. The hot air cylinder is used for chip disassembly and welding. Be careful not to heat it for a long time to avoid PCB blistering.
3. APW9+ power supply (output 14.5V‑21V), used for the test and measurement of the arithmetic board.
4. Fluke 15b+ Multimeter, tweezers, S17e‑v1.0 test fixture (conditionally configurable oscilloscope) .
5. Flux soleder paste, plate washer water plus absolute alcohol; plate washer water is used to clean up the flux residue and appearance after maintenance.
6. Tin planting fixture, planting tin steel mesh, solder paste; when replacing a new chip, you must plant the chip with tin.
7. Lead‑free alpha low temperature solder paste (OM550‑151 degrees melting point) , Used for welding heat sink after repair.
2. Job requirements
1. The maintenance personnel must have certain electronic knowledge, more than one year of maintenance experience, and be proficient in QFN package soldering technology.
2. After repairing, the hash board must be tested for more than two times and it is OK before it can pass!
3. Pay attention to the operation method when replacing the chip, there is no obvious deformation of the PCB board after replacing any accessories, check the replacement parts and whether there are few open circuits around them short circuit problem.
4. Determine the maintenance station object and the corresponding test software parameters and test fixtures.
5. Check whether the tools and fixtures can work normally.

3. Principle and structure
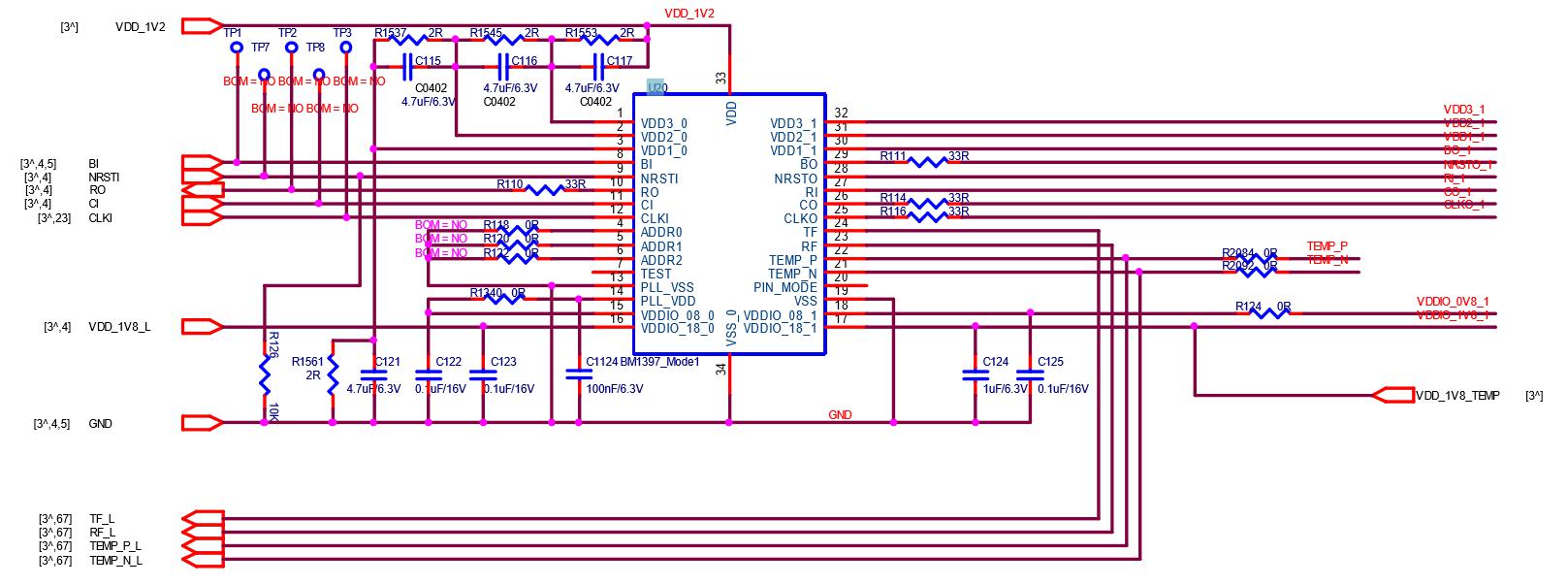
Principle overview:
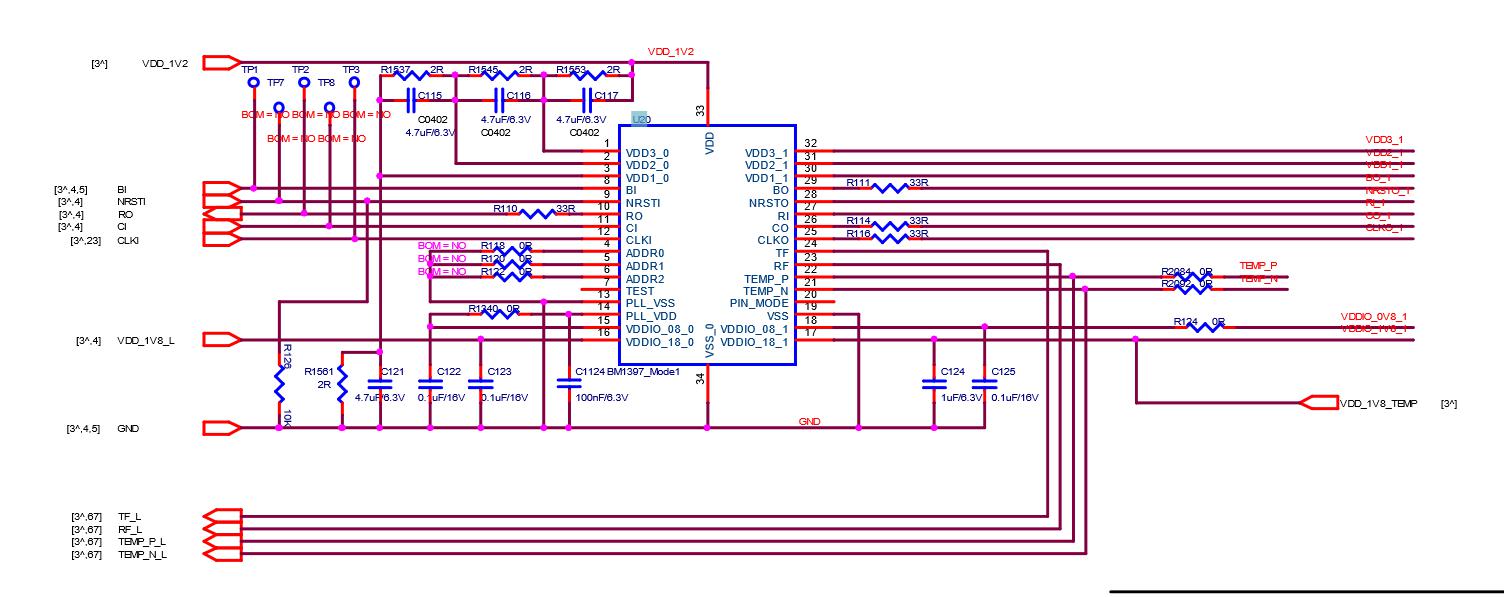
S17e is composed of 15 voltage domains in series, each voltage domain has 9 BM1396 chips, and the whole board has a total of 135 BM1396 chips.
1. The BM1396 chip has a built‑in step‑down diode, and the one with a step‑down diode function is determined by the specified pin of the chip.
2. BM1396 has 15 voltage domains; the S17e clock is a 25M single crystal oscillator, which is transmitted in series from the first chip to the last chip.
3. Each S17e chip has independent small heat sinks on the front and back. The front heat sink is SMT patch, and the back heat sink is after the initial test of the board. It is fixed by solder paste on the back of the IC. After the repair and replacement chip has passed the test, it needs to be soldered and fixed on the IC surface again.
have to be aware of is:
1. In the repair process, when replacing the electrical board components or chips, in order to reduce the damage to the PCB board and the chip due to the high temperature of the air gun, The small heat sink near the faulty component and the small heat sink on the back of the PCB must be removed before replacement.
2. There are test points on the front and back of the PCB. For maintenance during production, when the heat sink is not attached to the front of the PCB, the front test point can be used; the finished product is repaired (After‑sales maintenance), since the front and back sides of the PCB are covered with heat sinks, it is necessary to locate the fault through the test points of the PCB. Specially made the long and slender test lead probes into the gap of the heat sink for measurement, but since the small SMT heat sink is connected to the ground of each voltage domain, pay attention when measuring Insulate the test leads to avoid short circuit caused by the test leads.
Key point analysis :
1.
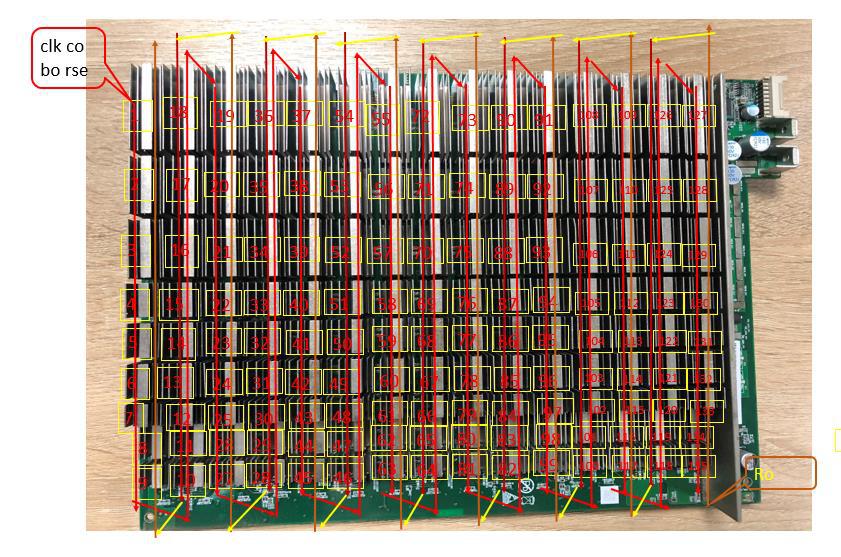
Figure 1, Signal trend
The picture above shows the signal trend of S17e:
Red is the flow of CLK signal, generated by Y1 25M crystal oscillator, transmitted from chip 1 to chip 135; standby and operation When the voltage is 0.8±0.1V.
Red is the direction of TX (CI, CO) signal flow, which enters from pin 7 of IO port, and then transmits from chip 01 to chip 135; not inserted The voltage of the IO line is 0, and the voltage of the calculation is 1.8V.
Yellow is the direction of RX (RI, RO) signal flow, from chip 135 to chip 00, then return to control from IO port 8 Board; when the IO signal is not inserted, the voltage is 1.8V, and the voltage is also 1.8V during calculation.
Red is the signal flow direction of B (BI, BO), which is pulled low from chip 00 to 135; when the IO line is not inserted, it is 0V when in standby, It is a pulse signal of about 0.3 during calculation.
Red is the flow direction of RST signal, which enters from pin 3 of IO port, and then transmits from chip 00 to chip 135; without IO signal inserted, it is 0V in standby mode, and 1.8V in operation.
Figure 3 shows the key circuits on the front of the T arithmetic board.
1. Test points between each chip (as shown in the figure after zooming in): Figure 2
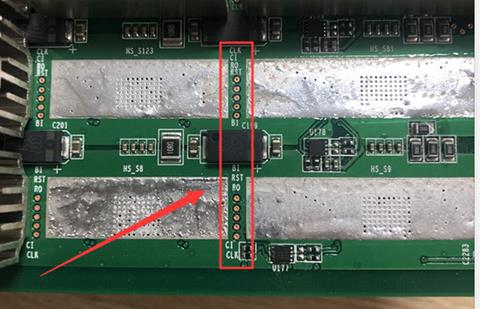
Figure 2, Test points between chips
When repairing, the test points between test chips are the most direct fault location method. The arrangement of the test points of the S17e hash board is:As shown on the top
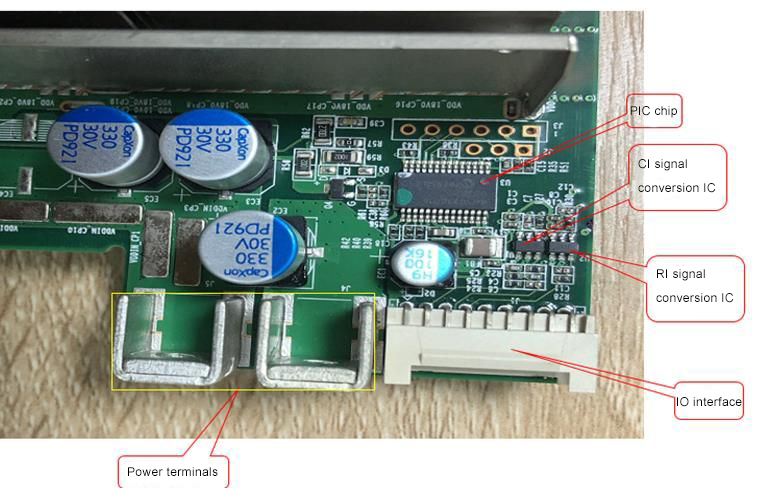
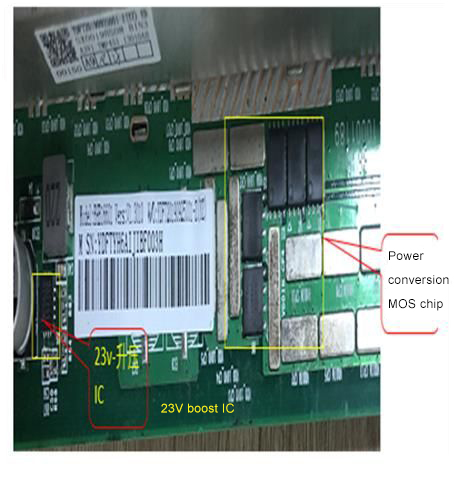


Figure 3, S17e the key circuits on the front of the operation board
2. Voltage domain: The whole board has 15 voltage domains, and each voltage has 9 chips. The total voltage domain voltage is 18V. The voltage of each voltage domain is 1.2V. The 9 chips in the same voltage domain are powered in parallel, and then connected in series with other voltage domains after being connected in parallel. The circuit structure is shown in Figure 4 below:
Figure 4 Yes S17e the key circuits on the front of the operation board
Principle analysis of voltage domain single chip (as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6 below):
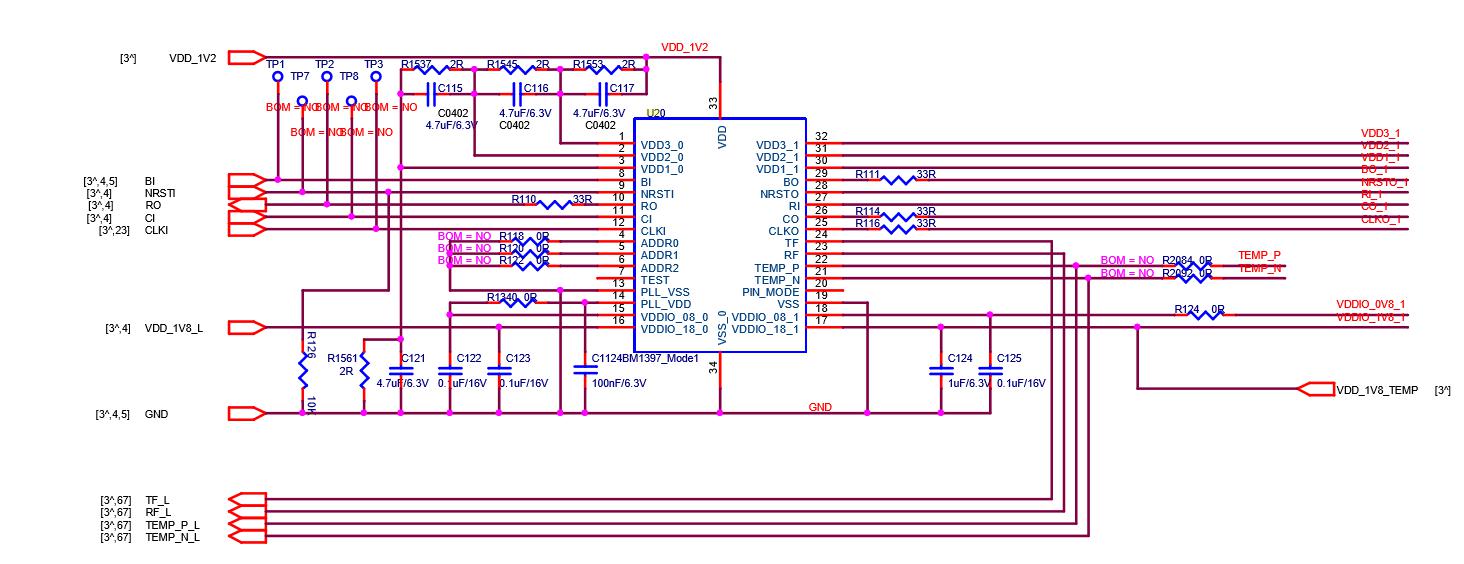
The above is the function of each pin of the BM1396 chip.
During maintenance, mainly test the test signal points before and after the chip (five before and after the chip: CLK, CO, RI, BO, RST);
Detection method:
1. When the fixture is not tested, APW9+ outputs 18.4V to power the fixture control board.
2. When the fixture starts to test, APW9+ will output 18.4V to supply positive power to the power terminal of the control board. During the test of the fixture, each
The voltages of the pilot are as follows:
CLK : 0.9V.
CO : 1.6‑1.8V. when the fixture just sends WORK, the DC level will be pulled down because the CO is negative, and the instantaneous voltage is about 1.5V.
RI: 1.6‑1.8V. During calculation, the abnormal or low voltage will cause the calculation board to be abnormal or the hash rate is 0.
BO: 0V. It is 0V when there is no operation, and there will be a pulse jump between 0.1‑0.3V during operation.
RST: 1.8V. Each time you press the test button of the fixture, the reset signal will be output again.
When the above‑mentioned test point status and voltage are abnormal, please estimate the fault point based on the circuit before and after the test point.
Visible from the above list:
CLK Signal: input from pin 12 of the chip and output from pin 25. When connecting across the voltage domain, it is connected from pin 8 to pin 29 of the next chip through a 0 ohm resistor connection;
TX Signal: from the chip 11 feet in, 26 feet out;
RX Signal: by the chip 10 Feet return, 27 Pin output
BO Signal: input from pin 8 of the chip and output from pin 29;
RST Signal: by the chip 9 Pin is in, 28 pin is output.
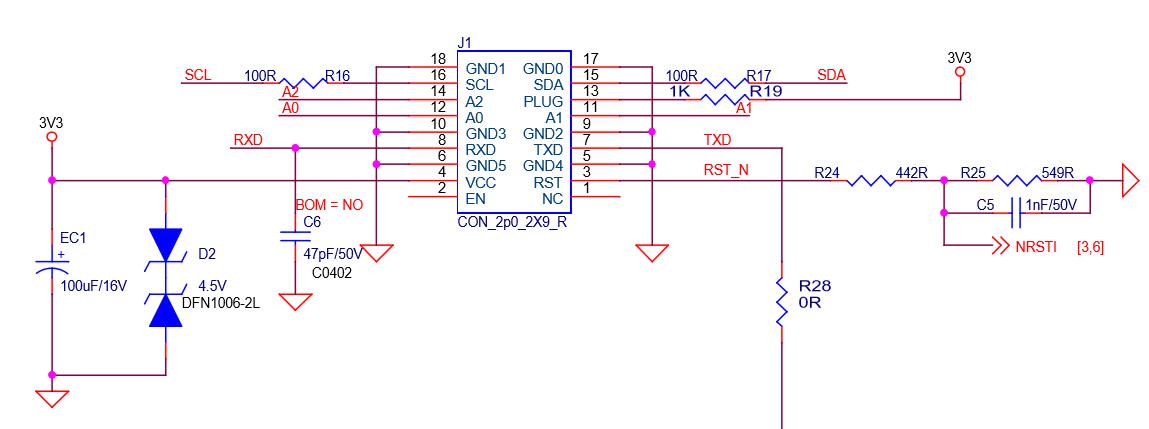
Figure 8 , IO Definition of each pin
As shown in FIG:
6, 10, 18, 5, 9, 17 pin: It is GND.
15, 16 pin (SDA, SCL): It is the I2C bus of DC‑DC PIC, which connects the communication between the control board and the PIC. The control board can read and write data of the PIC through it, thereby controlling the operation status of its hash board.
13 pin (PLUG0): It is the identification signal of the arithmetic board. This signal is pulled from the arithmetic board 1K resistance to 3.3V, so when the IO signal is plugged in, this pin Should be high level.
11, 12, 14 pin (A2, A1, A0): PIC address signal.
7, 8 pin (TXD, RXD): It is the channel of hash rate at the 3.3 end of the arithmetic board, which becomes the TX (CO) and RX (RI) signals after being divided by the resistance.
No., IO port pin terminal level is 3.3V, after dividing the voltage through the resistor, it becomes 1.8V.
3 pin (RST): It is the 3.3V end of the reset signal, which becomes 1.8V RST reset signal after being divided by resistors.
4 pin (D3V3): Supply the 3.3V power supply for the hash board. The 3.3V is provided by the control board, mainly to provide the working voltage for the PIC.
23V boost circuit:
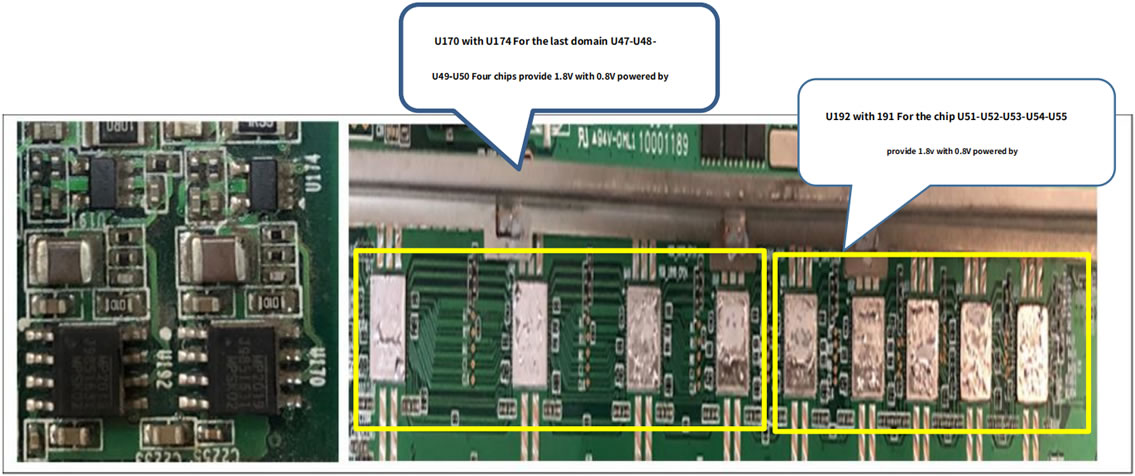
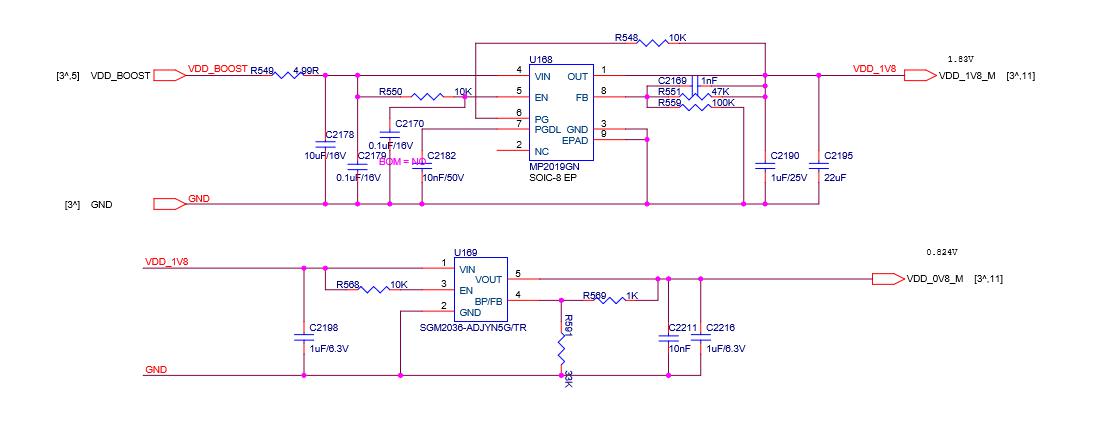
Responsible for boosting the DC‑DC (18v) to 23V. The principle is to increase the voltage of 18V to 23V through U6 L1 D4. The switching signal produced by U6 is the energy storage inductor through L1, and D4 is the boost rectifier diode to charge and discharge C47 C51 , So as to get the 23V of the positive electrode of EC10. The main 18v power supply voltage is as shown in the figure below. After U168‑U171 and U170‑U192 are stepped down, 1.8V is output to supply 1.8V to the chips in the last two domains. Pay special attention to the 1.8V output from U192 in these two domains to the chip U51 in the last domain. ‑U52‑U53‑U54‑U55's 1.8v power supply also provides 1.8V power supply for U191. Similarly, U191 outputs 0.8V and U51‑U52‑U53‑U54‑U55 provides 0.8v power supply, and U170 and U174 are the last ones. The U47‑U48‑U49‑U50 four chips of the domain provide 1.8V and 0.8V power supply. U171 and U190 provide 1.8V and 0.8V power supply for U118‑U117‑U116‑U115‑U112, and U168 and 169 provide 1.8V and 0.8V power supply for U110‑U111‑U113‑U114. The specific schematic and physical diagrams are as follows:
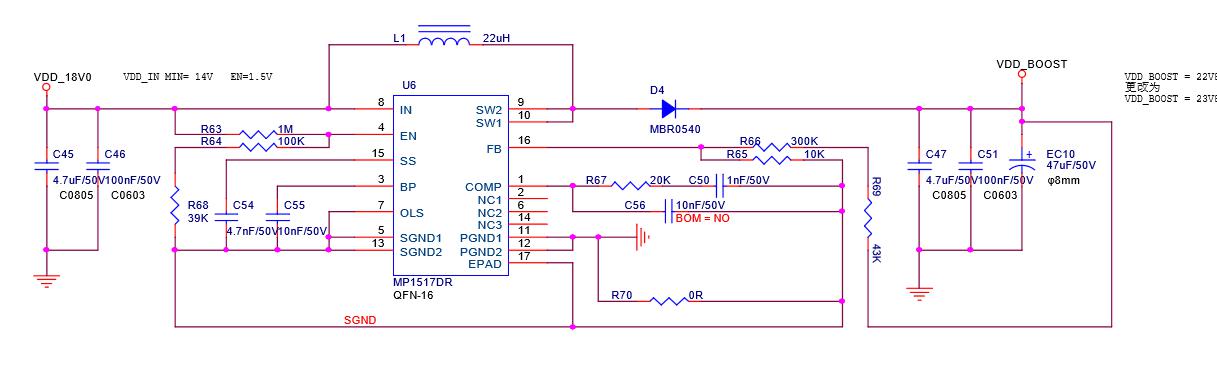
Figure 11, 14V Boost schematic

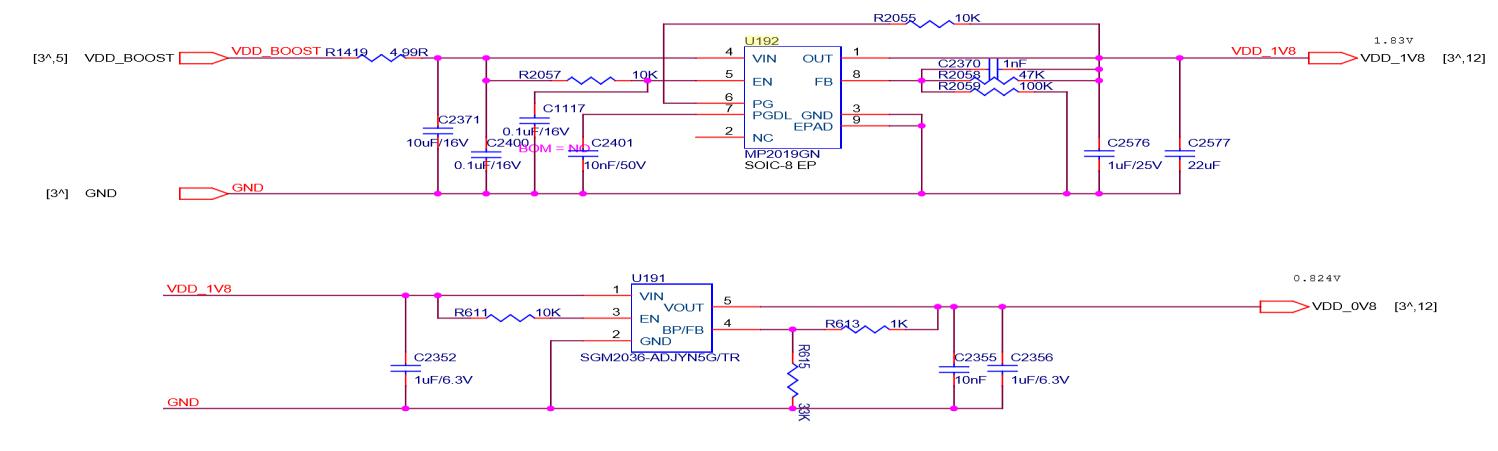
PIC Schematic diagram
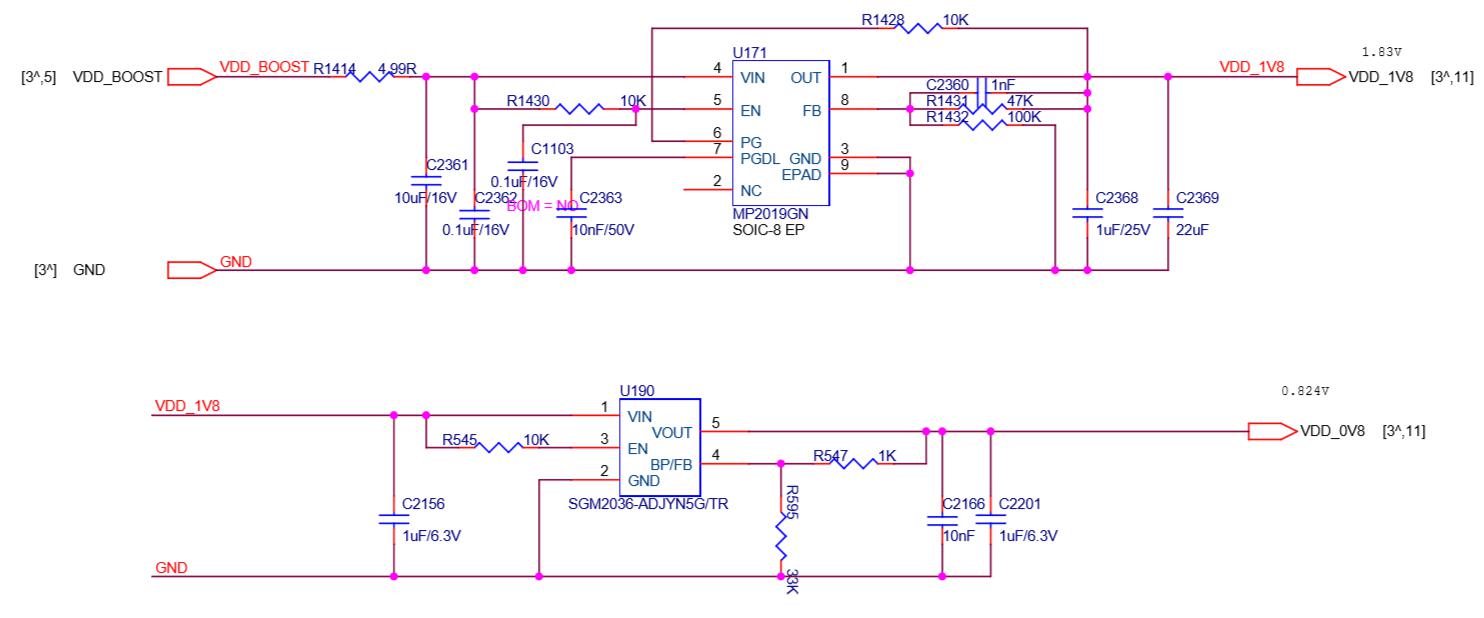
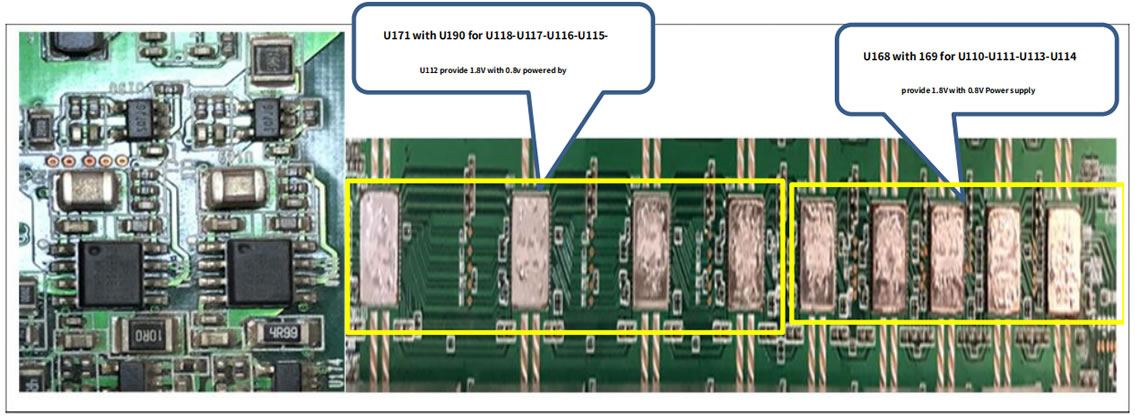

The 1.8V and 0.8V of the other voltage domains (1‑13 voltage domains) are the voltages of the three voltage domains after obtaining, each voltage domain voltage is 1.2, the three voltage domains are 3.6V, and each voltage domain has only 1 A 1.8V and 0.8V LDO powers 9 chips in a voltage domain.
DC‑PIC: Consists of PICC33EP. As shown in Figure 13, Figure 14:
The device that stores the frequency information and voltage value of the arithmetic board chip can also control the APW9+'s DC‑DC output voltage.
Figure 13 , PIC Schematic diagram

Figure 14, PIC Circuit
PIC When working, you need to control and issue one every minute Second heartbeat signal, if there is no heartbeat information, PIC will work for one minute and then shut down.
DC‑DC circuit: composed of 2N7002 and CMOS tube TPHRMDU3603NL. As shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16 below: The working principle is: PIC99 pin PICEN small signal is the first level voltage of a few tenths of a volt, Q4 pin 1 is low level, Q4 is non‑conducting, Q1‑Q2‑Q4‑Q5 is 4 When the pin is high, the 4 MOS transistors will not be turned on, and the hashrate board will not have 18V power supply. On the contrary, Q4—1 pin is high level. Q4's pin 2 and pin 3 are connected to the ground, Q1‑Q2‑Q4‑Q5 turns on 18V to supply power to the hash board.
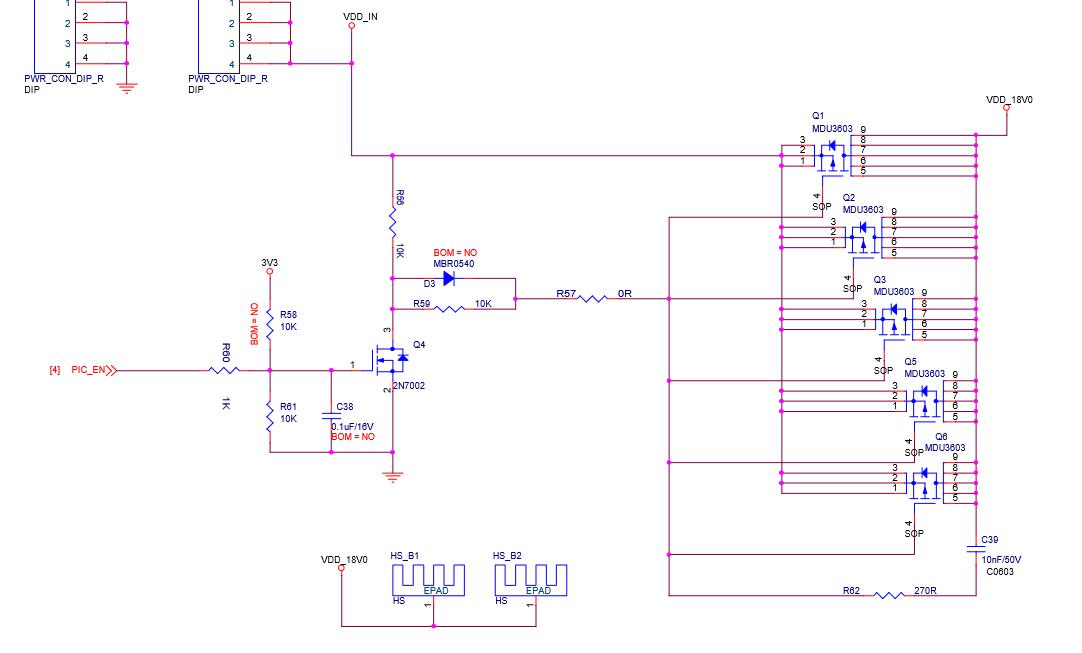
Figure 15 , DC‑DC Schematic diagram

Figure 16, DC‑DC Physical map
25M LCK is composed of Y 25MHZ passive crystal oscillator, as shown in Figure 17 and Figure 18:
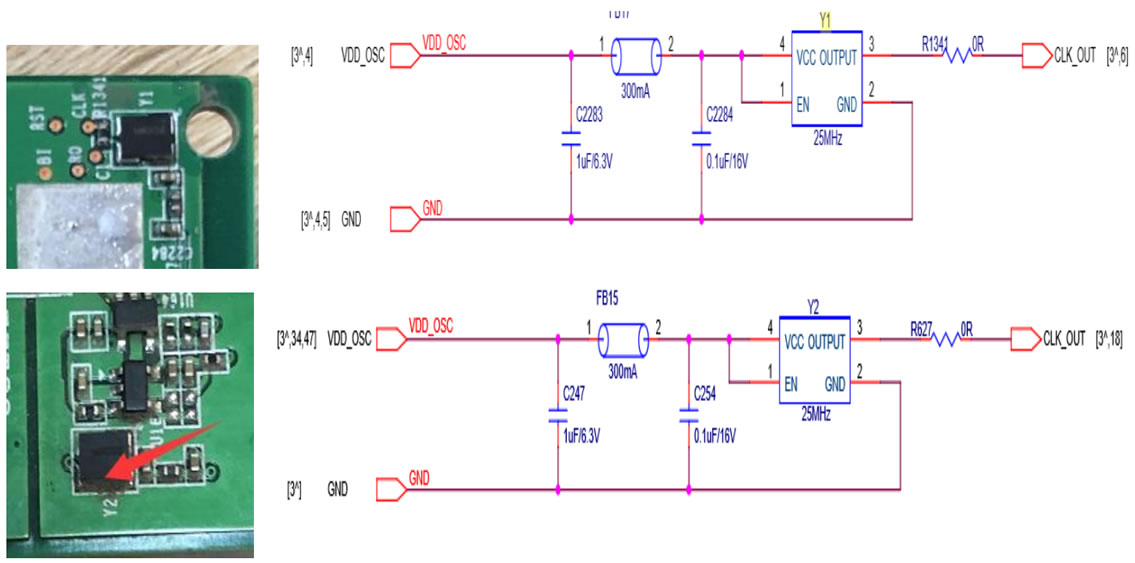
Figure 17&18, 25M LCK principle
Normally, the voltage at both ends of R134 is about 1V.
The power supply of Y1 and Y2 powers the 1.8V‑LDO‑1.8v of this domain, and the output voltage is 0.8‑1v.
Temperature sensing circuit: There are two temperature sensing circuits, one is TEMP (PCB), this is composed of sensor IC‑U178‑TMP451; the other is TEMP (CHIP), this is the built‑in temperature sensor group (BM1396 No. 22, 21st pin), these two temperature sensing parameters are collected and finally pass through the 23rd and 24th pins of BM1396, and then return to the FPGA of the control board from the RI. The principle is shown in Figure 21: (S17E has a total of 15 temperature sensors, all of which are The chip at the end of the air outlet).
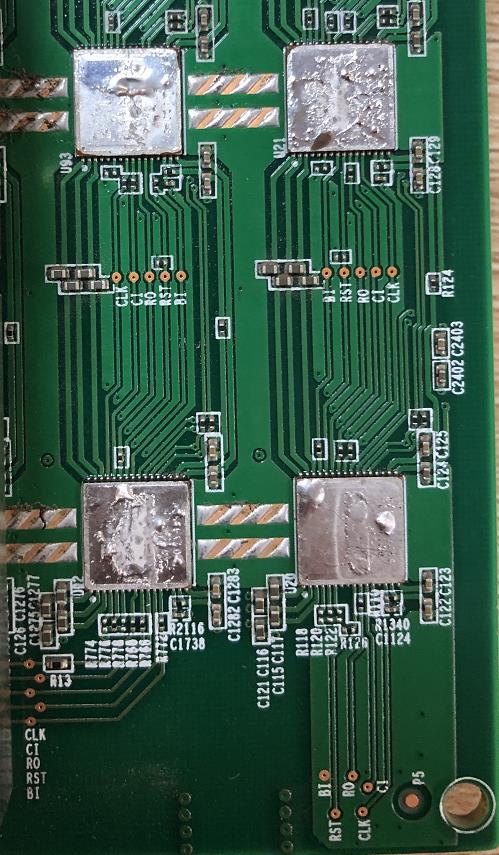
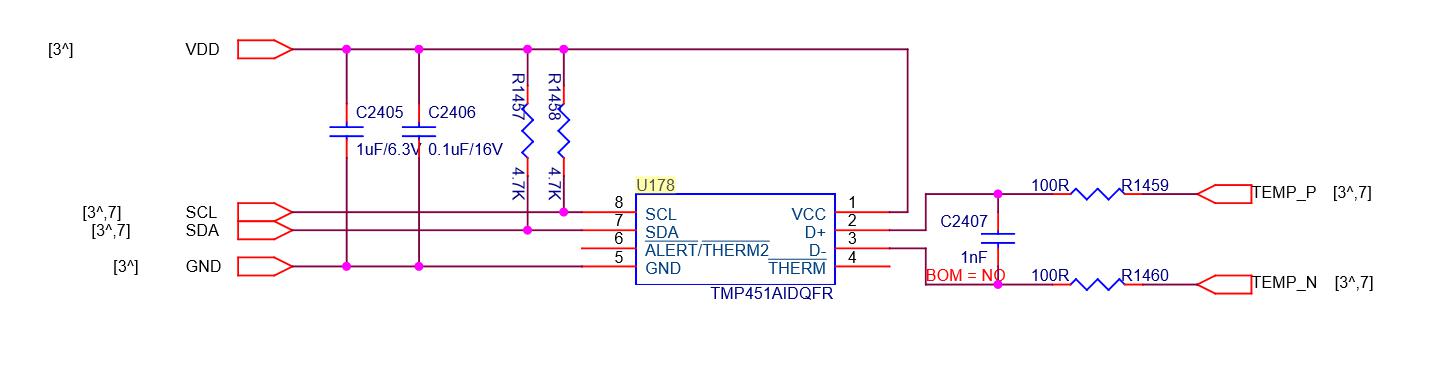

Special attention: C118‑119‑120 on pins 0‑1‑2‑3 of the U221 chip are the 4 smaller filter capacitors inside the chip, because the height of the dot capacitance is greater than the height of the chip, it is easy to cause heat sinks and capacitors Short circuit, our 1396 chip has 3833 cores. Each chip has 4 small domains, which means that the voltage of each chip is 1.2V, and the voltage of each of the 4 small domains is 0.3V.
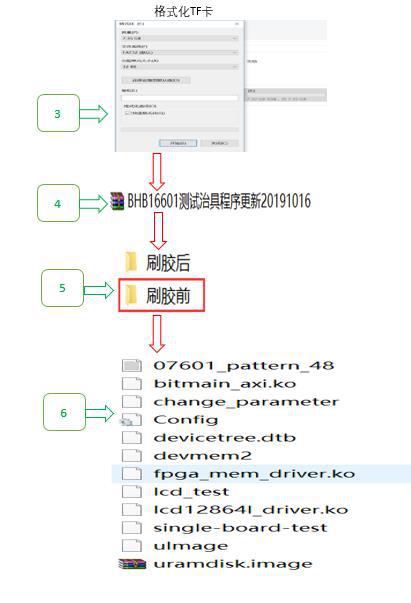
Test the production of TF card
1. Prepare a 4G or 8G TF card;
2. Prepare a card reader;
3. Decompress the BHB16601 test fixture;
4. Unzip the folder before brushing the glue;
5. Copy the decompressed file to the formatted TF card;
6. Eject the TF card and test that the T card is made successfully;


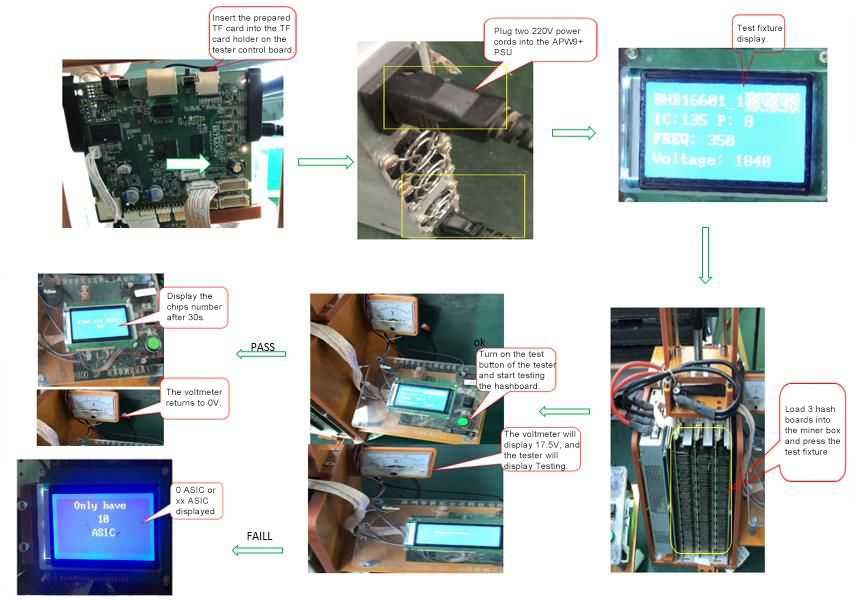
1. Wipe the completed TF card into the TF card socket of the fixture control board.
2. The power of APW9+ is connected to 220V power cord (2 220V power cords) .
3. The screen display after the jig is running.
4. Three boards must be inserted in the case. Press down the jig and the thimble of the jig contacts the power terminal of the hashrate board.
5. Click the fixture test switch to start testing the hash board.
6. The voltmeter displays 17.5V and the fixture screen displays Testing.
7. After 30 seconds, the screen displays the chip search (find all asic OK test time is 30 seconds). The pointer of
8. The voltmeter returns to 0V.
9. If the chip cannot be found or cannot be found, the screen will display ASIC=0 or ASIC=xx.
10. After the test is completed, you must wait for the pointer of the voltmeter to be OV, then you can separate the jig power supply thimble from the control board, take out the hash board, and mark the bad PCBA with the bad label and place it separately.
4. single board repair case analysis
Single board fixture test asic=0
Failure analysis:
1. Whether the fixture cable and the hash board are in good contact.
2. If it is S17e, the hashrate board J4‑J5 should have a voltage of 18.V during the fixture test.
3. When testing the fixture, measure whether there is voltage between 15 voltage domains.
3.1 If there is no voltage in the voltage domain, it depends on the normal working voltage of pin 4 of Q1‑2‑3‑5 that the high level is 3.3V, if it is low level, then See if pin 1 of Q4 is high at 3.3V. If Q4 does not have a 3.3V voltage, it means that U3‑PIC has lost its firmware or has no power supply.
3.2. If the power supply is normal and the voltage domain voltage is also available, then measure the RI signal of the chip to see if the RI signal has a voltage of 1.8V, and measure the RI The signal should be measured from the test point of the last chip. If the last chip is available, you can measure whether the 20th chip has RI ‑1.8v or not.
By analogy, when the chip has no RI output voltage, first measure it. The chip is powered by 1.8V. If 1.8V is not powered, then It is necessary to check the 1.8V power supply circuit. The 1.8V power supply circuit is obtained by dividing the voltage in the voltage domain and then powering the LDO 1 pin, and the LDO 5 pin output 1.8V voltage, (each voltage domain has a ‑1.8V LDO that powers the chip), If there is no output, there should be a problem with this LDO.
If 1.8V is normal, you can measure the resistance to ground of the test point after power off and compare it with the OK board to see if there is any abnormal resistance. If the resistance is Normally, there is no problem with soldering. It should be that the chip is bad. (Replant the removed chip and solder it to a good board for verification. If There is no RI signal to prove that this chip is broken, just replace it with a new one) .
The fault phenomenon is ASIC=7:
Analysis: ASIC=7
1. The single board test can find 7 chips. It can be judged that the RI signal is normal. If the 8th chip is not found, we will directly measure the 7th chip. The voltage of the U26‑CLK‑RST‑CO chip depends on whether the power supply is normal. If the CLK does not have a 0.8V voltage, it depends on the power supply of the CLK Circuit.
2. 2‑CLK circuit analysis: If the CLK is not 0.8V, first look at whether the 0.8V power supply of the bad chip voltage domain is normal. The 0.8V power supply circuit is After dividing the voltage in the voltage domain, it is the same as the 1.8V power supply. The maintenance method for the 5‑pin output 0.8V can refer to the 1.8V maintenance method. (It should be noted that the 4 chips in each domain of S17 have 2 output 0.8V LDO power supply, and each LDO supplies 2 chips).
3. If the 0.8V power supply circuit does not have a 0.8V output, then look at whether the 0.8V LDO power supply has a power supply voltage of about 3.2V, and if so, look at it. Whether the LDO is soldered or short‑circuited, if there is a 0.8V output, then look at the resistance of this chip to ground, if the resistance is correct, it should be the chip bad.
PATTERN‑N
For the PCBA of PATTERN‑NG, we first judge whether the chip is defective through the NONCE returned by each chip indicated by the LOG of the fixture test. If 1‑2 chips return NONCE insufficient (generally, the number of NONCE returned by a single chip is 8x383x0.98), just replace these two directly. For each chip, if it is 9 chips with a domain, the NONCE return does not reach 98%, basically it can be determined that the voltage of this domain is low.
5. Judgment criteria and failure analysis of the whole miner test
1. Connect the assembled whole miner to dual 220V power cords and fixed IP network cables (Figure 1).
2. Enter the test site monitoring interface to find the IP of the tested miner.
3. After the miner is turned on, the miner can run out of hash rate in about 3 minutes.
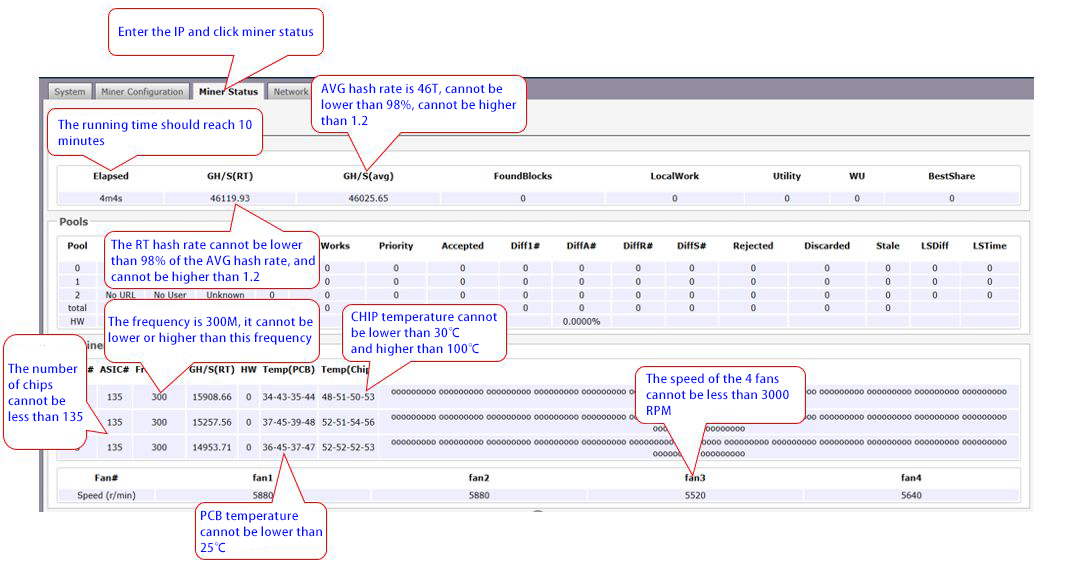
4. After the miner runs for 10 minutes, click on IP51 to enter the miner interface, and then enter the IP, enter the account name root and password root to enter the miner IP interface. To confirm whether the firmware version date is correct.
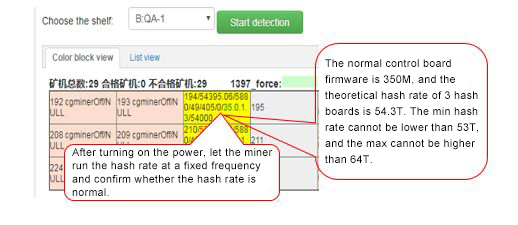
5. The normal master firmware is 300M, and the theoretical hash rate of 3 boards after 10 minutes of operation is 46T. The minimum hash rate cannot be lower than 98%T, the maximum hash rate. It cannot be higher than 1.2T, and it is considered bad if it exceeds the maximum and minimum hash rate.
6. The RT hashrate cannot be lower than 98% of the AVG hashrate and cannot be higher than 1.2.
7. The number of chains of the whole miner cannot be less than 3, the number of chips each cannot be less than 135, the frequency of each chain cannot be less than 300M, and the temperature of the PCB. It cannot be lower than 25 degrees, the temperature of the chip cannot be lower than 30 degrees, and it cannot be higher than 100 degrees. The number of fans cannot be less than 4, the speed of the fans. It cannot be less than 2000 revolutions.
Whether the whole miner is running normally depends on whether the miner can start normally and whether the hash rate is normal. To check whether the hash rate is normal, enter the miner first.
The IP of the device is shown in the above figure.
1. Whether the number of chains has detected 3 chains: If it is not detected enough, it depends on whether the flat cable has fallen off or the flat cable has not been plugged in properly.
If it takes to update the cable or the chain is still less, you can perform a single board test on the hash board of the less chain to see if it is OK;
1.1 If the hashrate board is OK, it can basically be determined as the control board, and it can be eliminated by the substitution elimination method;
1.2 If the hashrate board tests ASIC0, then repair it according to the single board repair method;
2. Check if the number of chips is enough: If the number of chips is not enough, you can directly enter the IP‑LOG to see how many chips are detected in that chain, and then. Repair according to the number of chips per board.
3. See if the operating frequency of the three chains is normal: frequency determines the hash rate, one chain hash rate = frequency x number of chip cores 383 x number of chips x 0.98. If you can’t reach this theoretical hash rate, it proves that the chips in this chain have a lot of bad CORE. If you want to increase the hash rate, you can enter the IP‑LOG to see that. If the frequency of the chip is lower, replace that chip.
4. Under normal miner operation, the temperature of PCB and chip of 3 chains is between 25 degrees and 95 degrees. If there is one chain, the temperature is only 25 degrees. Below degree, it proves that the hashrate boards of this chain are not working, and the veneer test is necessary to see if the veneer is normal. If it is higher than 95 degrees, it proves heat dissipation No, check whether the fan operation and ventilation of the miner are normal, and also pay attention to whether the heat sink has fallen off.
5. If you can't see any data after entering the IP, but only see the interface as shown in the figure below, you must enter the IP‑log to see what is printed in the log Regardless of the information, check and repair the miner according to the information. It may be a disconnection or other problems.
6. When the whole miner is repaired, it is repaired according to the mining status and LOG, and which one is considered to be the problem is directly replaced with a good part for verification. Make judgments.
Reference steps:
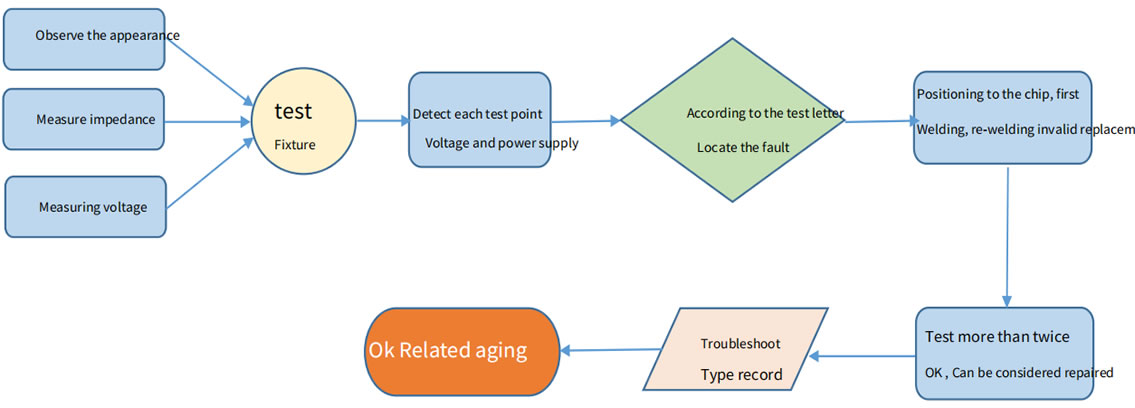
1. Routine inspection: First, visually inspect the hash board to be repaired to observe whether there is any displacement, deformation, or scorching of the small heat sink. If there is It must be dealt with first; if the small heat sink is displaced, remove it first, and then re‑soldering after the repair is passed.
Secondly, after the visual inspection is no problem, the impedance of each voltage domain can be tested first to detect whether there is a short circuit or an open circuit. It must be handle first.
Thirdly, check whether the voltage of each voltage domain reaches 1.2v, and the voltage difference of each voltage domain shall not exceed 0.3v. The voltage of a certain voltage domain is too high or If it is too low, the circuits in the adjacent voltage domain generally have abnormal phenomena. Need to investigate the reason first.
2. After confirming there is no problem in the toutine test (short circuit detection is necessary in routine test to avoid burning the chip or other materials due to short circuit when it's power-on), a test fixture can be used for chip detection and the detection results of the test fixture can be used to judge the location.
3. According to the displayed results of the test fixture, start from the vicinity of the faulty chip, and check the chip test points (CLK IN OUT/TX IN OUT/RX IN OUT/B IN OUT/RST IN OUT) and VDD VDD0V8 VDD1V8 and other voltages.
4. Then according to the signal flow direction, except for the RX signal, it is transmitted in the reverse direction (from 135 to chip 1), and several signals CLK CO BO RST are transmitted in the forward direction. (1‑135, find the abnormal fault point through the power supply sequence.
5. When locating the faulty chip, the chip needs to be welded again. The method is to add flux around the chip (preferably no‑clean flux) ,will When the solder joints of the chip pins are heated to a dissolved state, gently move up, down, left, and right to press the chip; to promote the chip pins and the pads to run in again, Collect tin. In order to achieve the effect of tinning again. If the fault remains the same after re‑soldering, you can directly replace the chip.
6. After the repair of the hash board, the test box must be checked for more than twice. The time of the two tests: For the first time, after replacing the parts, the hash board needs to be cooled down; after passing the test, it is put aside first. For the second time, after the hash board is completely cooled after a few minutes, the test is performed. Although each of the two tests lasts only a few minutes, it does not affect the work. The repaired board is put aside, and the second board is repaired, after the second board is repaired, it is placed and cooled, then the first board is tested. In way, the repair is staggered and there is no delay in the total length of time.
7. For the repaired board, first it is necessary to classify the faults and record the replaced part model, location, and cause, to feed back to production, after- sales, research and development.
8. After recording, install it into a complete miner for formal aging.
6. The type of failure
S17e common fault types are:
1. Remove the heat sink, heat sink shift, and deformation; before power on, the heat sink on the PCB board on the back of the hash board chip is not allowed to shift or touch, especially. Don't be heat sinks of different voltages. The contact of heat sinks of different voltage domains means that there is a possibility of short circuit at different voltage points. And make sure the hash board. Each heat sink on the board has good heat conduction and is firmly fixed.
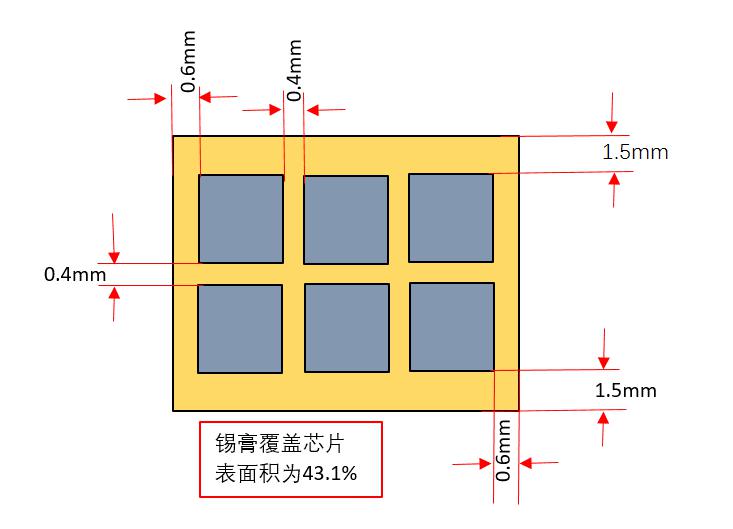
When replacing or reattaching the heat sink, you need to replant tin on the heat sink and chip before soldering. The requirement for tin planting: the thickness of the steel sheet is 0.12mm.
The area is more than 40% of the surface area of the BSM chip. details as follows:
2. When the impedance of some voltage domains deviates from the normal value, it indicates that there are open and short circuits in the abnormal voltage domain. Generally the chip is the most likely to cause it. But there are three chips in each voltage domain, and often only one has problem when fault occurs. The method of finding the problem chip can detect and compare the ground impedance of test points of each chip to find the abnormal point.
If there is a short circuit, first remove the cooling fin on the same voltage chip, and then observe whether the chip pin’s tin is connected.
If a short-circuit point cannot be found on the appearance, search the short-circuit point according to the resistance method or current cut-off method.
3. When the voltage in some voltage domains is too high or too low, there is usually an abnormal IO signal in the abnormal voltage domain or adjacent voltage domain, which causes the next voltage domain to work abnormally and the voltage to be unbalanced. The abnormal point can be found by detecting the signal and voltage of each test point, and some need to find the abnormal point by comparing the impedance of each test point.
Note that the CLK signal and the NRST signal are the two most likely to cause a voltage imbalance.
4. The lack of chips means when the test box is being checked, not all of the 135 chips are detected, and often not all the chips are actually detected. The actually lost (undetected) abnormal chips are not in the displayed position. At this time, it is necessary to accurately locate the abnormal chip through testing.
The locating method can use the TX cutoff method to find the location of the abnormal chip. That is, ground the TX signal of a chip, for example, after the tx output of the 120th chip is grounded in the voltage domain, theoretically, if all the chips in the front are normal, the test box should display that 120 chips are detected. If not all 120 chips are detected, it means that the abnormality is before the 120th chip; if 120 chips are detected, it means that the abnormal chip is after the 120th chip. Use this dichotomy to find out where the abnormal chip is located.
5. Broken chain
A broken chain is similar to lack of chip, but in a broken chain, not all chips that cannot be found are abnormal, but all the chips after the abnormal chip are invalid due to a certain chip abnormality. For example, a chip itself can work, but it will not forward other chip information; at this time, the entire signal chain will come to an abrupt end, and lose a large part of it, which is called broken chain.
Generally the broken chain can be displayed by the test box. For example, when the test box detects the chips, only 14 chips are detected. If the number of preset chips is not detected in the test box, it will not run, so it will only display how many chips are detected, at this time, according to the displayed number "14", the problem can be found by detecting the voltage and impedance of each test point before and after the 14th chip.
6. Not running, not running means that the test fixture fails to detect the chip information of the hash board, and displays NO hash board; this phenomenon is the most common see, the range of faults involved is also wider.
6.1 Non‑operation caused by abnormal voltage in a certain voltage domain; the problem can be found by measuring the voltage of each voltage domain.
6.2 The abnormality caused by a certain chip can be found by measuring the signal of each test point.
CLK signal: 0.9V; the signal is output from chip 00 to chip 134, but the current version has only one crystal oscillator, as long as there is a signal. If the LCK is abnormal, all subsequent signals will be abnormal. Search in order according to the signal transmission direction.
TX signal: 1.8V; this signal is composed of 00, 01, ,,,, , No. 134 chip, when a certain point of the dichotomy is abnormal, it can be detected forward.
RX signal: 1.8V; this signal is composed of 134,,,, ,, 01, 00 return, confirm the cause of the failure through the chip signal trend, S9 operation board. If it is not running, the signal has the highest priority, and the signal is searched first.
BO signal: 0V, this signal can be pulled low to high level when the chip detects that the RI return signal is normal, otherwise it is high level.
RST signal: 1.8V; after the arithmetic board is powered on and the IO signal is plugged in, this signal will change from 00, 01, , ,,,, 134 direction to the end A chip.
6.3 Caused by VDD of a certain chip.
It is possible to measure whether the potential difference of each voltage domain is normal. Generally, when the voltage is 1.2V, the test points of other voltage domains are normal. The voltage is also 1.2V to ensure the balance between the various voltage domains.
6.4 The VDD1V8 voltage of a certain chip is abnormal.
6.5 Determine whether a VDD1V8 voltage is normal by measuring the test points of each voltage. Generally, the IO voltage determines the voltage of each test point. When the IO voltage is 1.8V, the normal voltage of each test point in other voltage domains is also 1.8V.
7. Low hash rate can be divided into:
7.1 When the test fixture conducts testing, the box receives insufficient Nonce, and the hashrate is insufficient and displays NG. In this phenomenon, directly judge from the number of Nonce returning from each chip through the serial port print information of the test box. Generally, chips with returning Nonce number less than the set value should be trouble-checked to eliminate pseudo soldering and peripheral reason. Replace the chip directly.
7.2 When testing the test jig, if the hashrate is low after the miner is installed. Mostly this situation is related to the heat dissipation conditions of the chip. Special attention should be paid to the adhesive for the small cooling fin of each chip and the ventilation performance of the whole miner.
Another reason is that the voltage of a certain chip is critical and the whole miner is installed, after that, the difference between the 18V power supply and the power supply during the test results in a deviation between the test calculation power and the running calculation power, which can be tested with a test fixture after being reduced. After slightly adjusting the voltage of the 18V output of the DC adjustable power supply, test again to find the chip that returns the lowest voltage domain with the lowest number of Nonces.
8.A chip NG
When testing through the test box, the test box’s serial port information indicates that a chip's return Nonce is insufficient or zero. In addition to eliminating the problem of pseudo soldering and peripheral components, the chip can be directly replaced.
7. maintenance instructions
1. During maintenance, the maintenance personnel must be familiar with the function and flow direction of each test point, the normal voltage value and the ground impedance value.
2. You must be familiar with chip soldering to avoid blistering and deformation of the PCB or damage to the pins.
3. The bm1387 chip is packaged with 16 pins on both sides of the chip. The polarity and coordinates must be aligned during welding, and they must not be misaligned.
4. When replacing the chip, the thermally conductive fixing glue around the chip must be cleaned to prevent the IC from hanging in the air or poor heat dissipation during soldering, which may cause the chip to be secondary. damage.
Precautions:
1. Since the heat sink on the back of the chip is connected to the chip ground, special slender test leads must be used when testing the test point signals, and the test leads except for the contact terminals, except for the exposed metal, other places must be insulated with heat shrink tube to prevent the test point from touching the heat sink and the test point at the same time. In particular, the voltage difference between the upper and lower rows of circuit voltage is large, and will cause damage to the chip when contacting the ground (cooling fin) and test points in different voltage domains, and special attention shall be paid.
2. In soldering, since there are small cooling gins close to the PCB on the back of the chip, the heat conduction is fast. Therefore, it is necessary to use the bottom to assist heating (about 200 degrees) in soldering, which can improve the efficiency and reduce the damage to the PCB board. If there is no bottom heating device, remove the small cooling fin on the PCB on the back of the chip before replacing the chip.
If there is a new type of failure, please contact the engineering department of our company in time, we will analyze and update this content one after another!