


Innosilicon T2T model hash board maintenance manual (V1.3)
In the process of manufacturing and using the miner, if the user encounters chain loss, low hashrate, multiple hardware errors, etc., please refer to this manual for test and maintenance.
Note: This manual cannot cover all possible abnormal problems. If you encounter a problem that cannot be solved using this manual, please consult our relevant personnel, and they will update this manual when necessary.
Ⅰ. Overview
1. The circuit layout of the hash board and the distribution of test points
Take 3*31 model as an example. For other models, please refer to relevant design documents.
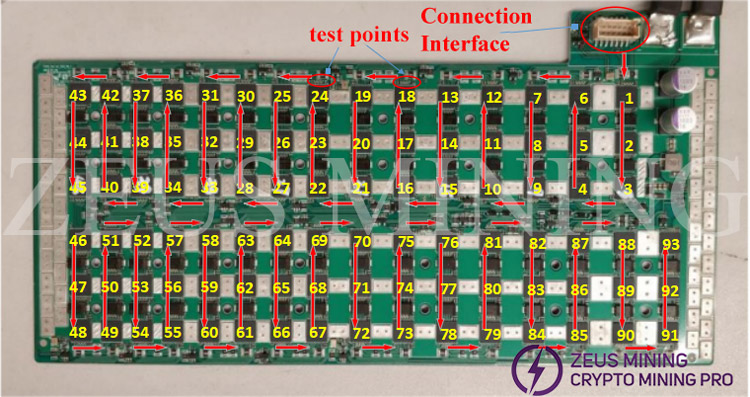
(1) The three adjacent chips in the figure are a voltage domain [(1,2,3), (4,5,6)...(91,92,93)]. There are a total of 31 voltage domains on this hash board, and the voltages of the three chips in each voltage domain are the same, and the average voltage of each voltage domain is about 0.45V at startup (T series machines)
(2) The red arrow in the figure shows the transmission direction of CLK and communication signals;
(3) There are 1 to 7 test points between each two chips (each model is different, please refer to the design file for details); test points 1 to 7 are CLK, RST, EN, SCK, CS, DI and DO signals respectively. Specifically as shown below:
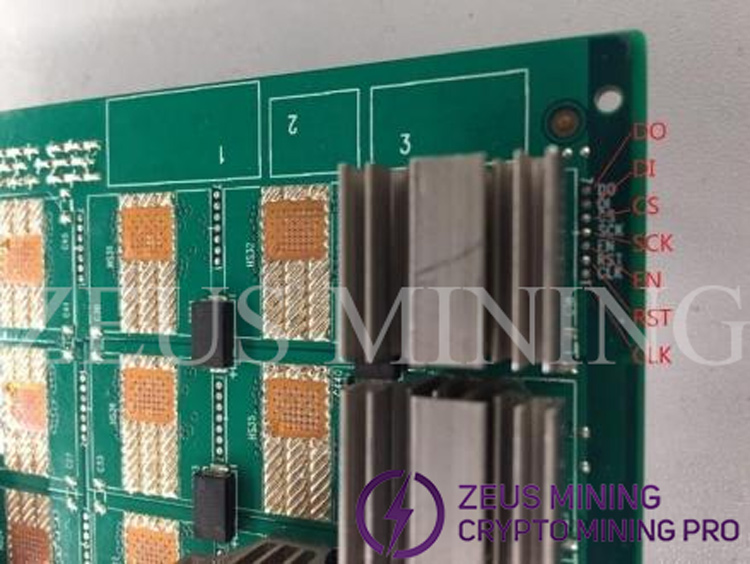
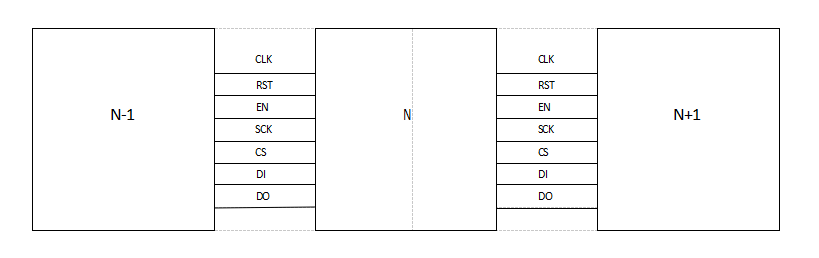
(4) Test points and connections between adjacent chips:
2. Description of the test software
Software | Application occasion | Purpose |
Measuring chain | After SMT, before sticking heat sink | It is used to quickly check soldering problems. It does not do a long time function test, but only tests whether the transmission of all chips is normal. |
Before pasting | After pasting the heat sink on the non-chip side | It is used to check various faults of the single board in the high power state as early as possible. Due to the lack of a heat sink, the operating frequency of the chip is lower than that of normal use. |
Binning after pasting | After all heat sinks are pasted | The test is carried out under 4 kinds of working voltages, and the boards are graded according to the measured hash rate. Boards of the same grade are loaded into a machine. |
Maintenance | Locating problems with a single hash board | The program will send communication commands indefinitely for maintenance personnel to use multimeters and oscilloscopes to check the necessary circuits. |
Ageing | The machine is aged before leaving the factory | Use the official factory firmware, if there is an exception, an error code will be displayed on the mass production management interface. |
3. Error code list of test software before and after pasting
If no problem is detected, "√" will be printed at the end of the log, otherwise it will be printed "×"。 When a problem is detected, the software will report the error type with the highest priority. The order of error priority is: E0>E9>E6>E4>E7>E5>
E3 > E1 > E2 > E8. The chip can be repaired or replaced according to the report.
Error code | Description | Remarks |
E0 | Cannot find chip type | Chain failure |
E1 | The number of good cores of a single chip is less than 30% | Statistics under operating frequency |
E2 | The number of good cores of a single chip is less than 90% | Statistics under operating frequency |
E3 | The single chip job test is all wrong | |
E4 | The PLL with the chip is not locked | |
E5 | The temperature of the chip is abnormal | 9999 or - 9999 is displayed in the software |
E6 | The voltage of the chip is abnormal | |
E7 | There is an error in the return process of the command, or the frequency increase fails | “E7:0” indicates that pll configuration failed |
E8 | The total error rate of job testing of the whole board is greater than 10% | |
E9 | The number of chips read is wrong | |
E10 | (Reserve) | |
E11 | Unable to find a suitable grade after pasting the heatsink | |
E12 | CRC error returned by the command | |
E13 | Failure to depressurize |
4. Error code list of aging software
Number | Problem | Methods of resolution | Notice |
1 | The IO of the control board is abnormal | Change the control board | The factory settings must be restored after completion |
2 | Network fault of control board | ||
3 | Hash board is failure | Change the hash board | After replacement, be sure to restore factory settings or re-aging after completion |
4 | Chip failure | ||
5 | The temperature of individual chips is too high | ||
6 | PSU failure | Change the power supply | It is recommended to restore factory settings or re-aging after completion |
7 | SPI line interference | Use shield wire | |
8 | SPI cable is not plugged properly | Check and re-plug SPI flat cable | |
9 | The power consumption of the whole machine is too high | Re-aging or frequency reduction (Efficiency mode) | |
10 | The ambient temperature is too high | Check and re-plug SPI flat cable | Improve the operating environment |
11 | Fan fault | Check the fan cable connection / check whether the fan model matches / check whether the fan installation direction is correct | Reference document “Summary of Frequently Asked Questions about the Control Board” |
12 | Mining pool settings error | Check pool settings or restore factory settings | |
13 | The network cable is not plugged properly | Check the network cable connection | |
14 | Network environment failure | Check the DHCP and DNS configurations of the switch |
Error code | Description | Err Message | Analysis |
0 | Normal | Normal | |
21 | One or more hash boards are not detected | The number of hash boards that have been detected. If there are more than one, separated by spaces | SPI cable not plugged in / IO fault of control board / Hash board fault |
22 | I2C communication of power supply is abnormal | PSU failure / Control board IO failure | |
23 | All hash board encore failure | Control board IO failure / PSU failure / hash board failure | |
24 | Partial hash board encore failure | The number of the normal encore hash board, if there are more than one, separated by spaces | Hash board failure / control board IO failure / PSU failure |
25 | Upscaling failed | Hash board number: wrong frequency point | SPI line interference / hash board failure |
26 | Failed to set voltage | Hash board No.: 1/2 | SPI line interference / hash board failure |
27 | Failed to bist | Hash board No.: 1/2 | SPI line interference / hash board failure |
28 | SPI error cannot be recovered automatically at runtime | Hash board number | SPI line interference / hash board failure / control board IO failure |
29 | I2C communication fails during operation and cannot be recovered automatically | - | PSU failure / control board IO failure |
30 | Unable to connect to the mining pool | - | Mining pool setting error / network cable not plugged in properly / network failure of the control board / network environment failure |
31 | Individual chips are damaged, resulting in falsely high hashrate. | Damaged chip number: hashboard number. If there are more than one, separated by spaces | Chip failure |
32 | Overtemperature | Hash board number | The ambient temperature is too high / fan failure / the temperature of individual chips is too high / the power consumption of the whole machine is too high |
33 | Failed to read temperature | Hash board number | Control board IO failure / hash board failure |
34 | SPI cable connection is abnormal | Hash board number | SPI port of the control board is inserted incorrectly / control board IO failure |
35 | Insufficient power supply | PSU failure | |
36 | The number of good cores of the chip is abnormal | Hash board number: chip number | Hash board failure |
37 | Wrong vid type of control board | vidtype, minertype, subtype, chipnum | Hash board failure |
II. Preparation of maintenance platform
Tools:serial port board / data cable / TF card / jumper cap / oscilloscope / multimeter
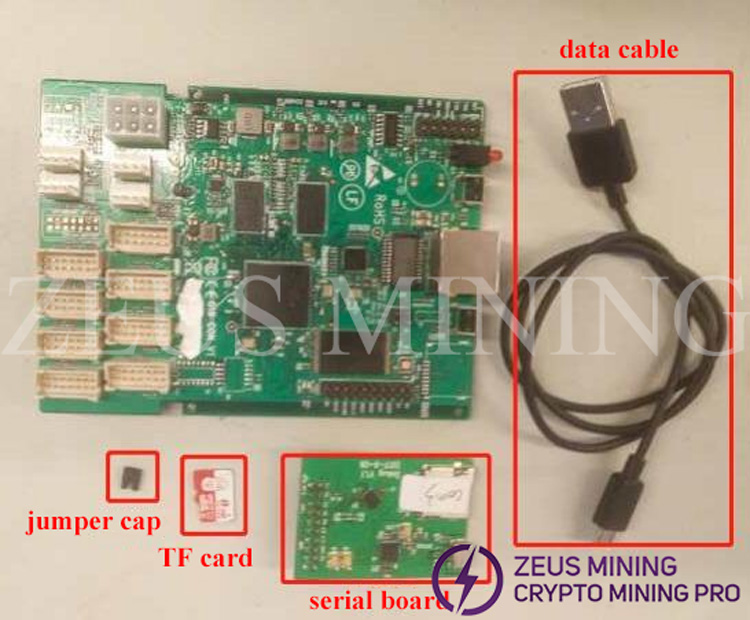
boot.bin
SecureCRT.exe
(1) Instructions for the test software *. bin
How to use: After shutting down, copy xxx.bin directly to the TF card, and insert the TF card into the slot of the serial port board. Then connect the serial port board to the control board, and use a jumper cap to connect to the J2 interface. Finally, boot it up.
(2) Instructions for the the serial port tool
Install the serial port test tool (SecureCRT.exe) on the computer, and set the baud rate: 115200, n, 8, 1.
The setting method is as follows:
Double-click the serial port icon to open the serial port tool as shown in the figure below, click "New Dialogue" in the red box in the dialog box.
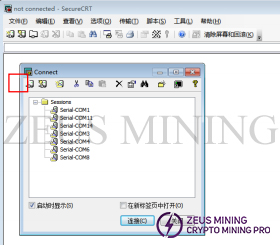
Select the serial in the New Session Wizard.

Set baud rate: 115200 and other options.
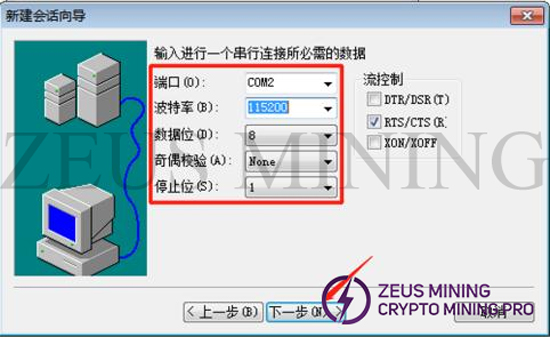
(3) Software instructions
① Software before and after pasting
The usage process is:
1) After inserting the SD card into the slot, check that the device is correct and power on.
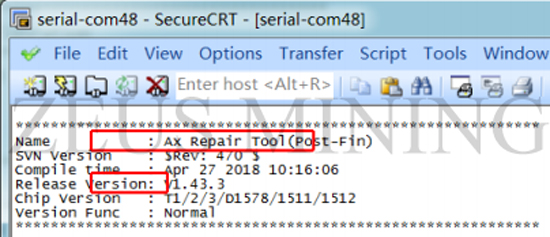
2) Open the serial port software to check whether the software version information is correct after power-on.
3) During the test, the test information of each stage and other prompt characters will be displayed to facilitate hardware testing and status monitoring.
4) After the test is finished, print the test result. If it is a multi-chain test, the test results will be printed together after the test is finished.
5) To test again, directly press the reset key on the control board or press the enter key according to the prompt characters of the software.
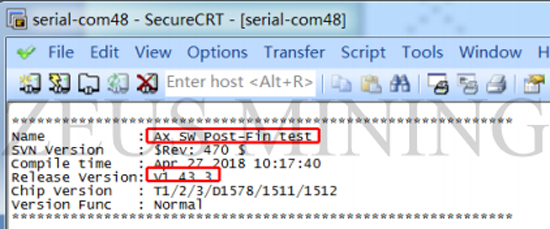
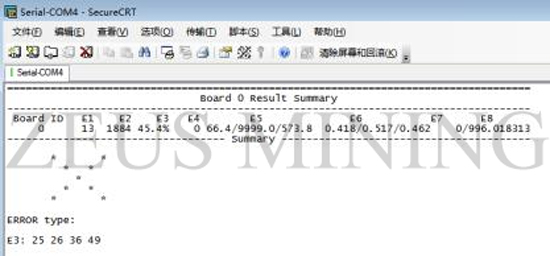
② Maintenance software
1) After inserting the SD card into the slot, check that the device is correct and power on.
2) Open the serial port software to check whether the version information of the software is correct after power-on.
3) During the test, the test information and LED lights of each stage will be displayed to facilitate hardware testing and status monitoring.
4) The software will continuously send a fixed command during operation, which can be used to measure voltage and signal.
5) After the measurement is completed, press the function key to continue running, and finally print the test results.
6) To test again, directly press the reset button on the control board or press the Enter button according to the characters prompted by the software.
It should be noted that the maintenance software can only test one circuit board at a time. When the function key is pressed, only when the corresponding indicator light goes out can it be ensured that the key is successfully captured.
2. Establish a test environment
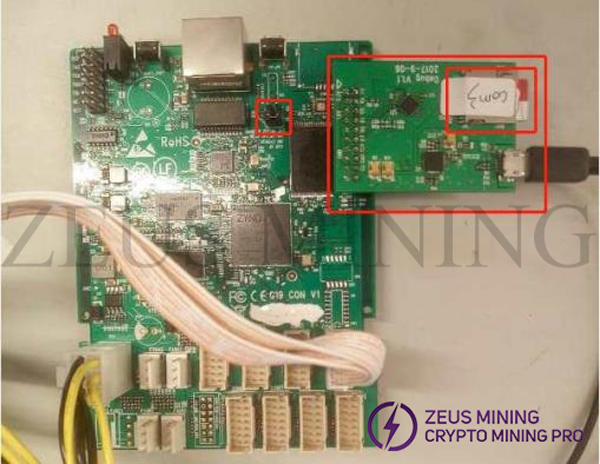

Take out the control board of the miner to be tested, place the control board and the serial port board as shown in the figure, insert the TF card, and insert the jumper cap into the J2 interface. Connect the serial port board and the computer with a data cable.
1. The basic process of repairing the aging of the whole miner
(1) Reproduce the bad aging problem and record the error code. If you need our company's research and development analysis, you also need to save the aging log.
(2) Check whether the power output corresponding to the defective board is normal.
(3) If it is a multi-channel control power supply, exchange the power channel of the bad board and the normal board (note that the order of the data line interface is adjusted at the same time), and then observe whether the bad phenomenon follows the hash board or the power supply. If it follows the power supply, replace the power supply again. do aging.
(4) Disconnect the power supply and network cable. Check whether the appearance of the machine is damaged. Check whether the power and data cables are loose or disconnected.
(5) Use the original machine power supply and the faulty hash board to do a sticky test in the bucket, and record the error code and log. If there is no abnormality after 5 consecutive tests, our R&D personnel will be notified for analysis.
(6) Use the original machine power supply and the faulty hash board, and do a post-stick test outside the barrel to see if the phenomenon still exists and make a record. If the chip surface is a heat sink fixed by screws, remove the heat sink on the chip surface, and then do a pre-stick test to see if the phenomenon still exists, and make a record.
(7) Continue to analyze in accordance with the faulty board repair process.
2. The basic process of repairing the single board
Before maintenance, please confirm that the power supply, control board, and various cables are connected properly.
(1) Use the pre-glue test software to test and get the error code Ex:x. Different next steps may be taken for different types of errors.
(2) Check the appearance of the board, and observe whether there are missing components, errors, or abnormal appearance. Check whether there are solder balls, foreign objects, etc. near the error chip.
(3) Run the maintenance procedure and check the input voltage with a multimeter. Check crystal oscillator supply. Check tail IO boost circuit. Check the LDO output of each stage.
(4) Use an oscilloscope to check the chip input and output signals CLK, SCK, DO, DI, CS, RSTN, START.
(5) If the output signal of the ASIC chip is found to be abnormal, do not easily replace the chip. According to the instructions in the following chapters, first try methods such as adding soldering, re-soldering, and swapping with other chips on this board.
(6) If the method of chip exchange is adopted, it can be observed whether the problem follows the chip.
(7) If the above method is invalid, then replace the chip. It is necessary to record in detail the specified information such as the cause of the problem of the removed chip in the maintenance report. Regularly send the maintenance report to our company for analysis.
3. Locate the broken chain with a maintenance-specific program
Copy the provided repair.bin to the TF card and plug it into the serial board. Connect power and data cables (no fan required), power on. According to the error message of the software before or after gluing, detect the test points of the relevant chip and its adjacent chips.
Description of function keys and indicators in the service software.
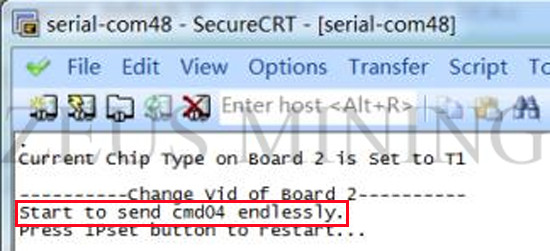
(1) After power on, the lights on the control board are on (red and green lights next to the reset button). If the power-on link is broken, the software will keep sending cmd04. After pressing the function key next to the USB card slot, the software will stop sending cmd04, and the program will continue to run, and the green light will be off at this time;
(2) If the power-on link is connected, the software will continue to send cmd04. Similarly, after pressing the function key, it will stop sending cmd04, and then the green light will go out;
(3) After the frequency configuration fails, the software will send cmd04 at the point of failure, press the function key, stop sending cmd04, the program continues to run, and the red light is off at this time;
(4) After the frequency configuration is successful, if the link breaks during the continuous reading process, the software will send cmd04 at the link break. After pressing the function key, the transmission will stop, and the red light will be off at the same time, and the program will continue to execute.
IV. Analysis of typical problems
1. E0: 1
This kind of problem is that the communication chain is completely broken, and most of them are caused by abnormal peripheral circuits. Known causes are:
(1) The power supply has no output or the output is abnormal.
(2) The solder connection between the communication interface and the plug-in pin is shorted.
(3) The data cable is not plugged in properly or the contact is poor or damaged, resulting in a short circuit.
(4) The components between the communication interface and the first chip have problems such as false soldering, short circuit, burning, displacement, and missing parts.
(5) The IO of the first chip was damaged by static electricity.
(6) The crystal oscillator is abnormal.
(7) Some components are missing.
If you encounter such problems, you need to follow the "5 Checklist" for a complete inspection.
The problem is that part of the communication link is broken, and it is broken at the Nth chip. Known causes are:
(1) The signal between the Nth and N-1th ASIC chips is abnormal, the pins of the two chips are falsely soldered, floating high, short-circuited, and IO is damaged.
(2) False soldering, short circuit, burning, displacement, missing parts and other problems occur in the peripheral components of the Nth chip.
Repair steps:
(1) Check the peripheral circuit, if there is no abnormality, go to the next step.
(2) Check the ground resistance of the IO of the Nth ASIC chip and the front and rear ASIC chips. If there is no abnormality, proceed to the next step. If there is any abnormality, remove the chip and compare it with the ground resistance of the IO of the new chip. If there is no obvious difference, go to the next step, otherwise replace the chip.
(3) Re-solder the Nth and N-1th chips, if there is still an abnormality, go to the next step.
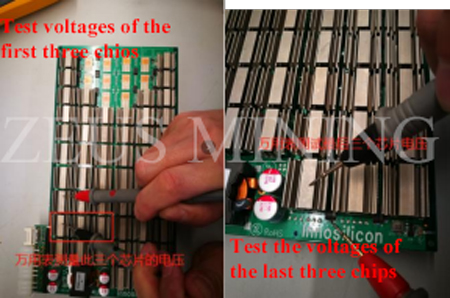
(4) In other cases, it is necessary to use a maintenance-specific program to assist in positioning. Check the chip when software executes to "Start to send cmd04 endlessly". At this time, you need to use a multimeter to measure the voltage of the abnormal chip (the measurement method is as shown in the figure below). And use an oscilloscope to measure the signals of the Nth chip and the N-1th chip. As shown in Figure 14, if the DO/CS/SCK output by the N-1 chip is abnormal (it can be compared with the normal waveform of the chip before the N-1th chip, if the waveform is inconsistent, it is abnormal), then replace the N- 1 chip. If the output of the Nth chip is abnormal, replace the Nth chip. If the output of the Nth chip is normal, but the input DI is abnormal, then replace the N+1th chip.


3. E6: N
The voltage of the Nth chip is abnormal.
Maintenance method:
(1) Use a multimeter to confirm whether the voltage of the chip is abnormal. If the voltage of the chip is too low, detect the SCK signal of the test points of the three chips of this level, and compare the chip with the SCK frequency jitter with other chips of different levels with higher voltage division. Swap. If the SCK signals are normal, replace chip N with other chips of different levels with higher voltage division.
(2) If the problem is with the chip, replace the chip.
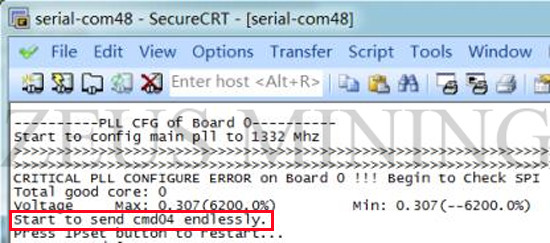
4. E7: 0
When E7:0 appears, you need to use maintenance software to locate the problem location, the location method is the same as E0, and test when the program runs to "CRITICAL PLL CONFIGURE ERROR on Board 0 !!! Begin to Check SPI ... "
5. E7: N
Indicates that the chip N does not respond, and you need to replace the chip. The checking method is the same as E0:N.
6. E1: N
The Nth chip lacks a core. If this problem occurs in a large area, submit it to our company for research and development analysis. If only a few hash boards have such problems, replace chip N.
7. E2
The total number of cores on the board is insufficient. At this time, it is necessary to check whether the total voltage of the circuit board is abnormal (refer to the method in E0 error), and if there is no abnormality, it needs to be returned to the factory for repair.
8. E3: N
The softbist error rate of the Nth chip is high. The method is the same as E1:N.
The pll of the Nth chip is not locked. Check the output CLK of the N-1th chip. If there is no abnormality, resolder the N-1th and Nth chips. If it still can't be solved, replace the Nth chip.
10. E5: N
The temperature of the Nth chip exceeds the standard, replace the chip. If the problem occurs over a large area, you need to check the heat sink. If the problem still cannot be solved, it needs to be returned to the factory.
11. E8
The temperature of the Nth chip exceeds the standard, replace the chip. If the problem occurs over a large area, you need to check the heat sink. If the problem still cannot be solved, it needs to be returned to the factory.
The softbist error rate of the whole board is high, you need to check whether the board voltage and the clock of each chip are abnormal. If abnormal, replace the abnormal chip
If there is no abnormality, it needs to be returned to the factory.。
Ⅴ. Checklist
This checklist is for maintenance reference.
Check items |
(1) Workmanship inspection |
CheckPoint 1. Whether the solder joints of the chip are full and whether there are tin beads |
CheckPoint 2. Whether any components fall off |
CheckPoint 3. Whether the chip is covered with silicone grease or heat conductive cotton |
(2) Check the error message of the software for the pre-glue or post-glue test |
CheckPoint 4. Correct identification of chip type |
CheckPoint 5. The reading status is normal at the default frequency (Frequency=60Mhz of all chips, Main PLL Lock=1, Temperature, Voltage are within a reasonable range) |
CheckPoint 6. Successfully raised to operating frequency (PLL frequency) |
CheckPoint 7. The reading status is normal under the operating frequency (Frequency=operating frequency/2, Main PLL Lock=1, Temperature, Voltage of all chips are within a reasonable range) |
CheckPoint 8. The error rate of Soft Bist is within a reasonable range (less than 10%) |
CheckPoint 9. The test software result is √ |
(3) PSU output |
CheckPoint 10. The voltage output from the power supply to the hash board is normal (see the indicators of specific models) |
CheckPoint 11. The voltage output from the power supply to the control board is 12V ± 10% |
(4) Control signal (measured after the hash board is powered on) |
CheckPoint 12. EN_CORE=3.3V±10% |
CheckPoint 13. RESET=1.8V±10% |
CheckPoint 14. START=1.8V±10% |
(5) Voltage of chip of hash board |
CheckPoint 15. The total CORE voltage should be consistent with the output voltage of the PSU If the VID setting is unreasonable or ineffective, it will cause abnormal or unstable operation. If the VID setting does not take effect, check whether the software and hardware programs of the control board are correct. |
CheckPoint 16. The voltage of IO at all levels shall always be 1.8V |